Related Research Articles

The Algonquian languages are a family of Indigenous languages of the Americas and most of the languages in the Algic language family are included in the group. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically similar Algonquin dialect of the Indigenous Ojibwe language (Chippewa), which is a senior member of the Algonquian language family. The term Algonquin has been suggested to derive from the Maliseet word elakómkwik, "they are our relatives/allies".

An extinct language is a language with no living descendants that no longer has any first-language or second-language speakers. In contrast, a dead language is a language that no longer has any first-language speakers, but does have second-language speakers or is used fluently in written form, such as Latin. A dormant language is a dead language that still serves as a symbol of ethnic identity to an ethnic group; these languages are often undergoing a process of revitalisation. Languages that have first-language speakers are known as modern or living languages to contrast them with dead languages, especially in educational contexts.
The Agaw or Central Cushitic languages are Afro-Asiatic languages spoken by several groups in Ethiopia and, in one case, Eritrea. They form the main substratum influence on Amharic and other Ethiopian Semitic languages.

The Misumalpan languages are a small family of languages spoken by indigenous peoples on the east coast of Nicaragua and nearby areas. The name "Misumalpan" was devised by John Alden Mason and is composed of syllables from the names of the family's three members Miskito, Sumo languages and Matagalpan. It was first recognized by Walter Lehmann in 1920. While all the languages of the Matagalpan branch are now extinct, the Miskito and Sumu languages are alive and well: Miskito has almost 200,000 speakers and serves as a second language for speakers of other indigenous languages in the Mosquito Coast. According to Hale, most speakers of Sumu also speak Miskito.

The Papuan Tip languages are a branch of the Western Oceanic languages consisting of 60 languages.
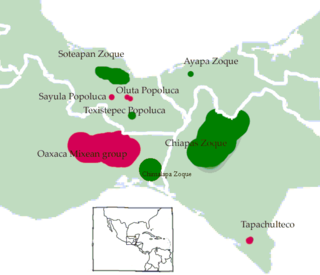
The Mixe–Zoque languages are a language family whose living members are spoken in and around the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, Mexico. The Mexican government recognizes three distinct Mixe–Zoquean languages as official: Mixe or ayook with 188,000 speakers, Zoque or o'de püt with 88,000 speakers, and the Popoluca languages of which some are Mixean and some Zoquean with 69,000 speakers. However, the internal diversity in each of these groups is great. Glottolog counts 19 different languages, whereas the current classification of Mixe–Zoquean languages by Wichmann (1995) counts 12 languages and 11 dialects. Extinct languages classified as Mixe–Zoquean include Tapachultec, formerly spoken in Tapachula, along the southeast coast of Chiapas.

The Darwin Region languages are a family of Australian Aboriginal languages of northern Australia proposed by linguist Mark Harvey. It unites the pair of Limilngan languages with two language isolates:
The Jingpho-Luish, Jingpho-Asakian, Kachin–Luic, or Kachinic languages are a group of Sino-Tibetan languages belonging the Sal branch. They are spoken in northeastern India, Bangladesh and Myanmar, and consist of the Jingpho language and the Luish languages Sak, Kadu, Ganan, Andro, Sengmai, and Chairel. Ethnologue and Glottolog include the extinct or nearly extinct Taman language in the Jingpo branch, but Huziwara (2016) considers it to be unclassified within Tibeto-Burman.

The Oroch language is a nearly extinct language spoken by the Oroch people in Siberia. It is a member of the southern group of the Tungusic languages and is closely related to the Nanai language and Udege language. It was spoken in the Khabarovsk Krai. The language is split into three dialects: Tumninsky, Khadinsky, and Hungarisky. At the beginning of the 21st century, a written form of the language was created. The Russian government and the scientific field disagree on whether the language is living or extinct.
The Bishuo language is an extinct or nearly extinct southern Bantoid language of Cameroon. It was spoken in the North West Province, Menchum Department, Furu-Awa Subdivision, Ntjieka, Furu-Turuwa and the Furu-Sambari villages. It was related to Bikya language. It was reported by Breton 1986 that the Bishuo people had shifted to Jukun, with apparently only one remaining person, over 60 years old, who knew any Bishuo.
Pakanha (Bakanha), or Ayabakan, is a nearly extinct Paman language spoken on the Cape York Peninsula of Queensland, Australia. In 1981, there were 10 speakers of the language, originally spoken by the aboriginal Pakanha people in the central part of the Cape York Peninsula.
Samre, is a nearly extinct Pearic language of Thailand and, formerly, Cambodia. The language is evidently extinct in Cambodia, but a 1998 survey found 20–30 speakers in Nonsi Subdistrict, Bo Rai District, Trat Province, Thailand and estimated the total number of people able to speak the language to be 200.
Tidikelt is a Zenati Berber language spoken in Algeria. It is one of the Mzab–Wargla languages. Tidikelt is spoken in the northwest of Tamanrasset Province, including in In Salah District. Tidikelt Tamazight has two dialects; Tidikelt and Tit. Tidikelt Tamazight is considered to be an endangered language, nearly extinct, with only 1,000 speakers of the language and decreasing.
Tanimbili (Tanibili), or Nyisunggu, is a nearly-extinct language spoken on the island of Utupua, in the easternmost province of the Solomon Islands.
Ririo is a nearly extinct indigenous language of Choiseul Province, Solomon Islands.
Masimasi is a nearly extinct Austronesian language spoken on an offshore island of Papua, Indonesia.
Liki, also known as Moar, is a nearly extinct Austronesian language spoken on offshore islands of Papua province, Indonesia.
Salas is a nearly extinct language of Seram, Indonesia.
Punan Batu is a nearly extinct language of Sarawak.
Amahai is a nearly extinct Austronesian language spoken in the Moluccas in eastern Indonesia. It might actually be two distinct languages.