Related Research Articles
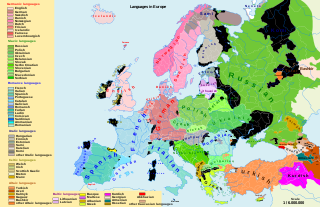
There are over 250 languages indigenous to Europe, and most belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language. The three largest phyla of the Indo-European language family in Europe are Romance, Germanic, and Slavic; they have more than 200 million speakers each, and together account for close to 90% of Europeans.
Ethnologue: Languages of the World is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It was first issued in 1951, and is now published by SIL International, an American evangelical Christian non-profit organization.
Luhya is a Bantu language of western Kenya.
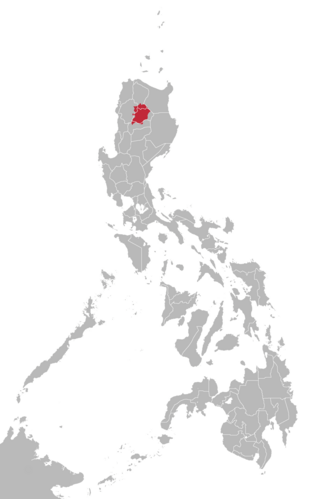
Kalinga is a dialect continuum of Kalinga Province in the Philippines, spoken by the Kalinga people, alongside Ilocano. The Banao Itneg variety is not one of the neighboring Itneg languages.

Cameroon is home to at least 250 languages, with some accounts reporting around 600. These include 55 Afro-Asiatic languages, two Nilo-Saharan languages, four Ubangian languages, and 169 Niger–Congo languages. This latter group comprises one Senegambian language (Fulfulde), 28 Adamawa languages, and 142 Benue–Congo languages . French and English are official languages, a heritage of Cameroon's colonial past as a colony of both France and the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1961. Eight out of the ten regions of Cameroon are primarily francophone and two are anglophone. The official percentage of French and English speakers is estimated by the Presidency of Cameroon to be 70% and 30% respectively.
The Sumba–Hawu languages are a group of closely related Austronesian languages, spoken in East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia.
Mijikenda is a Bantu dialect cluster spoken along the coast of East Africa, mostly in Kenya, where there are 2.6 million speakers but also in Tanzania, where there are 166,000 speakers. The name Mijikenda means "the nine settlements" or "the nine communities" and refers to the multiple language communities that make up the group. An older, derogatory term for the group is Nyika which refers to the "dry and bushy country" along the coast.
Kayan is a dialect cluster spoken by the Kayan people of Borneo. It is a cluster of closely related dialects with limited mutual intelligibility, and is itself part of the Kayan-Murik group of Austronesian languages.
Mumeng is a dialect chain of the Austronesian family in Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea. Dambi–Kumalu and Patep–Zenag–Gorakor have a degree of mutual intelligibility. Kapin may belong as well.
Kinabatangan is a language of Sabah, Malaysia.

Itneg is a South-Central Cordilleran dialect continuum found in the island of Luzon, Philippines. This language and Ilocano are spoken by the Itneg people in Abra.
Spurious languages are languages that have been reported as existing in reputable works, while other research has reported that the language in question did not exist. Some spurious languages have been proven to not exist. Others have very little evidence supporting their existence, and have been dismissed in later scholarship. Others still are of uncertain existence due to limited research.
West Arawe is an Austronesian dialect chain of West New Britain, Papua New Guinea. The principal varieties are Apalik, Gimi, Aiklep, and Arawe proper (Solong).
Kimaragang (Marigang), Tobilung, and Rungus are varieties of a single Austronesian language of Sabah, Malaysia. The three varieties share moderate mutual intelligibility. Children are not learning it well in some areas.
Atta is an Austronesian dialect cluster spoken by the Aeta (Agta) Negritos of the northern Philippines.
Tring is one of the languages of Borneo, in Sarawak, Malaysia. Ethnologue classifies the language as threatened.
Kodi is a Sumba language of Indonesia. The population figure may include Gaura, which Ethnologue counts as a dialect of both the Lamboya and Kodi languages. Kodi is an Austronesian language that is mainly spoken in Nusa Tenggara Timur province, the western part of the island of Sumba in eastern Indonesia. An alternate name for Kodi is Kudi and dialects of the language include Kodi Bokol, Kodi Bangedo, Nggaro (Nggaura) and is most alike to Wejewa. With only approximately 20,000 speakers, the Kodi language is an endangered language.
Masela (Marsela) is the language of Marsela Island in southern Maluku, Indonesia. Regional varieties are distinct; Ethnologue counts it as three languages.
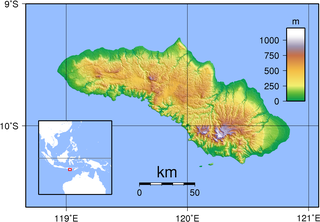
The Sumba languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian language family, spoken on Sumba, an island in eastern Indonesia. They are closely related to the Hawu-Dhao languages.
References
- ↑ Lamboya at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)