
Viperinae, or viperines, are a subfamily of vipers endemic to Europe, Asia and Africa. They are distinguished by their lack of the heat-sensing pit organs that characterize their sister group, the subfamily Crotalinae. Currently, 13 genera are recognized. Most are tropical and subtropical, although one species, Vipera berus, even occurs within the Arctic Circle. Like all vipers, they are venomous.

Bitis nasicornis is a viper species belonging to the genus Bitis, part of a subfamily known as "puff-adders", found in the forests of West and Central Africa. This large viper is known for its striking coloration and prominent nasal "horns". No subspecies are currently recognized. Its common names include butterfly viper, rhinoceros viper, river jack and many more. Like all other vipers, it is venomous.

Atheris is a genus of vipers known as bush vipers. They are found only in tropical subsaharan Africa and many species have isolated and fragmented distributions due to their confinement to rain forests. Like all other vipers, they are venomous. In an example of convergent evolution, they show many similarities to the arboreal pit vipers of Asia and South America. Seventeen species are currently recognized.
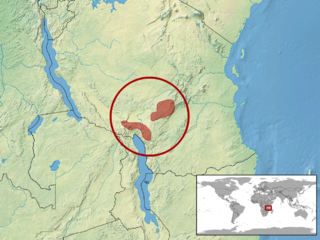
Atheris barbouri is a small and rare species of terrestrial viper endemic to the Uzungwe and Ukinga mountains of south-central Tanzania in Africa.
Proatheris is a monotypic genus created for the viper species, Proatheris superciliaris. This is a small terrestrial species endemic to East Africa. Like all other vipers, it is venomous. No subspecies are currently recognized.

Macrovipera, known as the large Palearctic vipers, is a genus of vipers that inhabit the semideserts and steppes of North Africa, the Near and Middle East, and the Milos Archipelago in the Aegean Sea. Like all other vipers, they are venomous. These snakes are responsible for a number of bites in Africa and Western Asia every year. They have a reputation for being ill-tempered and can inject a lot of venom, which is why they should be considered as very dangerous. Two species are currently recognized.

Vipera is a genus of vipers. It has a very wide range, being found from North Africa to just within the Arctic Circle and from Great Britain to Pacific Asia. The Latin name vīpera is possibly derived from the Latin words vivus and pario, meaning "alive" and "bear" or "bring forth"; likely a reference to the fact that most vipers bear live young. Currently, 21 species are recognized. Like all other vipers, the members of this genus are venomous.

Atheris nitschei is a species of venomous snake, a viper in the subfamily Viperinae of the family Viperidae. The species is native to Africa. There are no subspecies that are recognized as being valid.

The many-horned adder is a viper species. It is found in certain rocky desert areas, mostly along the Atlantic coast of southern Africa, in western South Africa and southwestern Namibia. It has characteristic tufts of "horns" above each eye. Like all other vipers, it is venomous. No subspecies are currently recognized.

Bitis inornata is a venomous viper species found only in Cape Province, South Africa. No subspecies are currently recognized.

Bitis parviocula is a venomous viper species found only in Ethiopia. It is large with a broad head and spectacular geometric markings. In 1995, the species was known from only three specimens, but additional information has surfaced since then. Little is known about its natural history or its venom. No subspecies are currently recognized.

Bitis worthingtoni, also known commonly as the Kenya horned viper and the Kenyan horned viper, is a species of venomous snake in the subfamily Viperinae of the family Viperidae. The species is endemic to Kenya. There are no subspecies that are recognized as being valid.

Bitis xeropaga, commonly known as the desert mountain adder or Lüderitz dwarf viper, is a viper species found in southern Namibia and northwestern Cape Province in South Africa. Like all other vipers, it is venomous. No subspecies are currently recognized.
Macrovipera lebetinus transmediterranea is a viper subspecies endemic to North Africa. Like all other vipers, it is venomous.

The Lebanon viper, also known as Bornmueller's viper, is a species of venomous snake in the subfamily Viperinae of the family Viperidae. The species is native to Western Asia. There are no recognized subspecies.

The Mount Bulgar viper, also called the Bulgardagh viper is a viper species endemic to the mountains of southern Turkey. Like all other vipers, it is venomous. No subspecies are currently recognized.

Vipera darevskii, known as Darevsky's viper, is a small species of viper, a venomous snake in the subfamily Viperinae of the family Viperidae. The species is native to northwestern Armenia, northeastern Turkey, and possibly also adjacent southern Georgia. There are no subspecies that are recognized as being valid.

Vipera monticola, also known as the Atlas mountain viper, is a viper species endemic to Morocco. Like all other vipers, it is venomous.

Montivipera raddei, also known as the Armenian viper and by many other common names, is a species of venomous snake in the subfamily Viperinae of the family Viperidae. The species is endemic to Armenia, Azerbaijan, Iran, Turkey, and possibly also Iraq. Two subspecies are currently recognized.

The Persian horned viper, known as the Persian horned viper, false horned viper, and by other common names, is a species of vipers endemic to the Middle East and Asia. Like all other vipers, it is venomous.

















