Related Research Articles
Sulka is a language isolate of New Britain, Papua New Guinea. In 1991, there were 2,500 speakers in eastern Pomio District, East New Britain Province. Villages include Guma in East Pomio Rural LLG. With such a low population of speakers, this language is considered to be endangered. Sulka speakers had originally migrated to East New Britain from New Ireland.
Mailu, or Magi (Magɨ), is a Papuan language of Papua New Guinea.
Amanab is a Papuan language spoken by 4,400 people in Amanab District, Sandaun Province, Papua New Guinea.
Sougb, or Sogh, is a Papuan language of the East Bird's Head language family spoken in the east of the Bird's Head Peninsula to the east of Meyah and to the south of Manokwari, including the area of Soug Jaya District, Teluk Wondama Regency. It consists of four dialects and is spoken by around 12,000 people in all. The language is alternatively known as Mantion, or Manikion, an originally derogatory term used by the Biak people.
Tifal is an Ok language spoken in Papua New Guinea. Dialects are Tifal (Tifalmin), Urap (Urapmin) and Atbal (Atbalmin).

Maʼya is an Austronesian language of the Raja Ampat islands in Southwest Papua, Indonesia. It is part of the South Halmahera–West New Guinea (SHWNG) subgroup and is spoken by about 6,000 people in coastal villages on the islands Misool, Salawati, and Waigeo, on the boundary between Austronesian and Papuan languages.
Roro may refer to:
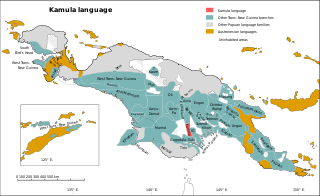
Kamula is a Trans–New Guinea language that is unclassified within that family in the classification of Malcolm Ross (2005). Noting insufficient evidence, Pawley and Hammarström (2018) leave it as unclassified.
Kwomtari is the eponymous language of the Kwomtari family of Papua New Guinea.
Kiwai is a Papuan language, or languages, of southern Papua New Guinea. Dialects number 1,300 Kope, 700 Gibaio, 1,700 Urama, 700 Arigibi, 3,800 Coast, 1,000 Daru, 4,500 Island, 400 Doumori. Wurm and Hattori (1981) classify Arigibi as a separate language.
Kokoda is a Papuan language of the Bird's Head Peninsula spoken by the Eme Yode people of Kokoda District, South Sorong Regency, Southwest Papua. The three dialects—Kokoda proper, Kasuweri, and Tarof—are divergent enough to sometimes be considered separate languages.
Mali or Gaktai is a Papuan language spoken in East New Britain Province on the island of New Britain, Papua New Guinea.
Rawa is one of the Finisterre languages of Papua New Guinea. The two dialects, Rawa and Karo, are on opposite sides of the Finisterre Range.
Urat is a Torricelli language spoken by a decreasing number of people in Papua New Guinea.
Kombio is a Torricelli language spoken by a decreasing number of people in Papua New Guinea, as people shift to Tok Pisin. It also goes by the name Endangen. Mwi dialect is divergent, but there is some degree of difficulty in comprehension between other major dialects as well.
Lamaholot, also known as Solor or Solorese, is a Central Malayo-Polynesian dialect cluster of Flores, Indonesia. The varieties may not be all mutually intelligible; Keraf (1978) reports that there are 18 languages under the name.
Mato is a minor Austronesian language of northern Papua New Guinea just inside Morobe Province. Mato is also referred to by the names Nenaya, Nengaya, and Nineia. Mato language has two minor variations, Tabares and Remuk, and the two variations are each spoken in three separate villages. While Mato is surrounded by several other languages, this has no effect on the grammar changes within Mato boundaries. The linguistic situation is very stable, due in part to the geographical isolation of the Mato people.
Barok is an Austronesian language spoken in New Ireland, Papua New Guinea.
Bola, or Bakovi, is an Oceanic language of West New Britain in Papua New Guinea. The Harua (Xarua) dialect developed on a palm plantation.
Gumawana is an Austronesian language spoken by people living on the Amphlett Islands of the Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea.