
The Chimakuan languages are a group of extinct languages that were spoken in northwestern Washington state, United States, on the Olympic Peninsula. They were spoken by Chimakum, Quileute and Hoh tribes. They are part of the Mosan sprachbund, and one of its languages is famous for having no nasal consonants. The two languages were about as close as English and German. Due to proximity, the Chimakuan languages are also similar to Wakashan.
Old English phonology is the pronunciation system of Old English, the Germanic language spoken on Great Britain from around 450 to 1150 and attested in a body of written texts from the 7th–12th centuries. Although its reconstruction is necessarily somewhat speculative, features of Old English pronunciation have been inferred partly from the sounds used in modern varieties of English, partly from the spellings used in Old English literature, partly from analysis of Old English poetry, and partly from comparison with other Germanic languages.

The Trans-Fly–Bulaka RiverakaSouth-Central Papuan languages form a hypothetical family of Papuan languages. They include many of the languages west of the Fly River in southern Papua New Guinea into southern Indonesian West Papua, plus a pair of languages on the Bulaka River a hundred km further west.
The Lakes Plain languages are a family of Papuan languages, spoken in the Lakes Plain of Indonesian New Guinea. They are notable for being heavily tonal and for their lack of nasal consonants.
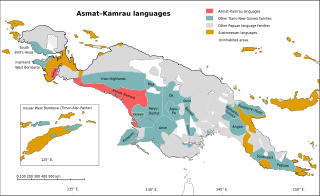
The Asmat – Kamrau Bay languages are a family of a dozen Trans–New Guinea languages spoken by the Asmat and related peoples in southern Western New Guinea. They are believed to be a recent expansion along the south coast, as they are all closely related, and there is little differentiation in their pronouns.

The Marind–Yaqai (Marind–Yakhai) languages are a well established language family of Papuan languages, spoken by the Marind-anim. They form part of the Trans–New Guinea languages in the classifications of Stephen Wurm and Malcolm Ross, and were established as part of the Anim branch of TNG by Timothy Usher.
The Dani or Baliem Valley languages are a family of clearly related Trans–New Guinea languages spoken by the Dani and related peoples in the Baliem Valley in the Highland Papua, Indonesia. Foley (2003) considers their Trans–New Guinea language group status to be established. They may be most closely related to the languages of Paniai Lakes, but this is not yet clear. Capell (1962) posited that their closest relatives were the Kwerba languages, which Ross (2005) rejects.
The Timor–Alor–Pantar (TAP) languages are a family of languages spoken in Timor, Kisar, and the Alor archipelago in Southern Indonesia. It is the westernmost Papuan language family that survives, and one of two such outlier families in east Nusantara.

The Kamula–Elevala languages are a small family of the Trans–New Guinea languages spoken in the region of the Elevala River.
The Yareban or Musa River languages are a small family of Trans–New Guinea languages spoken near the Musa River in the "Bird's Tail" of New Guinea. They are classified within the Southeast Papuan branch of Trans–New Guinea.
The Manubaran languages are a small family of Trans–New Guinea languages spoken around Mount Brown in the "Bird's Tail" of New Guinea. They are classified within the Southeast Papuan branch of Trans–New Guinea.
The Kwalean or Humene–Uare languages are a small family of Trans–New Guinea languages spoken in the "Bird's Tail" of New Guinea. They are classified within the Southeast Papuan branch of Trans–New Guinea.
The Ottilien or Watam-Awar-Gamay languages are a small family of clearly related languages,
Wahgi is a Trans–New Guinea language of the Chimbu–Wahgi branch spoken by approximately 100,000 people in the highlands of Papua New Guinea. Like other Chimbu languages, Wahgi has some unusual lateral consonants.
Proto-Tai is the reconstructed proto-language of all the Tai languages, including modern Lao, Shan, Tai Lü, Tai Dam, Ahom, Northern Thai, Standard Thai, Bouyei, and Zhuang. The Proto-Tai language is not directly attested by any surviving texts, but has been reconstructed using the comparative method.
Sikaritai (Sikwari) is a Lakes Plain language of Papua, Indonesia. It is named after Sikari village in Rafaer District, Mamberamo Raya Regency. Alternate names are Aikwakai, Araikurioko, Ati, Tori, Tori Aikwakai.
Maklew is a language of the proposed Trans-Fly – Bulaka River family in South Papua, Indonesia. It is known to be spoken in Welbuti village, Merauke Regency. It is thought to be closely related to the Yelmek Language.
The Oirata–Makasae, or Eastern Timor, languages are a small family of Papuan languages spoken in eastern Timor and the neighboring island of Kisar.

The Anim or Fly River languages are a language family in south-central New Guinea established by Usher & Suter (2015). The names of the family derive from the Fly River and from the Proto-Anim word *anim 'people'.
Proto-Trans–New Guinea is the reconstructed proto-language ancestral to the Trans–New Guinea languages. Reconstructions have been proposed by Malcolm Ross and Andrew Pawley.






