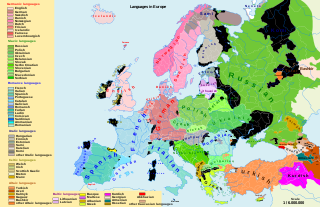
There are over 250 languages indigenous to Europe, and most belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language. The three largest phyla of the Indo-European language family in Europe are Romance, Germanic, and Slavic; they have more than 200 million speakers each, and together account for close to 90% of Europeans.
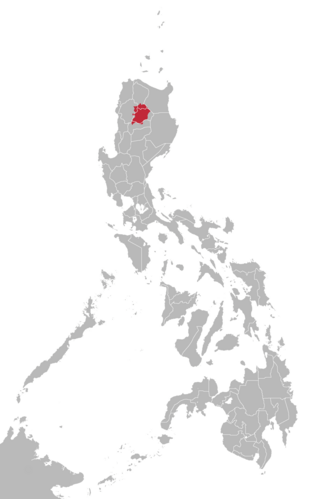
Kalinga is a dialect continuum of Kalinga Province in the Philippines, spoken by the Kalinga people, alongside Ilocano. The Banao Itneg variety is not one of the neighboring Itneg languages.
Wetarese is an Austronesian language of Wetar, an island in the south Maluku, Indonesia, and of the nearby island Liran.
Ngiri is a Bantu language closely related to Lingala.
Tetela, also Sungu, is a Bantu language of northern Kasai-Oriental Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is spoken by the Tetela people.
Melanau is an Austronesian language spoken in the coastal area of the Rajang delta on northwest Borneo, Sarawak, Malaysia and Brunei. There are several dialects—Mukah-Oya, Balingian, Bruit, Dalat, Lawas, Igan, Sarikei, Segahan, Prehan, Segalang, and Siteng.

The Santa Cruz language, locally known as Natqgu or Natügu, is the main language spoken on the island of Nendö or 'Santa Cruz', in the Solomon Islands.
Yaka, also spelled Iaca and Iyaka, is a Bantu language spoken in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Angola. There are two dialects, Yaka proper, which comprises 99% of speakers, and Ngoongo. The alleged varieties Pelende and Lonzo are political rather than ethnolinguistic entities.
Eton, or Ìtón, is a Bantu language spoken by the Eton people of Cameroon.
Yangum is a Torricelli dialect cluster of Papua New Guinea. Gel is nearly extinct. The principal variety is Mon, which is also known as Aiku, Malek, Menandon ~ Minendon; these names have been used for all Yangum varieties plus the closely related Ambrak.
Ding is a Bantu language that is spoken in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Ede is a dialect continuum of Benin and Togo that is closely related to the Yoruba language. The best-known variety is Ife.
Kayan is a dialect cluster spoken by the Kayan people of Borneo. It is a cluster of closely related dialects with limited mutual intelligibility, and is itself part of the Kayan-Murik group of Austronesian languages.
Berawan is an Austronesian language of Sarawak.
Lamaholot, also known as Solor or Solorese, is a Central Malayo-Polynesian dialect cluster of Flores, Indonesia. The varieties may not be all mutually intelligible; Keraf (1978) reports that there are 18 languages under the name.

Itneg is a South-Central Cordilleran dialect continuum found in the island of Luzon, Philippines. This language and Ilocano are spoken by the Itneg people in Abra.
Kimaragang (Marigang), Tobilung, and Rungus are varieties of a single Austronesian language of Sabah, Malaysia. The three varieties share moderate mutual intelligibility. Children are not learning it well in some areas.
Wagawaga is an Oceanic language spoken on the southeastern tip of Papua New Guinea. The Gamadoudou, Soma’a, and Sileba dialects may be a separate language, Yaleba.
Masela (Marsela) is the language of Marsela Island in southern Maluku, Indonesia. Regional varieties are distinct; Ethnologue counts it as three languages.




