Related Research Articles

Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, Pacificans, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Oceania or any other island located in the Pacific Ocean.

In addition to its classical and modern literary form, Malay had various regional dialects established after the rise of the Srivijaya empire in Sumatra, Indonesia. Also, Malay spread through interethnic contact and trade across the south East Asia Archipelago as far as the Philippines. That contact resulted in a lingua franca that was called Bazaar Malay or low Malay and in Malay Melayu Pasar. It is generally believed that Bazaar Malay was a pidgin, influenced by contact among Malay, Hokkien, Portuguese, and Dutch traders.
Tukang Besi is an Austronesian language spoken in the Tukangbesi Islands in southeast Sulawesi in Indonesia by a quarter million speakers. A Tukang Besi pidgin is used in the area.
The Wutun language is a Mandarin–Amdo–Bonan creole language. It is spoken by about 4,000 people, most of whom are classified as Monguor (Tu) by the Chinese government. Wutun speakers reside in two villages of Tongren County, eastern Qinghai province, China. It is also known as the Ngandehua language.

Stephen Adolphe Wurm was a Hungarian-born Australian linguist.
Lungalunga, frequently though ambiguously called Minigir, is spoken by a small number of the Tolai people of Papua New Guinea, who live on the Gazelle Peninsula in East New Britain Province. It is often referred to in the linguistics literature as the Tolai "dialect" with an.
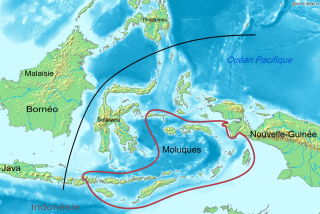
The Central Malayo-Polynesian languages (CMP) are a proposed branch in the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The languages are spoken in the Lesser Sunda and Maluku Islands of the Banda Sea, in an area corresponding closely to the Indonesian provinces of East Nusa Tenggara and Maluku and the nation of East Timor, but with the Bima language extending to the eastern half of Sumbawa Island in the province of West Nusa Tenggara and the Sula languages of the Sula archipelago in the southwest corner of the province of North Maluku. The principal islands in this region are Sumbawa, Sumba, Flores, Timor, Buru, and Seram. The numerically most important languages are Bima, Manggarai of western Flores, Uab Meto of West Timor, and Tetum, the national language of East Timor.

The Austronesian peoples refer to people sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, and are meant to refer to a large group of peoples from places such as Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, parts of Mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak languages that have been categorized by some as Austronesian languages. They also include indigenous ethnic minorities in Vietnam, Cambodia, Myanmar, Thailand, Hainan, the Comoros, and the Torres Strait Islands. The nations and territories predominantly populated by those referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples are sometimes known collectively as Austronesia.
Tidore is a language of North Maluku, Indonesia, spoken by the Tidore people. The language is centered on the island of Tidore, but it is also spoken in some areas of the neighbouring Halmahera. Historically, it was the primary language of the Sultanate of Tidore, a major Moluccan Muslim state.
Bomberai Peninsula is located in the Western New Guinea region. It is south of the Bird's Head Peninsula, and Bintuni Bay separates the two peninsulas. To the west lies the Sebakor Bay and to the south Kamrau Bay. On the southeast Arguni Bay lies between the peninsula and the Bird's Neck Isthmus.
The Central Maluku languages are a proposed subgroup of the Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian language family which comprises around fifty languages spoken principally on the Seram, Buru, Ambon and the Sula Islands, Indonesia. None of the languages have as many as fifty thousand speakers, and several are extinct.
The Tangwang language is a variety of Mandarin Chinese heavily influenced by the Mongolic Santa language (Dongxiang). It is spoken in a dozen or so villages in Dongxiang Autonomous County, Gansu Province, China. The linguist Mei W. Lee-Smith calls this creole language the "Tangwang language", based on the names of the two largest villages where it is spoken.

Larantuka Malay, also known as Nagi, is a Malay-based creole language spoken in the eastern part of Flores in Indonesia, especially in Larantuka. It is a derivative of Malay which is thought to originate from Malacca. It is a language with unspecified linguistic affiliation. According to 2007 data, this language is spoken by 20,000 speakers, mainly the people of East Flores. Larantuka Malay is the mother tongue of the Nagi people. Then it also functions as a second language for several nearby communities.
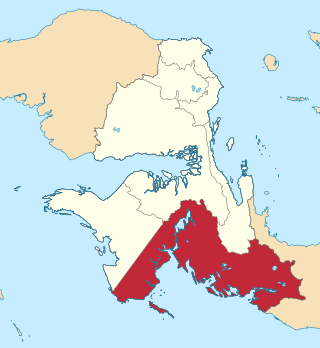
Kaimana Regency is a regency in the south of West Papua province of Indonesia. It covers an area of 18,500 sq. km, and had a population of 46,249 at the 2010 Census and 62,256 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 65,490. The administrative centre is the town of Kaimana. The Mairasi languages are spoken in the regency, among other languages.
Mpur is a language isolate spoken in and around Mpur and Amberbaken Districts in Tambrauw Regency of the Bird's Head Peninsula, New Guinea. It is not closely related to any other language, and though Ross (2005) tentatively assigned it to the West Papuan languages, based on similarities in pronouns, Palmer (2018), Ethnologue, and Glottolog list it as a language isolate.

The North Halmahera (NH) languages are a family of languages spoken in the northern and eastern parts of the island of Halmahera and some neighboring islands in Indonesia. The southwestern part of the island is occupied by the unrelated South Halmahera languages, which are a subgroup of Austronesian. They may be most closely related to the languages of the Bird's Head region of West Papua, but this is not well-established.
Semimi, or Etna Bay, is a Papuan language spoken in Kaimana Regency, West Papua, Indonesia.
Mele-Fila (Ifira-Mele) is a Polynesian language spoken in Mele and Ifira on the island of Efate in Vanuatu. In spite of their differences, Mele and Fila are two dialects of the same language and are mutually intelligible. French and English are also fairly common among the residents of Efate.
Kuri, or Nabi, is a small Austronesian language of the Bomberai Peninsula of New Guinea. Lexically it is very close to Irarutu.
Bass Strait Pidgin was an unattested English-based pidgin language spoken in the Bass Strait islands of Australia. It likely developed in the early 1800s as a result of contact between European sealers and Aboriginal women abducted from Tasmania.
References
- ↑ Kowiai at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Charles Grimes & Owen Edwards (in process) Wallacean subgroups: unravelling the prehistory and classification of the Austronesian languages of eastern Indonesia and Timor-Leste. Summary presentation at the 15th International Conference on Austronesian Linguistics.
- ↑ Wurm, Stephen A.; Mühlhäusler, Peter; Tryon, Darrell T. (2011-02-11). Atlas of Languages of Intercultural Communication in the Pacific, Asia, and the Americas: Vol I: Maps. Vol II: Texts. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-081972-4.
- ↑ Ronsumbre, Adolof (2020). Ensiklopedia Suku Bangsa di Provinsi Papua Barat. Yogyakarta: Penerbit Kepel Press. ISBN 978-602-356-318-0.