Related Research Articles

Ga is a Kwa language spoken in Ghana, in and around the capital Accra. There are also some speakers in Togo, Benin and Western Nigeria. It has a phonemic distinction between three vowel lengths.
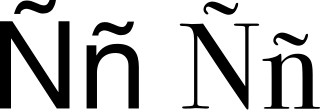
Ñ, or ñ, is a letter of the modern Latin alphabet, formed by placing a tilde on top of an upper- or lower-case ⟨n⟩. It became part of the Spanish alphabet in the eighteenth century when it was first formally defined, but it has subsequently been used in other languages, such as Galician, Asturian, the Aragonese Grafía de Uesca, Basque, Chavacano, some Philippine languages, Chamorro, Guarani, Quechua, Mapudungun, Mandinka, Papiamento, and Tetum alphabets, as well as in Latin transliteration of Tocharian and many Indian languages, where it represents or. It represents in Crimean Tatar, Kazakh, ALA-LC romanization for Turkic languages, the Common Turkic Alphabet, Nauruan and romanized Quenya. In Breton and in Rohingya, it denotes nasalization of the preceding vowel.

A digraph or digram is a pair of characters used in the orthography of a language to write either a single phoneme, or a sequence of phonemes that does not correspond to the normal values of the two characters combined.
The phonology of Portuguese varies among dialects, in extreme cases leading to some difficulties in intelligibility. Portuguese is a pluricentric language and has some of the most diverse sound variations of any language. This article on phonology focuses on the pronunciations that are generally regarded as standard. Since Portuguese is a pluricentric language—and differences between European Portuguese (EP), Brazilian Portuguese (BP), and Angolan Portuguese (AP) can be considerable—varieties are distinguished whenever necessary.

The Mandinka language, or Mandingo, is a Mande language spoken by the Mandinka people of Guinea, northern Guinea-Bissau, the Casamance region of Senegal, and in The Gambia where it is one of the principal languages.
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic, is the oldest form of the Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive written texts. It was used from c. 600 to c. 900. The main contemporary texts are dated c. 700–850; by 900 the language had already transitioned into early Middle Irish. Some Old Irish texts date from the 10th century, although these are presumably copies of texts written at an earlier time. Old Irish is thus forebear to Modern Irish, Manx and Scottish Gaelic.
The phonology of Japanese features a phonemic inventory of about 15 consonants, plus a five-vowel system of commonly seen in other languages. There is a relatively simple phonotactic distribution of phonemes, allowing for few consonant clusters. Traditionally, autochthonous Japanese linguistics has described the language as having a unit of timing called the mora, with each mora taking up about the same length of time. In this way, the disyllabic may be analyzed as, dissected into four moras:, ,, and.

Ligurian or Genoese is a Gallo-Italic language spoken primarily in the territories of the former Republic of Genoa, now comprising the area of Liguria in Northern Italy, parts of the Mediterranean coastal zone of France, Monaco, the village of Bonifacio in Corsica, and in the villages of Carloforte on San Pietro Island and Calasetta on Sant'Antioco Island off the coast of southwestern Sardinia. It is part of the Gallo-Italic and Western Romance dialect continuum. Although part of Gallo-Italic, it exhibits several features of the Italo-Romance group of central and southern Italy. Zeneize, spoken in Genoa, the capital of Liguria, is the language's prestige dialect on which the standard is based.
Genoese, locally called zeneise or zeneize, is the prestige dialect of Ligurian, spoken in and around the Italian city of Genoa, the capital of Liguria, in Northern Italy.

Central Italian refers to the dialects of Italo-Romance spoken in the so-called Area Mediana, which covers a swathe of the central Italian peninsula. Area Mediana is also used in a narrower sense to describe the southern part, in which case the northern one may be referred to as the Area Perimediana, a distinction that will be made throughout this article. The two areas are split along a line running approximately from Rome in the southwest to Ancona in the northeast.
Ndrumbea, variously spelled Ndumbea, Dubea, Drubea and Païta, is a New Caledonian language that gave its name to the capital of New Caledonia, Nouméa, and the neighboring town of Dumbéa. It has been displaced to villages outside the capital, with fewer than a thousand speakers remaining. Gordon (1995) estimates that there may only be two or three hundred. The Dubea are the people; the language has been called Naa Dubea "language of Dubea".
Tẹẹ, or Tai, is an Ogoni language and the language of the Tai tribe of the Ogoni people of Rivers State, Nigeria. It is to a limited degree mutually intelligible with Khana, the main Ogoni language, but its speakers consider it to be a separate language.
In linguistics, pre-stopping, also known as pre-occlusion or pre-plosion, is a phonological process involving the historical or allophonic insertion of a very short stop consonant before a sonorant, such as a short before a nasal or a lateral, or a short before a nasal. The resulting sounds are called pre-stopped consonants, or sometimes pre-ploded or pre-occluded consonants, although technically may be considered an occlusive/stop without the pre-occlusion.
Palatals are consonants articulated with the body of the tongue raised against the hard palate. Consonants with the tip of the tongue curled back against the palate are called retroflex.
Wahgi is a Trans–New Guinea language of the Chimbu–Wahgi branch spoken by approximately 100,000 people in the highlands of Papua New Guinea. Like other Chimbu languages, Wahgi has some unusual lateral consonants.
Farefare or Frafra, also known by the regional name of Gurenne (Gurene), is a Niger–Congo language spoken by the Frafra people of northern Ghana, particularly the Upper East Region, and southern Burkina Faso. It is a national language of Ghana, and is closely related to Dagbani and other languages of Northern Ghana, and also related to Mossi, also known as Mooré, the national language of Burkina Faso.
Kuteb also known as Ati, Kutev, Mbarike is a Nigerian ethnic language. The Kuteb people mostly live in the southern part of Taraba state in Nigeria, with a thousand-or-so speakers across the border in Cameroon. In Nigeria, it is spoken mostly in Takum and Ussa LGAs, and Yangtu SDA Taraba State.

The small group of Hachijō dialects, natively called Shima Kotoba, depending on classification, either are the most divergent form of Japanese, or comprise a branch of Japonic. Hachijō is currently spoken on two of the Izu Islands south of Tokyo as well as on the Daitō Islands of Okinawa Prefecture, which were settled from Hachijō-jima in the Meiji period. It was also previously spoken on the island of Hachijō-kojima, which is now abandoned. Based on the criterion of mutual intelligibility, Hachijō may be considered a distinct Japonic language, rather than a dialect of Japanese.
French exhibits perhaps the most extensive phonetic changes of any of the Romance languages. Similar changes are seen in some of the northern Italian regional languages, such as Lombard or Ligurian. Most other Romance languages are significantly more conservative phonetically, with Spanish, Italian, and especially Sardinian showing the most conservatism, and Portuguese, Occitan, Catalan, and Romanian showing moderate conservatism.