
Quebec French, also known as Québécois French, is the predominant variety of the French language spoken in Canada. It is the dominant language of the province of Quebec, used in everyday communication, in education, the media, and government.

Alsatian is the group of Alemannic German dialects spoken in most of Alsace, a formerly disputed region in eastern France that has passed between French and German control five times since 1681.
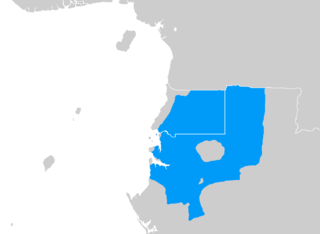
Fang is a Central African language spoken by around 1 million people, most of them in Equatorial Guinea, and northern Gabon, where it is the dominant Bantu language; Fang is also spoken in southern Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, and small fractions of the islands of São Tomé and Príncipe. It is related to the Bulu and Ewondo languages of southern Cameroon.
The Ladakhi language is a Tibetic language spoken in the Indian union territory of Ladakh. It is the predominant language in the Buddhist-dominated district of Leh, and a minority language in the district of Kargil. Though a member of the Tibetic family, Ladakhi is not mutually intelligible with Standard Tibetan. Ladakhis and Tibetans usually communicate with each other in Hindi or English as they do not understand each other's languages clearly.

Maewo is an island in Vanuatu in Penama province, 105 km to the east of Espiritu Santo.
Guéré (Gere), also called Wè (Wee), is a Kru language spoken by over 300,000 people in the Dix-Huit Montagnes and Moyen-Cavally regions of Ivory Coast.
Mwotlap is an Oceanic language spoken by about 2,100 people in Vanuatu. The majority of speakers are found on the island of Motalava in the Banks Islands, with smaller communities in the islands of Ra and Vanua Lava, as well as migrant groups in the two main cities of the country, Santo and Port Vila.
The phonology of Quebec French is more complex than that of Parisian or Continental French. Quebec French has maintained phonemic distinctions between and, and, and, and. The latter phoneme of each minimal pair has disappeared in Parisian French, and only the last distinction has been maintained in Meridional French though all of those distinctions persist in Swiss and Belgian French.
Sa or Saa language is an Austronesian language spoken in southern Pentecost Island, Vanuatu. It had an estimated 2,500 speakers in the year 2000.
Raga is the language of northern Pentecost Island in Vanuatu. Like all Vanuatu languages, Raga belongs to the Oceanic subgroup of the Austronesian languages family. In old sources the language is sometimes referred to by the names of villages in which it is spoken, such as Bwatvenua (Qatvenua), Lamalanga, Vunmarama and Loltong.

The Kwasio language, also known as Ngumba / Mvumbo, Bujeba, and Gyele / Kola, is a language of Cameroon, spoken in the south along the coast and at the border with Equatorial Guinea by some 70,000 members of the Ngumba, Kwasio, Gyele and Mabi peoples. Many authors view Kwasio and the Gyele/Kola language as distinct. In the Ethnologue, the languages therefore receive different codes: Kwasio has the ISO 639-3 code nmg, while Gyele has the code gyi. The Kwasio, Ngumba, and Mabi are village farmers; the Gyele are nomadic Pygmy hunter-gatherers living in the rain forest. The Bagyeli are mostly forager and hunters. They use dogs, traps, machetes, spears, and nets to hunt and catch animals for food. Deforestation has affected their subsistence, and they have recently begun to benefit from selling baskets and meat to tourists.
Boiken is one of the more populous of the Ndu languages of Sepik River region of northern Papua New Guinea. It is spoken around Boiken Creek in Yangoru-Saussia District, East Sepik Province and adjacent islands off the north coast of northern Papua New Guinea.
Nyimang, also known as Ama, is an Eastern Sudanic language spoken in the Nuba Mountains of Sudan by the Nyimang people who are a sub-group of the Nuba people.
Mundang is an Mbum language of southern Chad and northern Cameroon, spoken by the Mundang people.
Tenetehára is a Tupi–Guarani language spoken in the state of Maranhão in Brazil. Sociolinguistically, it is two languages, each spoken by the Guajajara and the Tembé people, though these are mutually intelligible. Tembé was spoken by less than a quarter of its ethnic population of 820 in 2000; Guajajara, on the other hand, is more robust, being spoken by two-thirds of its 20,000 people.

Mao, also known as Sopvoma, is a Sino-Tibetan language of the Angami–Pochuri linguistic sub-branch. It is spoken primarily in Senapati district, northwestern Manipur and in Nagaland, India. It is similar to Angami. The speakers of this language use Meitei language as their second language (L2) according to the Ethnologue.

Ute is a dialect of the Colorado River Numic language, spoken by the Ute people. Speakers primarily live on three reservations: Uintah-Ouray in northeastern Utah, Southern Ute in southwestern Colorado, and Ute Mountain in southwestern Colorado and southeastern Utah. Ute is part of the Numic branch of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Other dialects in this dialect chain are Chemehuevi and Southern Paiute. As of 2010, there were 1,640 speakers combined of all three dialects Colorado River Numic. Ute's parent language, Colorado River Numic, is classified as a threatened language, although there are tribally-sponsored language revitalization programs for the dialect.
Avava (Navava), also known as Katbol, Tembimbe-Katbol, or Bangsa’ is an Oceanic language of central Malekula, Vanuatu. It has nasalized fricatives and a bilabial trill.
Sungwadaga or Central Maewo, also known as Peterara after one of its dialects, is an Oceanic language spoken on Maewo, Vanuatu.
Lenakel, or West Tanna, is a dialect chain spoken on the western coast of Tanna Island in Vanuatu.






