
Macro-Arawakan is a proposed language family of South America and the Caribbean centered on the Arawakan languages. Sometimes, the proposal is called Arawakan, and the central family is called Maipurean.

The Cariban languages are a family of languages indigenous to northeastern South America. They are widespread across northernmost South America, from the mouth of the Amazon River to the Colombian Andes, and they are also spoken in small pockets of central Brazil. The languages of the Cariban family are relatively closely related. There are about three dozen, but most are spoken only by a few hundred people. Macushi is the only language among them with numerous speakers, estimated at 30,000. The Cariban family is well known among linguists partly because one language in the family—Hixkaryana—has a default word order of object–verb–subject. Prior to their discovery of this, linguists believed that this order did not exist in any spoken natural language.
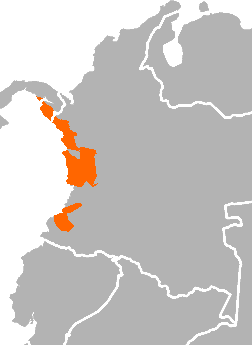
The Choco languages are a small family of Native American languages spread across Colombia and Panama.
Paezan may be any of several hypothetical or obsolete language-family proposals of Colombia and Ecuador named after the Paez language.

The Borôroan languages of Brazil are Borôro and the extinct Umotína and Otuke. They are sometimes considered to form part of the proposed Macro-Jê language family, though this has been disputed.

Pano-Tacanan is a proposed family of languages spoken in Peru, western Brazil, Bolivia and northern Paraguay. There are two close-knit branches, Panoan and Tacanan, with 33 languages. There are lexical and grammatical similarities between the two branches, but it has not yet been demonstrated that these are genetic.

Arawakan, also known as Maipurean, is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branches migrated to Central America and the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean and the Atlantic, including what is now the Bahamas. Almost all present-day South American countries are known to have been home to speakers of Arawakan languages, the exceptions being Ecuador, Uruguay, and Chile. Maipurean may be related to other language families in a hypothetical Macro-Arawakan stock.

The Nadahup languages, also known as Makú (Macú) or Vaupés–Japurá, form a small language family in Brazil, Colombia, and Venezuela. The name Makú is pejorative, being derived from an Arawakan word meaning "without speech". Nadahup is an acronym of the constituent languages.
Boran is a small language family, consisting of just two languages.
The Piaroa–Saliban, also known as Saliban, are a small proposed language family of the middle Orinoco Basin, which forms an independent island within an area of Venezuela and Colombia dominated by peoples of Carib and Arawakan affiliation.

Guahibo, the native language of the Guahibo people, is a Guahiban language that is spoken by about 23,006 people in Colombia and additional 8,428 in Venezuela. There is a 40% rate of monolingualism, and a 45% literacy rate.

The Guahibo people are an indigenous people native to the Llanos or savanna plains in eastern Colombia and in southern Venezuela near the Colombian border. Their population was estimated at 23,772 people in 1998.

Achagua, or Achawa, is an Arawakan language spoken in the Meta Department of Colombia, similar to Piapoco. It is estimated that 250 individuals speak the language, many of whom also speak Piapoco or Spanish.
Ticuna–Yuri is a small family, perhaps even a dialect continuum, consisting of at least two, and perhaps three, known languages of South America: the major western Amazonian language Ticuna, the poorly attested and extinct Yurí, and the scarcely known language of the largely uncontacted Carabayo. Kaufman also adds Munichi to the family.
Macro-Puinavean is a hypothetical proposal linking some very poorly attested languages to the Nadahup family. The Puinave language is sometimes linked specifically with the Nadahup languages and Nukak-Kakwa group, as Puinave–Maku. Paul Rivet (1920) and other researchers proposed decades ago the hypothesis of a Puinave-Makú family. Later, Joseph Greenberg (1987) grouped the Puinave-Makú languages, together with the Tucano family, the Katukinan, Waorani and Ticuna languages in the Macro-Tukano trunk.
Witotoan is a small language family of southeastern Colombia and the neighbouring region of Peru.
Taruma (Taruamá) is a divergent language of northeastern South America. It has been reported to be extinct several times since as far back as 1770, but Eithne Carlin discovered the last three speakers living in Maruranau among the Wapishana, and is documenting the language. The people and language are known as Saluma in Suriname.
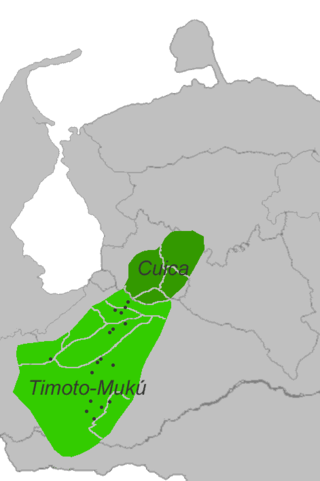
The Timotean languages were spoken in the Venezuelan Andes around what is now Mérida. It is assumed that they are extinct. However, Timote may survive in the so-far unattested Mutú (Loco) language, as this occupies a mountain village (Mutús) within the old Timote state.
The Upper Amazon Maipurean languages, a.k.a. North Amazonian or Inland Northern Maipuran, are Arawakan languages of the northern Amazon in Colombia, Venezuela, Peru, and Brazil.
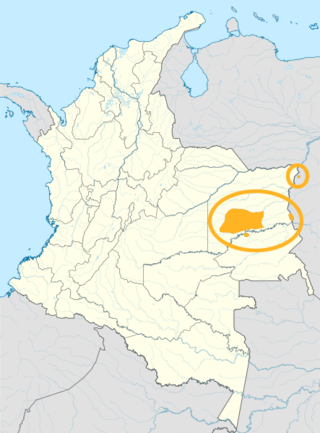
Piapoco is an Arawakan language of Colombia and Venezuela.













