Related Research Articles
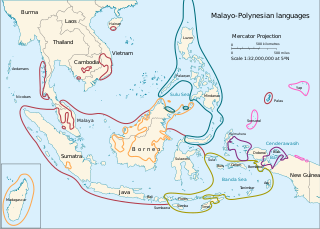
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula, with Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier.
Wolio is an Austronesian language spoken in and around Baubau on Buton Island, Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. It belongs to the Wotu–Wolio branch of the Celebic subgroup. Also known as Buton, it is a trade language and the former court language of the Sultan at Baubau. Today it is an official regional language; street signs are written in the Buri Wolio alphabet, based on the Arabic script.
Moronene is an Austronesian language spoken in Bombana Regency, Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. It belongs to the Bungku–Tolaki branch of the Celebic subgroup.
The Muna–Buton languages are a group of languages spoken on the islands of Muna and Buton off the coast of South East Sulawesi province, Indonesia. They belong to the Celebic subgroup of the Austronesian family.
The Kaili–Pamona languages are a branch of the Celebic subgroup in the Austronesian language family spoken in western Central Sulawesi province, Indonesia.
The Saluan–Banggai languages are a group of closely related languages spoken in eastern Central Sulawesi province, Indonesia. They belong to the Celebic subgroup of the Austronesian family.
The Wotu–Wolio languages are a group of closely related languages spoken in Sulawesi that belong to the Celebic subgroup of the Austronesian family.
The Tomini–Tolitoli languages are a disputed subgroup in the Austronesian language family spoken off the Gulf of Tomini and the district of Tolitoli in northern Central Sulawesi province, Indonesia, consisting of two branches, viz. "Tomini" and "Tolitoli". The unity of this group has not yet been demonstrated, and it may well be that the two branches actually are not closer to each other than to other languages of Sulawesi.
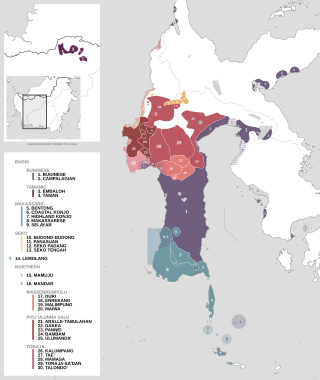
The South Sulawesi languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are primarily spoken in the Indonesian provinces of South Sulawesi and West Sulawesi, with a small outlying pocket in West Kalimantan.
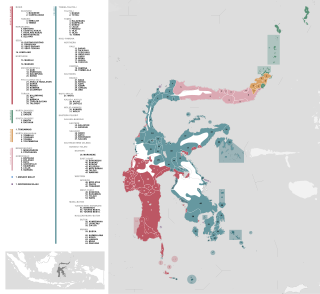
On the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, 114 native languages are spoken, all of which belong to the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. With a total number of 17,200,000 inhabitants, Sulawesi displays a high linguistic diversity when compared with the most densely populated Indonesian island Java, which hosts 4–8 languages spoken by 145,100,000 inhabitants.
Mamuju is an Austronesian language spoken on the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia.
The Badaic languages are a group of three closely related Austronesian languages spoken in the North Lore and South Lore districts in Poso Regency, Central Sulawesi, Indonesia, viz. Bada (Bada’), Behoa (Besoa), and Napu. The three languages are 80–91% lexically similar and to a great degree mutually intelligible, but their speakers are culturally distinct.
Kulisusu is an Austronesian language of Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is part of a dialect chain with two minor languages, Koroni and Taloki.
Bungku is an Austronesian language of Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is quite close to Wawonii. It was a local lingua franca before independence.
Padoe is an Austronesian language of the Celebic branch. It was traditionally spoken in the rolling plains south of Lake Matano in South Sulawesi province. In the 1950s, a portion of the Padoe-speaking population fled to Central Sulawesi to escape the ravages of the Darul Islam / Tentara Islam Indonesia (DI/TII) revolt. In 1991, it was estimated there were 5,000 speakers of Padoe in all locations.
Kamaru is an Austronesian language spoken on Buton Island, Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. It belongs to the Wotu–Wolio branch of the Celebic subgroup.
Wotu is an endangered Austronesian language of South Sulawesi, Indonesia. It belongs to the Wotu–Wolio branch of the Celebic subgroup.
Kalao, or Kalaotoa, is an Austronesian language of Kalao Island, South Sulawesi, Indonesia. It belongs to the Wotu–Wolio branch of the Celebic subgroup.
Laiyolo (Layolo) or Loa’ is an Austronesian language of South Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is spoken at the southern tip of Selayar Island and belongs to the Wotu–Wolio branch of the Celebic subgroup.
The Seko languages are a group of four closely related Austronesian languages spoken in West Sulawesi and South Sulawesi provinces, Indonesia. They make up a primary branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup. The languages of the Seko branch are: Seko Padang, Seko Tengah, Panasuan and Budong-Budong.
References
- 1 2 Mead, David (2003a). "Evidence for a Celebic supergroup" (PDF). In Lynch, John (ed.). Issues in Austronesian historical phonology. Pacific Linguistics 550. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University. pp. 115–141.
- ↑ Mead, David (2003b). "The Saluan-Banggai microgroup of eastern Sulawesi" (PDF). In Lynch, John (ed.). Issues in Austronesian historical phonology. Pacific Linguistics 550. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University. pp. 65–86.
- ↑ Zobel, Erik (2020). "The Kaili–Wolio Branch of the Celebic Languages". Oceanic Linguistics. University of Hawai'i Press. 59 (1/2): 297–346. doi:10.1353/ol.2020.0014.
- ↑ Smith, Alexander D. (2017). "The Western Malayo-Polynesian Problem". Oceanic Linguistics. 56 (2): 435–490. doi:10.1353/ol.2017.0021.