Related Research Articles

The Austroasiatic languages, are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China. Austroasiatic constitute the majority languages of Vietnam and Cambodia. There are around 117 million speakers of Austroasiatic languages. Of these languages, only Vietnamese, Khmer, and Mon have a long-established recorded history. Only two have official status as modern national languages: Vietnamese in Vietnam and Khmer in Cambodia. The Mon language is a recognized indigenous language in Myanmar and Thailand. In Myanmar, the Wa language is the de facto official language of Wa State. Santali is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India. The rest of the languages are spoken by minority groups and have no official status.

The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant and expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis.
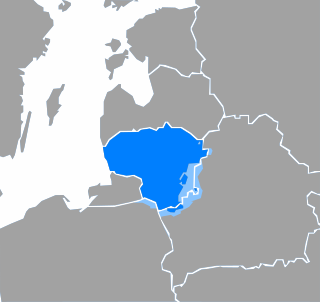
Lithuanian is an Eastern Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the official language of Lithuania and one of the official languages of the European Union. There are approximately 2.8 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 200,000 speakers elsewhere.
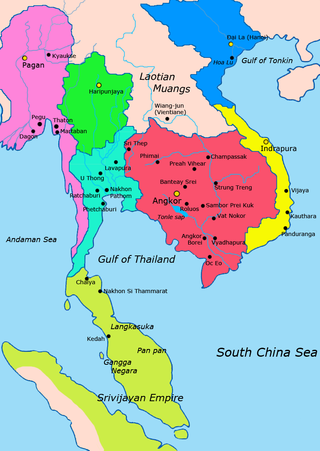
Champa was a collection of independent Cham polities that extended across the coast of what is contemporary present-day central and southern Vietnam from approximately the 2nd century AD until 1832, when the last remaining principality of Champa was annexed by the Vietnamese Nguyễn dynasty under its emperor Minh Mạng as part of its expansionist Nam tiến policy. The kingdom was known variously as Nagaracampa, Champa (ꨌꩌꨛꨩ) in modern Cham, and Châmpa (ចាម្ប៉ា) in the Khmer inscriptions, Chiêm Thành in Vietnamese and Zhànchéng in Chinese records.

The Bahnaric languages are a group of about thirty Austroasiatic languages spoken by about 700,000 people in Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos. Paul Sidwell notes that Austroasiatic/Mon–Khmer languages are lexically more similar to Bahnaric and Katuic languages the closer they are geographically, independently of which branch of the family they belong to, but that Bahnaric and Katuic do not have any shared innovations that would suggest that together they form a branch of the Austroasiatic family, rather forming separate branches.

Arawakan, also known as Maipurean, is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branches migrated to Central America and the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean and the Atlantic, including what is now the Bahamas. Almost all present-day South American countries are known to have been home to speakers of Arawakan languages, the exceptions being Ecuador, Uruguay, and Chile. Maipurean may be related to other language families in a hypothetical Macro-Arawakan stock.

The Karen or Karenic languages are tonal languages spoken by some 4.5 million Karen people. They are of unclear affiliation within the Sino-Tibetan languages. The Karen languages are written using the Karen script. The three main branches are Sgaw, Pwo and Pa'O. Karenni and Kayan are a branch of Karen languages. They are unusual among the Sino-Tibetan languages in having a subject–verb–object word order; other than Karen, Bai and the Chinese languages, Sino-Tibetan languages have a subject–object–verb order. This is likely due to influence from neighboring Mon and Tai languages.

The Kenyah people are an indigenous, Austronesian-speaking people of Borneo, living in interior North and East Kalimantan, Indonesia and Sarawak, Malaysia.

The Lun Bawang is an ethnic group found in Central Northern Borneo. They are indigenous to the southwest of Sabah, and the northern region of Sarawak, highlands of North Kalimantan, Brunei.
The Melanau–Kajang languages or Central Sarawak languages are a group of languages spoken in Kalimantan, Indonesia and Sarawak, Malaysia by the Kenyah, Melanau and related peoples.
The North Sarawakan languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken in the northeastern part of the province of Sarawak, Borneo, and proposed in Blust.

The Senoi are a group of Malaysian peoples classified among the Orang Asli, the indigenous peoples of Peninsular Malaysia. They are the most numerous of the Orang Asli and widely distributed across the peninsula. The Senois speak various branches of Aslian languages, which in turn form a branch of Austroasiatic languages. Many of them are also bilingual in the national language, the Malaysian language.
Proto-Austroasiatic is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austroasiatic languages. Proto-Mon–Khmer has been reconstructed in Harry L. Shorto's Mon–Khmer Comparative Dictionary, while a new Proto-Austroasiatic reconstruction is currently being undertaken by Paul Sidwell.
Proto-Hmong–Mien (PHM), also known as Proto-Miao–Yao, is the reconstructed ancestor of the Hmong–Mien languages. Lower-level reconstructions include Proto-Hmongic and Proto-Mienic.
Sarawak's population is very diverse, comprising many races and ethnic groups. Sarawak has more than 40 sub-ethnic groups, each with its own distinct language, culture and lifestyle. This makes Sarawak demography very distinct and unique compared to its Peninsular counterpart. However, it largely mirrors to other territories in Borneo - Sabah, Brunei and Kalimantan.
Mainstream Kenyah, also known as Usun Apau and Bakung, is a Kayan dialect cluster of North Kalimantan, Indonesia, and Sarawak, Malaysia. Dialects fall into four clusters:
Spurious languages are languages that have been reported as existing in reputable works, while other research has reported that the language in question did not exist. Some spurious languages have been proven to not exist. Others have very little evidence supporting their existence, and have been dismissed in later scholarship. Others still are of uncertain existence due to limited research.

The Apo Kayan people are one of the Dayak people groups that are spread throughout Sarawak of Malaysia, East Kalimantan and North Kalimantan of Indonesia. The earliest Apo Kayan people are from the riverside of the Kayan River, Bulungan Regency, East Kalimantan, Indonesia. According to the Apo Kayan Dayak legend, the Kayan people are the forefathers of which all smaller sub-ethnic Dayak people that are found along the Kayan River came from. Today, the population of the Apo Kayan people are estimated about 64,900.

Paul James Sidwell is an Australian linguist based in Canberra, Australia who has held research and lecturing positions at the Australian National University. Sidwell, who is also an expert and consultant in forensic linguistics, is most notable for his work on the historical linguistics of the Austroasiatic language family, and has published reconstructions of the Bahnaric, Katuic, Palaungic, Khasic, and Nicobaric proto-languages. Sidwell is currently the President of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society (SEALS) and also regularly organises the International Conference on Austroasiatic Linguistics (ICAAL).
References
- ↑ Soriente, Antonia. 1997. The classification of Kenyah languages: A preliminary assessment. In SEALS XIV(2): Papers from the 14th meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society (2004), ed. by Wilaiwan Khanittana and Paul Sidwell, 49–62. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.
- ↑ Smith, Alexander D. "On the Classification of Kenyah and Kayanic Languages." In Oceanic Linguistics, Volume 54, Number 2, December 2015, pp. 333-357.
- ↑ Kaufman, Daniel. 2018. Between mainland and island Southeast Asia: Evidence for a Mon-Khmer presence in Borneo. Ronald and Janette Gatty Lecture Series. Kahin Center for Advanced Research on Southeast Asia, Cornell University. (handout / slides)