Related Research Articles
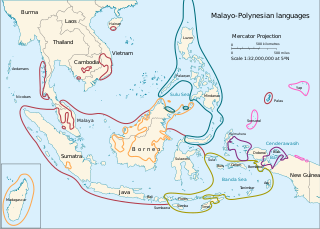
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula, with Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken on the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier.
Kiput is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in northern Sarawak, Borneo, Malaysia.

The Malayic languages are a branch of the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The most prominent member is Malay, a pluricentric language given national status in Brunei and Singapore while also the basis for national standards Malaysian in Malaysia and Indonesian in Indonesia. The Malayic branch also includes local languages spoken by ethnic Malays, further several languages spoken by various other ethnic groups of Sumatra, Indonesia and Borneo even as far as Urak Lawoi in the southwestern coast of Thailand.

Bintulu is a coastal town on the island of Borneo in the central region of Sarawak, Malaysia. Bintulu is located 610 kilometres northeast of Kuching, 216 kilometres northeast of Sibu, and 200 kilometres southwest of Miri. With a population of 114,058 as of 2010, Bintulu is the capital of the Bintulu District of the Bintulu Division of Sarawak, Malaysia.

Lun Bawang or Lundayeh is the language spoken by the Lun Bawangs. It belongs to the Malayo-Polynesian family.
The Barito languages are around twenty Austronesian languages of Indonesia (Borneo), plus Malagasy, the national language of Madagascar, and the Sama–Bajaw languages around the Sulu Archipelago. They are named after the Barito River located in South Kalimantan, Indonesia.
The Greater North Borneo languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The subgroup historically covers languages that are spoken throughout much of Borneo and Sumatra, as well as parts of Java, and Mainland Southeast Asia. The Greater North Borneo hypothesis was first proposed by Robert Blust (2010) and further elaborated by Alexander Smith. The evidence presented for this proposal are solely lexical. Despite its name, this branch has been now widespread within the Maritime Southeast Asia region.

The Bali–Sasak–Sumbawa languages are a group of closely related languages spoken in Indonesia in the western Lesser Sunda Islands. The three languages are Balinese on Bali, Sasak on Lombok, and Sumbawa on western Sumbawa.
The Sabahan languages are a group of Austronesian languages centered on the Bornean province of Sabah.
The North Sarawakan languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken in the northeastern part of the province of Sarawak, Borneo, and proposed in Blust.

Kelabit is one of the most remote languages of Borneo, on the Sarawak–North Kalimantan border. It is spoken by one of the smallest ethnicities in Borneo, the Kelabit people.
The Greater Central Philippine languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family, defined by the change of Proto-Malayo-Polynesian *R to *g. They are spoken in the central and southern parts of the Philippines, eastern and western parts of Sabah, Malaysia and in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia. This subgroup was first proposed by Robert Blust (1991) based on lexical and phonological evidence, and is accepted by most specialists in the field.

Tatau District is one of the two districts of Bintulu Division in Sarawak, Malaysia. It has a total area of 4,945.80 square kilometres. The largest town in the district is Tatau.

Sebauh is a district of Bintulu Division, Sarawak, Malaysia. It shares a boundary with Miri, Baram, Kapit Division, Belaga and Tatau. It has a total area of roughly 5,262.90 square kilometres. Sebauh town is a main administrative and economy centre of Sebauh district.

The Bintulu District is one of two districts of Bintulu Division in Sarawak, Malaysia. It has a total area of 7,220.40 square kilometres. Bintulu District has a sub-district, which is Sebauh. There are two towns in Bintulu District, namely Bintulu, which is the capital of both Bintulu District and Bintulu Division, and Sebauh.
The Bima language, or Bimanese, is an Austronesian language spoken on the eastern half of Sumbawa Island, Indonesia, which it shares with speakers of the Sumbawa language. Bima territory includes the Sanggar Peninsula, where the extinct Papuan language Tambora was once spoken. Bima is an exonym; the autochthonous name for the territory is Mbojo and the language is referred to as Nggahi Mbojo. There are over half a million Bima speakers. Neither the Bima nor the Sumbawa people have alphabets of their own for they use the alphabets of the Bugis and the Malay language indifferently.
Molbog is an Austronesian language spoken in the Philippines and Sabah, Malaysia. The majority of speakers are concentrated at the southernmost tip of the Philippine province of Palawan, specifically the municipalities of Bataraza and Balabac. Both municipalities are considered as bastions for environmental conservation in the province. The majority of Molbog speakers are Muslims.
Saʼban is one of the remoter languages of Borneo, on the Sarawak–Kalimantan border. The language is known as hmeu Saʼban in the Saʼban language.
Tring is one of the languages of Borneo, in Sarawak, Malaysia. Ethnologue classifies the language as threatened.

Rejang is an Austronesian language predominantly spoken by the Rejang people in southwestern parts of Sumatra (Bengkulu), Indonesia. There are five dialects, spread from mountainous region to the coastal region of Bengkulu, including the Musi (Musai) dialect, the Lebong dialect, the Kebanagung dialect, the Rawas (Awes) dialect, and the Pesisir dialect.