| Northern South Sulawesi | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Indonesia (Sulawesi) |
| Linguistic classification | Austronesian
|
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | nort2894 |
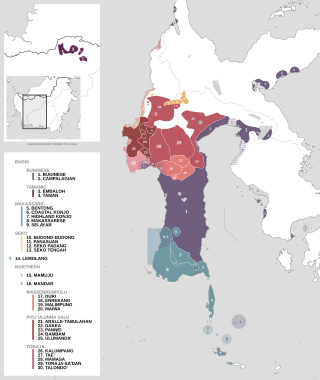
The Northern South Sulawesi languages are a subgroup of the South Sulawesi languages in the Austronesian language family. They are spoken in an area that stretches from the western peninsula of Sulawesi to the Gulf of Bone, Indonesia. [1] Its most prominent members are Mandar and Toraja.
Northern South Sulawesi is divided into five branches: [2] [1]
The Pitu Ulunna Salu, Massenrempulu and Toraja branches were already recognized by van der Veen (1929) as distinct units. [3]
The South Sulawesi languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are primarily spoken in the Indonesian provinces of South Sulawesi and West Sulawesi, with a small outlying pocket in West Kalimantan.
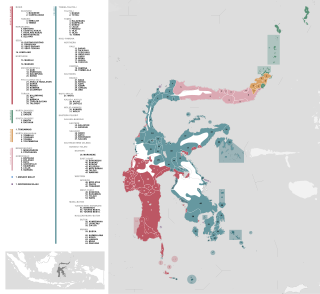
On the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, 114 native languages are spoken, all of which belong to the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. With a total number of 17,200,000 inhabitants, Sulawesi displays a high linguistic diversity when compared with the most densely populated Indonesian island Java, which hosts 4–8 languages spoken by 145,100,000 inhabitants.

The Mandarese are an ethnic group in the Indonesian province of West Sulawesi in Sulawesi. The Mandar language belongs to the Northern subgroup of the South Sulawesi languages group of the Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian language family. The closest language to Mandar is the Toraja-Sa'dan language.
Limola is an Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is spoken in two villages in North Luwu Regency, South Sulawesi. It is classified as a member of the Badaic subgroup of the South Sulawesi languages.
Enrekang is an Austronesian language spoken on Sulawesi, Indonesia. It belongs to the Northern branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup, and is closely related to Duri and Maiwa.
Duri is an Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is the prestige variety of the Massenrempulu languages.
Ulumandaʼ is an Austronesian language of West Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is nearly intelligible with other Pitu Ulunna Salu languages, but Ulumanda’ is distinguished by an unusual series of front vowels.
Bambam is an Austronesian language of West Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is spoken in the Mambi and Tabang districts of Mamasa Regency, and in the Matangnga district of Polewali Mandar Regency. Together with Aralle-Tabulahan, Ulumanda', Pannei and Dakka, Bambam belongs to the Pitu Ulunna Salu languages, which form a subbranch within the Northern branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup.
Toraja-Saʼdan is an Austronesian language spoken in South Sulawesi, Indonesia. It shares the name Taeʼ with East Toraja. Most of the Toraja language mapping was done by Dutch missionaries working in Sulawesi, such as Nicolaus Adriani and Hendrik van der Veen.
Taeʼ is a language spoken in South Sulawesi, Indonesia. It belongs to the Austronesian language family and is one of the languages of the ten tribes that inhabit the Tana Luwu region of South Sulawesi. The Taeʼ language is used by most of the inhabitants of the three regencies of Tana Luwu, and the city of Palopo. Taeʼ is part of the South Sulawesi group of languages. It is closely related to Toraja, and more distantly to Mandar, Massenrempulu, and Mamuju. Taeʼ is used as a lingua franca from south of the border with Buriko Wajo Regency to Malili East Luwu Regency, as well as in Tana Toraja and Massenrempulu.
Mamasa is an Austronesian language spoken in West Sulawesi, Indonesia. This language is the native language of the Mamasa people which is related to the Toraja people.

Coastal Konjo is an Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia, which belongs to the Makassaric branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup. It is spoken along the coast in the southeastern corner of South Sulawesi in the regencies of Sinjai, Bulukumba and Bantaeng. It is closely related to, but distinct from Highland Konjo, which also belongs to the Makassaric languages.

Highland Konjo is an Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia, which belongs to the Makassaric branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup. It is spoken in the interior parts of Bone, Bulukumba, Gowa, and Sinjai regencies of South Sulawesi province, in the area to the northwest of Mount Lompobatang. It is closely related to, but distinct from Coastal Konjo, which also belongs to the Makassaric languages.
Maiwa is an Austronesian language spoken by around 50,000 people in South Sulawesi, Indonesia. It belongs to the Northern branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup, and is closely related to Duri, Enrekang and Malimpung.
Malimpung is a language spoken by around 5,000 people in South Sulawesi, Indonesia. It belongs to the Northern branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup, and is closely related to Duri, Enrekang and Maiwa.

The Bonerate people are an ethnic group in South Sulawesi, Indonesia. They inhabit around the Selayar island group such as Bonerate, Madu, Kalaotoa, and Karompa islands.
Pannei is an Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is nearly intelligible with other Pitu Ulunna Salu languages.
Dakka is an endangered Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is spoken in the Wonomulyo district of Polewali Mandar Regency, and belongs to the Northern branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup.
The Seko languages are a group of four closely related Austronesian languages spoken in West Sulawesi and South Sulawesi provinces, Indonesia. They make up a primary branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup. The languages of the Seko branch are: Seko Padang, Seko Tengah, Panasuan and Budong-Budong.

The Makassar languages are a group of languages spoken in the southern part of South Sulawesi province, Indonesia, and make up one of the branches of the South Sulawesi subgroup in the Austronesian language family. The most prominent member of this group is Makassarese, with over two million speakers in the city of Makassar and neighboring areas.