Related Research Articles
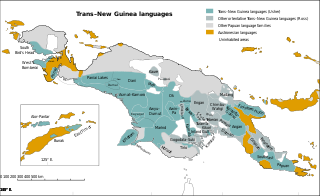
Trans–New Guinea (TNG) is an extensive family of Papuan languages spoken in New Guinea and neighboring islands, perhaps the third-largest language family in the world by number of languages. The core of the family is considered to be established, but its boundaries and overall membership are uncertain. The languages are spoken by around 3 million people. There have been three main proposals as to its internal classification.
Indo-Pacific is a hypothetical language macrofamily proposed in 1971 by Joseph Greenberg and now believed to be spurious. It grouped together the Papuan languages of New Guinea and Melanesia with the languages of the Andaman Islands and, tentatively, the languages of Tasmania, both of which are remote from New Guinea. The valid cognates Greenberg found turned out to be reflexes of the less extensive Trans–New Guinea family. Recently the Kusunda language, which is generally seen as a language isolate, is also included in the Indo-Pacific proposal. Greenberg did not include "Australian" in his original 1971 proposal.
The Left May or Arai languages are a small language family of half a dozen closely related but not mutually intelligible languages in the centre of New Guinea, in the watershed of the Left May River. There are only about 2,000 speakers in all. Foley (2018) classifies them separately as an independent language family, while Usher (2020) links them with the Amto–Musan languages.

The Trans-Fly – Bulaka RiverakaSouth-Central Papuan languages form a hypothetical family of Papuan languages. They include many of the languages west of the Fly River in southern Papua New Guinea into southern Indonesian West Papua, plus a pair of languages on the Bulaka River a hundred km further west.

The Eastern Trans-Fly languages are a small independent family of Papuan languages spoken in the Oriomo Plateau to the west of the Fly River in New Guinea.

Papua New Guinea, a sovereign state in Oceania, is the most linguistically diverse country in the world. According to Ethnologue, there are 839 living languages spoken in the country. In 2006, Papua New Guinea Prime Minister Sir Michael Somare stated that "Papua New Guinea has 832 living languages ," Languages with statutory recognition are Tok Pisin, English, Hiri Motu, and Papua New Guinean Sign Language. Tok Pisin, an English-based creole, is the most widely spoken, serving as the country's lingua franca. Papua New Guinean Sign Language became the fourth officially recognised language in May 2015, and is used by the deaf population throughout the country.
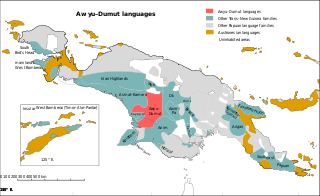
The Greater Awyu or Digul River languages, known in earlier classifications with more limited scope as Awyu–Dumut (Awyu–Ndumut), are a family of perhaps a dozen Trans–New Guinea languages spoken in eastern West Papua in the region of the Digul River. Six of the languages are sufficiently attested for a basic description; it is not clear how many of the additional names may be separate languages.

The Turama–Kikorian languages are a family identified by Arthur Capell (1962) and part of the Trans–New Guinea languages (TNG) family in the classifications of Stephen Wurm (1975) and Malcolm Ross (2005). The family is named after the Turama River and Kikori River of southern Papua New Guinea; the alternative name is based more narrowly on the Omati River.

The Teberan languages are a well established family of Papuan languages that Stephen Wurm (1975) grouped with the Pawaia language as a branch of the Trans–New Guinea phylum.

The Kamula–Elevala languages are a small family of the Trans–New Guinea languages spoken in the region of the Elevala River.
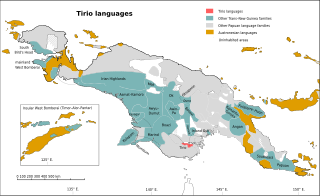
The Tirio languages are a family of Trans–New Guinea languages in the classification of Malcolm Ross. The Tirio languages have about 40% of their lexicon in common.
The Northern Adelbert or Pihom–Isumrud languages are a family of two dozen languages in the Madang stock of New Guinea. The occupy the coastal northern Adelbert Range of mountains, vs. the Southern Adelbert languages, another branch of Madang.

The Bulaka River languages are a pair of closely related Papuan languages, Yelmek and Maklew, on the Bulaka River in Indonesian West Papua. They are ethnically Yab (Jab); their speech is Yabga (Jabga).

The Yam languages, also known as the Morehead River languages, are a family of Papuan languages. They include many of the languages south and west of the Fly River in Papua New Guinea and Indonesian West Papua.

The Pahoturi languages are a small family of Papuan languages spoken around the Pahoturi. This family includes six language varieties including Agöb (Dabu), Em, Ende, Kawam, Idi, and Taeme, which are spoken in the Pahoturi River area south of the Fly River, just west of the Eastern Trans-Fly languages. Ross (2005) tentatively includes them in the proposed Trans-Fly – Bulaka River family.
Wipi, also known as Gidra, Jibu or Oriomo, is a Papuan language of New Guinea. It is a member of the Eastern Trans-Fly family, the other languages of this family being Gizrra, Meriam Mir and Bine. The family has influenced the neighbouring Kiwai language as well as Kalau Lagau Ya.

Tabo, also known as Waia (Waya), is a Papuan language of Western Province, Papua New Guinea, just north of the Fly River delta. The language has also been known as Hiwi and Hibaradai.
The Sogeram languages are a family of languages in the Madang stock of New Guinea. They are named after the Sogeram River.

The Anim or Fly River languages are a group of Trans–New Guinea families in south-central New Guinea established by Usher & Suter (2015). The names of the family derive from the Fly River and from the Proto-Anim word *anim 'people'.

Oriomo-Bituri Rural LLG is a local-level government (LLG) of Western Province, Papua New Guinea. Eastern Trans-Fly languages are spoken in the LLG.
References
- ↑
- ↑ The family is called 'East Trans-Fly' in Usher, an unfortunate synonym with what others call the Eastern Trans-Fly family, which constitutes one of its branches.
- ↑ Evans, Nicholas (2018). "The languages of Southern New Guinea". In Palmer, Bill (ed.). The Languages and Linguistics of the New Guinea Area: A Comprehensive Guide. The World of Linguistics. 4. Berlin: De Gruyter Mouton. pp. 641–774. ISBN 978-3-11-028642-7.