Related Research Articles

The Mamberamo is the second-longest river on the island of New Guinea, after Sepik River and the second largest in Oceania by discharge volume after Fly. It is located in the Indonesian province of Papua. It is the second largest river in Indonesia by volume of discharge after Kapuas and also the widest.

The East Geelvink Bay or East Cenderawasih languages are a language family of a dozen Papuan languages along the eastern coast of Geelvink Bay in Indonesian Papua, which is also known as Sarera Bay or Cenderawasih.
The Lower Mamberamo languages are a recently proposed language family linking two languages spoken along the northern coast of Papua province, Indonesia, near the mouth of the Mamberamo River. They have various been classified either as heavily Papuanized Austronesian languages belonging to the SHWNG branch, or as Papuan languages that had undergone heavy Austronesian influence. Glottolog 3.4 classifies Lower Mamberamo as Austronesian, while Donohue classifies it as Papuan. Kamholz (2014) classifies Warembori and Yoke each as coordinate primary subgroups of the South Halmahera–West New Guinea languages.
The Foja Range languages, or Tor–Kwerba in more limited scope, are a family of about two dozen Papuan languages. They are named after the Foja Mountains of western New Guinea.
Isirawa is a Papuan language spoken by about two thousand people on the north coast of Papua province, Indonesia. It's a local trade language, and use is vigorous. Stephen Wurm (1975) linked it to the Kwerba languages within the Trans–New Guinea family, and it does share about 20% of its vocabulary with neighboring Kwerba languages. However, based on its pronouns, Malcolm Ross (2005) felt he could not substantiate such a link, and left it as a language isolate. The pronouns are not, however, dissimilar from those of Orya–Tor, which Ross links to Kwerba, and Donahue (2002) accept it as a Greater Kwerba language.
The Burmeso language – also known as Taurap – is spoken by some 300 people in Burmeso village along the mid Mamberamo River in Mamberamo Tengah subdistrict, Mamberamo Raya Regency, Papua province, Indonesia. It is surrounded by the Kwerba languages to the north, the Lakes Plain languages to the south, and the East Cenderawasih Bay languages to the west.
Warembori is a moribund language spoken by about 600 people in Warembori village, Mamberamo Hilir District, Mamberamo Raya Regency, located around river mouths on the north coast of Papua, Indonesia.
Airoran is a language of Indonesia, spoken in the north coast area on the lower Apauwer River of Papua, in the villages of Subu, Motobiak, Isirania, etc. It is rather divergent from other Kwerba languages, though clearly related.

The West Trans–New Guinea languages are a suggested linguistic linkage of Papuan languages, not well established as a group, proposed by Malcolm Ross in his 2005 classification of the Trans–New Guinea languages. Ross suspects they are an old dialect continuum, because they share numerous features that have not been traced to a single ancestor using comparative historical linguistics. The internal divisions of the languages are also unclear. William A. Foley considers the TNG identity of the Irian Highlands languages at least to be established.
The half dozen Kwerba languages form a small language family spoken in Jayapura Regency of Indonesian West Papua.
The Dani–Kwerba languages were a hypothetical language family proposed by Arthur Capell in 1962 and adopted by Stephen Wurm as part of his Trans–New Guinea (TNG) phylum. Malcolm Ross reassigned the Dani languages to a West Trans–New Guinea linkage and the Kwerba languages to his Tor–Kwerba family, outside of TNG altogether.

Mamberamo Raya Regency or Greater Mamberamo Regency is one of the regencies (kabupaten) in Papua Province, Indonesia. Tt was created on 15 March 2007 from parts of Sarmi Regency and Waropen Regency. The regency gets its name from the Mamberamo River. The largest regency by land in Papua province, It covers an area of 23,813.91 km2, but had a population of only 18,365 at the 2010 Census which had almost doubled to 36,483 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 38,636. The administrative centre is at the town of Burmeso in Mamberamo Tengah.
Samarokena is a poorly documented Papuan language spoken in Indonesian Papua.
Kwerba is a Papuan language of Indonesia. Alternate names are Airmati (Armati), Koassa, Mataweja, Naibedj, Segar Tor, Tekutameso.
Nisa and Anasi (Bapu), are dialects of a Papuan language of the Indonesian province of Papua, on the eastern shore of Cenderawasih Bay in Sawai District, Mamberamo Raya Regency. Language use is vigorous.
Taworta, or Diebroud, is a Lakes Plain language spoken in Central Mamberamo, Highland Papua, Indonesia.
Eritai (Eri), or Baburiwa, is a Lakes Plain language of Irian Jaya, Indonesia. It is named after Erai village in East Central Mambermano District, Mamberamo Raya Regency.
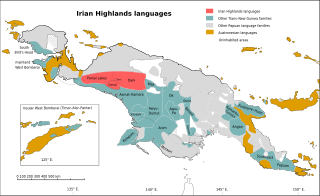
The West Papuan Highland languages, also known as the Irian Highland languages, are a branch of the Trans–New Guinea language family proposed by Larson & Larson (1972) and confirmed by Timothy Usher. William A. Foley considers their Trans–New Guinea identity to be established.
Hopea novoguineensis is a rainforest tree species in the Dipterocarpaceae family. It is found in New Guinea and on Halmahera, Maluku Province, Indonesia. The tree produces good timber.
References
- ↑ Kwerba Mamberamo at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)