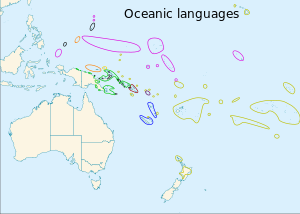
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori and Tolai languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic.
Yapese is a language spoken by the people on the island of Yap. It belongs to the Austronesian languages, more specifically to the Oceanic branch of that family. It has been difficult to classify it further, but Yapese may prove to be one of the Admiralty Islands languages. The Yapese language refers to the language spoken specifically on the Yap Main Islands, and does not include the Chuukic languages spoken in the Yap Neighboring Islands: Ulithian, Woleaian, and Satawalese.

The family of Southeast Solomonic languages forms a branch of the Oceanic languages. It consists of some 26 languages covering the Eastern Solomon Islands, from the tip of Santa Isabel to Makira. The fact that there is little diversity amongst these languages, compared to groups of similar size in Melanesia, suggests that they dispersed in the relatively recent past. Bugotu and Gela are two of the most conservative languages.
The nine South Vanuatu languages form a family of the Southern Oceanic languages, spoken in Tafea Province of Vanuatu.

The Western Oceanic languages is a linkage of Oceanic languages, proposed and studied by Ross (1988). They make up a majority of the Austronesian languages spoken in New Guinea.

The twenty Micronesian languages form a family of Oceanic languages. Micronesian languages are known for their lack of plain labial consonants; they have instead two series, palatalized and labio-velarized labials, similar to the related Loyalty Islands languages.
The Manus languages are a subgroup of about two dozen Oceanic languages located on Manus Island and nearby offshore islands in Manus Province of Papua New Guinea. The exact number of languages is difficult to determine because they form a dialect continuum. The name Manus originally designated an ethnic group whose members spoke closely related languages and whose coastal dwellers tended to build their houses on stilts out over the sea.
The Huon Gulf languages are Western Oceanic languages spoken primarily in Morobe Province of Papua New Guinea. They may form a group of the North New Guinea languages, perhaps within the Ngero–Vitiaz branch of that family.
Terence Michael Crowley was a linguist specializing in Oceanic languages as well as Bislama, the English-lexified Creole recognized as a national language in Vanuatu. From 1991 he taught in New Zealand. Previously, he was with the Pacific Languages Unit of the University of the South Pacific in Vanuatu (1983–90) and with the Department of Language and Literature at the University of Papua New Guinea (1979–83).

The Southern Oceanic languages are a linkage of Oceanic languages spoken in Vanuatu and New Caledonia. It was proposed by John Lynch in 1995 and supported by later studies. It appears to be a linkage rather than a language family with a clearly defined internal nested structure.
Western Fijian, also known as Wayan is an Oceanic language spoken in Fiji by about 57,000 people.
Proto-Oceanic is a proto-language that historical linguists since Otto Dempwolff have reconstructed as the hypothetical common ancestor of the Oceanic subgroup of the Austronesian language family. Proto-Oceanic is a descendant of the Proto-Austronesian language (PAN), the common ancestor of the Austronesian languages.

Erromangan, or Sie (Sye), is the primary language spoken on the island Erromango in the Tafea region of the Vanuatu islands. The other Erromanga languages are either moribund or extinct. Although the island is quite large (887 km2), the total number of speakers of Erromango is estimated at 1900.
The family of Northwest Solomonic languages is a branch of the Oceanic languages. It includes the Austronesian languages of Bougainville and Buka in Papua New Guinea, and of Choiseul, New Georgia, and Santa Isabel in Solomon Islands.
Teanu is the main language spoken on the island of Vanikoro, in the easternmost province of the Solomon Islands.

Baluan-Pam is an Oceanic language of Manus Province, Papua New Guinea. It is spoken on Baluan Island and on nearby Pam Island. The number of speakers, according to the latest estimate based on the 2000 Census, is 2,000. Speakers on Baluan Island prefer to refer to their language with its native name Paluai.
Lenakel, or West Tanna, is a dialect chain spoken on the western coast of Tanna Island in Vanuatu.
Loniu is an Austronesian language spoken along the southern coast of Los Negros Island in the Manus Province, immediately east of Manus Island in Manus Province, Papua New Guinea. Loniu is spoken in the villages of Loniu and Lolak, and there are estimated to be 450–500 native speakers, although some live in other Manus villages or on the mainland of Papua New Guinea.
Darrell T. Tryon was a New Zealand-born linguist, academic, and specialist in Austronesian languages. Specifically, Tryon specialised in the study of the languages of the Pacific Islands, particularly Vanuatu, the Solomon Islands, and the French-speaking Pacific.
Proto-Admiralty Islands is the reconstructed ancestor of the Admiralty Islands languages of the Admiralty Islands, located in Papua New Guinea. It belongs to the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian languages.