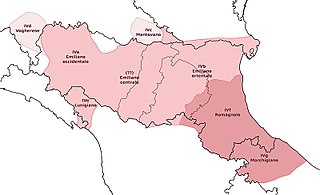
Emilian-Romagnol is a linguistic continuum that is part of the Gallo-Italic languages spoken in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna. It is divided into two main varieties, Emilian and Romagnol.
The Manus languages are a subgroup of about two dozen Oceanic languages located on Manus Island and nearby offshore islands in Manus Province of Papua New Guinea. The exact number of languages is difficult to determine because they form a dialect continuum. The name Manus originally designated an ethnic group whose members spoke closely related languages and whose coastal dwellers tended to build their houses on stilts out over the sea.

The UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger was an online publication containing a comprehensive list of the world's endangered languages. It originally replaced the Red Book of Endangered Languages as a title in print after a brief period of overlap before being transferred to an online-only publication.
The Boruca language is the native language of the Boruca people of Costa Rica. Boruca belongs to the Isthmian branch of the Chibchan languages. Though exact speaker numbers are uncertain, UNESCO’s Atlas of the World’s Languages in Danger has listed Boruca as "critically endangered". It was spoken fluently by only five women in 1986, while 30 to 35 others spoke it non-fluently. The rest of the tribe's 1,000 members speak Spanish.
Orang Seletar (Slitar) is a language of the Orang Laut of the south coast of the Malay Peninsula. It is very close to Malay, and may be counted as a dialect of that language. The speaking population is unknown, but is likely in the range of a few thousand. The language is considered critically endangered by UNESCO.
Orang Kanaq is one of the Malayic languages, grouped under the Austronesian languages. It is spoken by the Orang Kanaq, one of the 19 Orang Asli groups in Peninsular Malaysia. The language is believed to have been extinct since the 1950s according to the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger.

Kryts (Kryc) is a Lezgic language of the Northeast Caucasian language family spoken in parts of the Quba Rayon of Azerbaijan by 6,000 people in 1975. Its dialects are Kryts, Jek, Khaput, Yergyudzh, and Alyk, which are all quite distinct to the point of only partial mutual intelligibility, therefore they could also be considered separate languages in a dialect continuum.
The Hermit language is an extinct West Manus language formerly spoken on Hermit, Luf and Maron Islands in western Manus Province, Papua New Guinea. It has been replaced by Seimat.
Lower Nossob is an extinct Khoisan language once spoken along the Nossob River on the border of South Africa and Botswana, near Namibia. It was closely related to the Taa language.
Rongpo or Rangpo is a West Himalayish language spoken in Uttarakhand, India.
Gurdjar (Kurtjar) is a Paman language of the Cape York Peninsula, Queensland, Australia. There are two dialects, Gurdjar proper, and Rip. According to the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger, the language is classified as extinct.
Kafoa, or Jafoo, is a Papuan language of Alor Island in the Alor archipelago of Indonesia. Although Kafoa speakers refer to both themselves and their language with the name "Kafoa", this word is not well known in the area. Kafoa speakers are frequently multilingual, also speaking Malay, Klon and Abui. Children are typically initially taught Malay by their parents and later acquire Kafoa after having reached school age.
Zazao is an Oceanic language spoken in the Solomon Islands. Its speakers live on Santa Isabel Island. It is classified as “critically endangered” by the UNESCO Atlas of the World’s Languages in Danger, because its speakers usually speak the Cheke Holo language or the Zabana language.
Zire (Sîshëë), also known as Nerë, is an extinct Oceanic language of New Caledonia. It has been extinct since April 2006. Zire is sometimes considered a dialect of Ajië.
Seru or Sru Dayak is an extinct Austronesian language of Sarawak in Borneo. Smith (2017) classifies it as a Punan language. The language is unattested and unwritten.
The Yaw dialect of Burmese is spoken by 200,000 people near the Chin Hills in Magway Division, particularly in Gangaw District, which comprises Saw, Htilin, and Gangaw. Yaw was classified as a "definitely endangered" language in UNESCO's 2010 Atlas of the World’s Languages in Danger.
The Southern Ryukyuan languages form one of two branches of the Ryukyuan languages. They are spoken on the Sakishima Islands in Okinawa Prefecture. The three languages are Miyako and Yaeyama and Yonaguni. The Macro-Yaeyama languages have been identified as "critically endangered" by UNESCO and Miyako as "definitely endangered".

Degree of endangerment is an evaluation assigned by UNESCO to the languages in the Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger. Evaluation is given according to nine criteria, the most important of which is the criterion of language transmission between generations.




