Related Research Articles
The Muna–Buton languages are a group of languages spoken on the islands of Muna and Buton off the coast of South East Sulawesi province, Indonesia. They belong to the Celebic subgroup of the Austronesian family.
The Kaili–Pamona languages are a branch of the Celebic subgroup in the Austronesian language family spoken in western Central Sulawesi province, Indonesia.
The Wotu–Wolio languages are a group of closely related languages spoken in Sulawesi that belong to the Celebic subgroup of the Austronesian family.
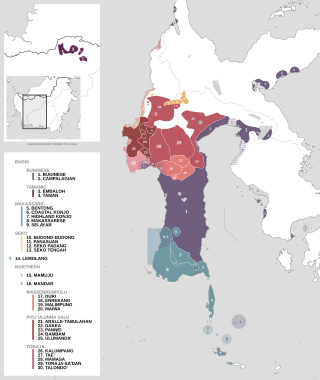
The South Sulawesi languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are primarily spoken in the Indonesian provinces of South Sulawesi and West Sulawesi, with a small outlying pocket in West Kalimantan.

The Celebic languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages spoken on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, formerly called Celebes. Almost all of the languages spoken in the provinces of Central Sulawesi and Southeast Sulawesi belong to the Celebic group. A few Celebic languages are located in South Sulawesi province. By number of languages, Celebic is the largest subgroup of Austronesian languages on Sulawesi.
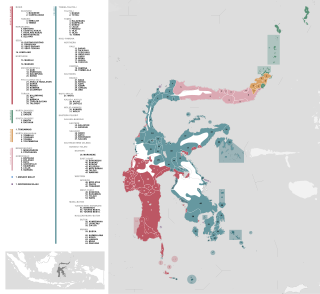
On the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, 114 native languages are spoken, all of which belong to the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. With a total number of 17,200,000 inhabitants, Sulawesi displays a high linguistic diversity when compared with the most densely populated Indonesian island Java, which hosts 4–8 languages spoken by 145,100,000 inhabitants.
Limola is an Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is spoken in two villages in North Luwu Regency, South Sulawesi. It is classified as a member of the Badaic subgroup of the South Sulawesi languages.
Enrekang is an Austronesian language spoken on Sulawesi, Indonesia. It belongs to the Northern branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup, and is closely related to Duri and Maiwa.
Duri is an Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is the prestige variety of the Massenrempulu languages.

Coastal Konjo is an Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia, which belongs to the Makassaric branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup. It is spoken along the coast in the southeastern corner of South Sulawesi in the regencies of Sinjai, Bulukumba and Bantaeng. It is closely related to, but distinct from Highland Konjo, which also belongs to the Makassaric languages.
Talondoʼ is an endangered Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia.
Rampi is a language of Central and South Sulawesi, Indonesia.
Budong-Budong is an Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia, spoken in the village of Tongkou, Budong-Budong District, Central Mamuju Regency. Together with Seko Padang, Seko Tengah and Panasuan, it belongs to the Seko branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup.
Kalumpang is an Austronesian dialect cluster of Sulawesi, Indonesia. Its dialects are only slightly closer to each other than they are to related languages.
Pannei is an Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is nearly intelligible with other Pitu Ulunna Salu languages.
Dakka is an endangered Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is spoken in the Wonomulyo district of Polewali Mandar Regency, and belongs to the Northern branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup.
Aralle-Tabulahan is an Austronesian language that belongs to the South Sulawesi subgroup. It is spoken in Mamasa Regency, West Sulawesi, Indonesia.
The Seko languages are a group of four closely related Austronesian languages spoken in West Sulawesi and South Sulawesi provinces, Indonesia. They make up a primary branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup. The languages of the Seko branch are: Seko Padang, Seko Tengah, Panasuan and Budong-Budong.

The Makassar languages are a group of languages spoken in the southern part of South Sulawesi province, Indonesia, and make up one of the branches of the South Sulawesi subgroup in the Austronesian language family. The most prominent member of this group is Makassarese, with over two million speakers in the city of Makassar and neighboring areas.
The Northern South Sulawesi languages are a subgroup of the South Sulawesi languages in the Austronesian language family. They are spoken in an area that stretches from the western peninsula of Sulawesi to the Gulf of Bone. Its most prominent members are Mandar and Toraja.
References
- ↑ Mamuju at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ Friberg, Timothy; Laskowske, Thomas V. (1989). "South Sulawesi Languages" (PDF). In J.N. Sneddon (ed.). Studies in Sulawesi Linguistics Part 1. NUSA 17. Jakarta: Badan Penyelenggara Seri Nusa. pp. 1–17.
- ↑ "Mamuju". Ethnologue. Archived from the original on 2016-08-14. Retrieved 2016-10-15.
- ↑ Zobel, Erik (2020). "The Kaili–Wolio Branch of the Celebic Languages". Oceanic Linguistics. 59 (1/2): 297–346. doi:10.1353/ol.2020.0014.