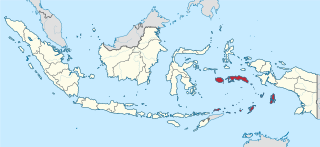
Maluku is a province of Indonesia. It comprises the central and southern regions of the Maluku Islands. The largest city and capital of Maluku province is Ambon on the small Ambon Island. It is directly adjacent to North Maluku, Southwest Papua, and West Papua in the north, Central Sulawesi, and Southeast Sulawesi in the west, Banda Sea, Australia, East Timor and East Nusa Tenggara in the south and Arafura Sea, Central Papua and South Papua in the east. The land area is 57803.81 km2, and the total population of this province at the 2010 census was 1,533,506 people, rising to 1,848,923 at the 2020 census, the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 1,908,753. Maluku is located in Eastern Indonesia.
The Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian (CEMP) languages form a proposed branch of the Malayo-Polynesian languages consisting of over 700 languages.
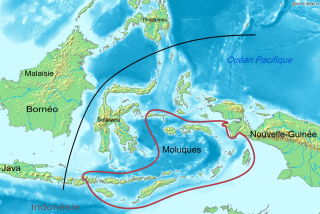
The Central Malayo-Polynesian languages (CMP) are a proposed branch in the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The languages are spoken in the Lesser Sunda and Maluku Islands of the Banda Sea, in an area corresponding closely to the Indonesian provinces of East Nusa Tenggara and Maluku and the nation of East Timor, but with the Bima language extending to the eastern half of Sumbawa Island in the province of West Nusa Tenggara and the Sula languages of the Sula archipelago in the southwest corner of the province of North Maluku. The principal islands in this region are Sumbawa, Sumba, Flores, Timor, Buru, and Seram. The numerically most important languages are Bima, Manggarai of western Flores, Uab Meto of West Timor, and Tetum, the national language of East Timor.
Tidore is a language of North Maluku, Indonesia, spoken by the Tidore people. The language is centered on the island of Tidore, but it is also spoken in some areas of the neighbouring Halmahera. Historically, it was the primary language of the Sultanate of Tidore, a major Moluccan Muslim state.
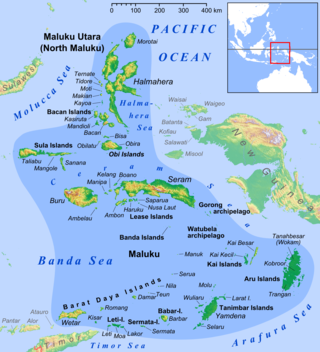
Watubela is an archipelago in the Maluku Islands, east of Ceram and north of Kai Islands, southeast of the Gorong archipelago, and southwest of the Bomberai Peninsula of Papua, Indonesia. It includes the islands of Watubela itself, Kesui and Teor. The total land area is 60.99 km2, of which Watubela and Kesui together cover 37.58 km2 and Teor covers 23.41 km2.
The Central Maluku languages are a proposed subgroup of the Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian language family which comprises around fifty languages spoken principally on the Seram, Buru, Ambon, Kei, and the Sula Islands. None of the languages have as many as fifty thousand speakers, and several are extinct.
The Kei–Tanimbar languages are a small group of Austronesian languages spoken on the Kei and Tanimbar islands in the southern Maluku Islands, and on the north side of the Bomberai Peninsula. The languages include:
Ternate is a language of northern Maluku, eastern Indonesia. It is spoken by the Ternate people, who inhabit the island of Ternate, as well as many other areas of the archipelago. It is the dominant indigenous language of North Maluku, historically important as a regional lingua franca. A North Halmahera language, it is unlike most languages of Indonesia which belong to the Austronesian language family.

The North Halmahera (NH) languages are a family of languages spoken in the northern and eastern parts of the island of Halmahera and some neighboring islands in Indonesia. The southwestern part of the island is occupied by the unrelated South Halmahera languages, which are a subgroup of Austronesian. They may be most closely related to the languages of the Bird's Head region of West Papua, but this is not well-established.
West Damar, or North Damar, is an Austronesian language of Damar Island, one of the Maluku Islands of Indonesia. In spite of rather low cognacy rates with its neighboring languages, it can be classified as part of the Babar languages based on qualitative evidence.
Luhu is an extinct Austronesian language spoken in the west of Seram Island in eastern Indonesia. It was spoken in Luhu village on Hoamoal Peninsula at the western end of Seram, and in Boano and Kelang islands, off the western tip of Seram Island.
Wemale is an Austronesian language spoken on western Seram Island in Indonesia. It is classified by Collins (1983) as a member of the Central Maluku subgroup.
Manusela is an Austronesian language spoken in Seram, Indonesia. It is classified by Collins (1983) as a member of the Central Maluku subgroup.
Manipa is an Austronesian language of eastern Indonesia. It is primarily spoken in the island of Manipa, which is located between Buru island and Seram island in the province of Maluku.
Geser is an Austronesian language of the east end of Seram and the Gorom Islands, Indonesia. It is closely related to Watubela.
Bati is an Austronesian language of eastern Seram Island, Indonesia. It is closely related to Geser and Watubela.
Teun is an Austronesian language originally spoken on Teun Island and Nila Island in Maluku, Indonesia. Speakers were relocated to Seram due to volcanic activity on Teun.
Nila is an extinct Austronesian language originally spoken on Nila Island in Maluku, Indonesia. Speakers were relocated to Seram due to volcanic activity on Nila.
Serua is an extinct Austronesian language originally spoken on Serua Island in Maluku, Indonesia. Speakers were relocated to Seram due to volcanic activity on Serua. The language continues in communities in Waipia in Seram, where the islanders were resettled, along with those also from Nila and Teun. Here, the older generation retained the island language as a strong form of identity. It was found to be extinct in 2024.
Kamarian is an extinct Austronesian language. It was spoken at the southwestern coast of Seram Island in the Moluccas in eastern Indonesia.



