Related Research Articles
Signing Exact English is a system of manual communication that strives to be an exact representation of English language vocabulary and grammar. It is one of a number of such systems in use in English-speaking countries. It is related to Seeing Essential English (SEE-I), a manual sign system created in 1945, based on the morphemes of English words. SEE-II models much of its sign vocabulary from American Sign Language (ASL), but modifies the handshapes used in ASL in order to use the handshape of the first letter of the corresponding English word.
Malaysian Sign Language is the principal language of the deaf community of Malaysia. It is also the official sign language used by the Malaysian government to communicate with the deaf community and was officially recognised by the Malaysian government in 2008 as a means to officially communicate with and among the deaf, particularly on official broadcasts and announcements. BIM has many dialects, differing from state to state.
Kod Tangan Bahasa Malaysia (KTBM), or Manually Coded Malay, is a signed form of the Malay language recognized by the government in Malaysia and the Malaysian Ministry of Education. It aids teachers in teaching the Malay language to deaf students in formal education settings. It is not a language but a manually coded form of Malay. It was adapted from American Sign Language, with the addition of some local signs, plus grammatical signs to represent Malay affixation of nouns and verbs. It is used in Deaf schools to teach the Malay language.
Oralism is the education of deaf students through oral language by using lip reading, speech, and mimicking the mouth shapes and breathing patterns of speech. Oralism came into popular use in the United States around the late 1860s. In 1867, the Clarke School for the Deaf in Northampton, Massachusetts, was the first school to start teaching in this manner. Oralism and its contrast, manualism, manifest differently in deaf education and are a source of controversy for involved communities. Listening and Spoken Language, a technique for teaching deaf children that emphasizes the child's perception of auditory signals from hearing aids or cochlear implants, is how oralism continues on in the current day.
Icelandic Sign Language is the sign language of the deaf community in Iceland. It is based on Danish Sign Language; until 1910, deaf Icelandic people were sent to school in Denmark, but the languages have diverged since then. It is officially recognized by the state and regulated by a national committee.
Tan Seng Giaw is a veteran Malaysian from the Democratic Action Party (DAP).
e-pek@k is a project that facilitates the usage of information and communication technologies to provide the services for the hearing impaired community in Malaysia.

Tan Sri Dato' Seri Utama Dr. Rais bin Yatim is a Malaysian politician and lawyer who served as the 18th President of the Dewan Negara from September 2020 to June 2023, 8th Menteri Besar of Negeri Sembilan from 1978 to 1982 and the Member of Parliament (MP) for Jelebu from November 1999 to May 2013.

The Ministry of Education is a ministry of the Government of Malaysia that is responsible for education system, compulsory education, pre-tertiary education, technical and vocational education and training (TVET), curriculum standard, textbook, standardised test, language policy, translation, selective school, comprehensive school.
Singapore Sign Language, or SgSL, is the native sign language used by the deaf and hard of hearing in Singapore, developed over six decades since the setting up of the first school for the Deaf in 1954. Since Singapore's independence in 1965, the Singapore deaf community has had to adapt to many linguistic changes. Today, the local deaf community recognises Singapore Sign Language (SgSL) as a reflection of Singapore's diverse culture. SgSL is influenced by Shanghainese Sign Language (SSL), American Sign Language (ASL), Signing Exact English (SEE-II) and locally developed signs.
Indonesian Sign Language is any of several related deaf sign languages of Indonesia, at least on the island of Java. It is based on American Sign Language, with local admixture in different cities. Although presented as a coherent language when advocating for recognition by the Indonesian government and use in education, the varieties used in different cities may not be mutually intelligible.
Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Pendidikan Khas Persekutuan is a school in Penang, Malaysia. Currently located at 600H, Vale of Tempe Road, 11200 Tanjung Bungah, it was the pioneer deaf school in Malaysia.
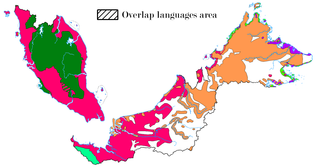
The indigenous languages of Malaysia belong to the Mon-Khmer and Malayo-Polynesian families. The national, or official, language is Malay which is the mother tongue of the majority Malay ethnic group. The main ethnic groups within Malaysia are the Malay people, Han Chinese people and Tamil people, with many other ethnic groups represented in smaller numbers, each with its own languages. The largest native languages spoken in East Malaysia are the Iban, Dusunic, and Kadazan languages. English is widely understood and spoken within the urban areas of the country; the English language is a compulsory subject in primary and secondary education. It is also the main medium of instruction within most private colleges and private universities. English may take precedence over Malay in certain official contexts as provided for by the National Language Act, especially in the states of Sabah and Sarawak, where it may be the official working language. Furthermore, the law of Malaysia is commonly taught and read in English, as the unwritten laws of Malaysia continue to be partially derived from pre-1957 English common law, which is a legacy of past British colonisation of the constituents forming Malaysia. In addition, authoritative versions of constitutional law and statutory law are continuously available in both Malay and English.

Deaf education is the education of students with any degree of hearing loss or deafness. This may involve, but does not always, individually-planned, systematically-monitored teaching methods, adaptive materials, accessible settings, and other interventions designed to help students achieve a higher level of self-sufficiency and success in the school and community than they would achieve with a typical classroom education. There are different language modalities used in educational setting where students get varied communication methods. A number of countries focus on training teachers to teach deaf students with a variety of approaches and have organizations to aid deaf students.
Ugandan Sign Language (USL) is the deaf sign language of Uganda.
The history of deaf education in the United States began in the early 1800s when the Cobbs School of Virginia, an oral school, was established by William Bolling and John Braidwood, and the Connecticut Asylum for the Deaf and Dumb, a manual school, was established by Thomas Hopkins Gallaudet and Laurent Clerc. When the Cobbs School closed in 1816, the manual method, which used American Sign Language, became commonplace in deaf schools for most of the remainder of the century. In the late 1800s, schools began to use the oral method, which only allowed the use of speech, as opposed to the manual method previously in place. Students caught using sign language in oral programs were often punished. The oral method was used for many years until sign language instruction gradually began to come back into deaf education.
Deaf Education in Kenya is a constantly changing section of the Kenyan education system that is focused on educating deaf, hard-of-hearing, and hearing-impaired Kenyan students. There are many organizations in Kenya made to protect the rights of Deaf Kenyans and promote progress in deaf education. The state of Kenyan deaf education is constantly changing and improving.
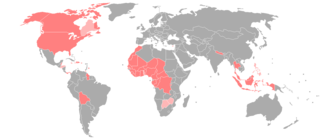
American Sign Language (ASL) developed in the United States, starting as a blend of local sign languages and French Sign Language (FSL). Local varieties have developed in many countries, but there is little research on which should be considered dialects of ASL and which have diverged to the point of being distinct languages.

Harriet Burbank Rogers was an American educator, a pioneer in the oral method of instruction of the deaf. She was the first director of Clarke School for the Deaf, the first U.S. institution to teach the deaf by articulation and lip reading rather than by signing. Her advocacy for oralist instruction children increased utilization of oral-only communication models in many American schools.
Kassim Ahmad was a Malaysian Muslim philosopher, intellectual, writer, poet and an educator. He was also a socialist politician in the early days of Malaya and later Malaysia and was detained without trial from 1976 to 1981 under Malaysia's Internal Security Act.
References
- ↑ Penang Sign Language at Ethnologue (16th ed., 2009)
