Related Research Articles

Modern Standard Hindi, commonly referred to as Hindi, is the standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in Devanagari script. It is the official language of India alongside English and the lingua franca of North India. Hindi is considered a Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas. It is an official language in nine states and three union territories and an additional official language in three other states. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India.

Suva is the capital and the most populous city of Fiji. It is the home of the country's largest metropolitan area and serves as its major port. The city is located on the southeast coast of the island of Viti Levu, in Rewa Province, Central Division.

Asia is home to hundreds of languages comprising several families and some unrelated isolates. The most spoken language families on the continent include Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Japonic, Dravidian, Indo-European, Afroasiatic, Turkic, Sino-Tibetan, Kra–Dai and Koreanic. Many languages of Asia, such as Chinese, Sanskrit, Arabic, Tamil or Telugu, have a long history as a written language.
Bihari languages are a group of the Indo-Aryan languages. The Bihari languages are mainly spoken in the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal, and also in Nepal. The most widely spoken languages of the Bihari group are Bhojpuri, Magahi and Maithili.

Fijian is an Austronesian language of the Malayo-Polynesian family spoken by some 350,000–450,000 ethnic Fijians as a native language. The 2013 Constitution established Fijian as an official language of Fiji, along with English and Fiji Hindi and there is discussion about establishing it as the "national language". Fijian is a VOS language.
Lau or LAU may refer to:
Lauan may refer to:
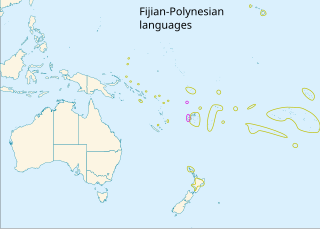
The Central Pacific languages, also known as Fijian–Polynesian languages, are a branch of the Oceanic languages spoken in Fiji and Polynesia.
The Lau Islands of Fiji are situated in the southern Pacific Ocean, just east of the Koro Sea. Of this chain of about sixty islands and islets, about thirty are inhabited. The Lau Group covers a land area of 188 square miles, and had a population of 10,683 at the most recent census in 2007. While most of the northern Lau Group are high islands of volcanic origin, those of the south are mostly carbonate low islands.

Fiji Hindi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by Indo-Fijians. It is an Eastern Hindi and Bihari language, considered to be a koiné language based on Awadhi that has also been subject to considerable influence by Bhojpuri, other Eastern Hindi and Bihari dialects, and Standard Hindi-Urdu. It has also borrowed some vocabulary from English, Fijian, Telugu, Tamil, Bengali, Punjabi, Gujarati, and Malayalam. Many words unique to Fiji Hindi have been created to cater for the new environment that Indo-Fijians now live in. First-generation Indians in Fiji, who used the language as a lingua franca in Fiji, referred to it as Fiji Baat, "Fiji talk". It is closely related to Caribbean Hindustani and the Bhojpuri-Hindustani spoken in Mauritius and South Africa. It is largely mutually intelligible with the languages of Awadhi and Bhojpuri, as well as with the Bihari languages of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhesh, Koshi, Bagmati, Gandaki and Lumbini, and the dialects of Eastern Hindi of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Lumbini, but differs in phonetics and vocabulary with Modern Standard Hindi and Urdu.
The Citizens Federation was the political expression of a predominantly Indo-Fijian trade union movement, and was a forerunner of the present day National Federation Party.
Gone Dau is an East Fijian language spoken by about 500 people on the islands of Gone and Dau, Fiji.
Lomaiviti is an East Fijian language spoken by about 1,600 people on a number of islands of Fiji.
Western Fijian, also known as Wayan is an Oceanic language spoken in Fiji by about 57,000 people.
Namosi-Naitasiri-Serua is an Oceanic language spoken in Fiji by about 1,600 people.

Fiji has three official languages under the 1997 constitution : English, Fijian and Fiji Hindi. The Fijian language is spoken as the first language by most indigenous Fijians who make up around 54% of the population.

There are two official languages of Norfolk Island, English and Norfuk. English, due to the influence of Great Britain and Australia, the two colonial powers who administered Norfolk Island, is the dominant language of the pair. Norfuk, a creole language based on English and Tahitian and brought to the island by the descendants of the Bounty mutineers from Pitcairn Island was spoken by 580 people according to the 1989 census. It is closely related to Pitkern spoken on Pitcairn Island. Many Norfolk Islanders also speak Fijian.
Two Men of Fiji is a 1959 Australian television documentary. It was directed by Brett Porter for the Shell Film Unit. It was filmed by Hone Glendinning and Roger Mirams in Fiji over a two-month period and was screened theatrically in Fiji.

The Bhojpuri Wikipedia is the Bhojpuri language version of Wikipedia, run by the Wikimedia Foundation. The site was launched on 21 February 2003. Bhojpuri is today written in the Devanagari script. Bhojpuri is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in northern-eastern India and the Terai region of Nepal. It is chiefly spoken in western Bihar and eastern Uttar Pradesh. The language is a minority language in Fiji, Guyana, Mauritius, South Africa, Suriname, and Trinidad and Tobago.
LLX or llx may refer to:
References
- ↑ Lauan at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)