| Mission type | Technology demonstration |
|---|---|
| Operator | Ecuadorian Civilian Space Agency |
| COSPAR ID | 2013-066AB |
| SATCAT no. | 39441 |
| Website | www |
| Mission duration | Design: 1 year Elapsed: 8 years, 5 months, 29 days |
| Orbits completed | 15,074 [1] |
| Spacecraft properties | |
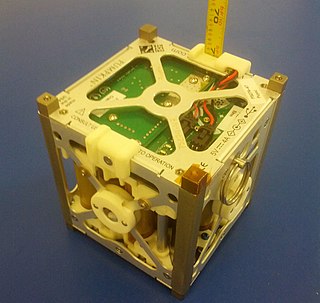
| Spacecraft type | 1U CubeSat |
| Manufacturer | Ecuadorian Civilian Space Agency |
| Launch mass | 1.2 kg (2.6 lb) |
| Dimensions | 10×10 cm (3.9×3.9 in) [2] |
| Power | 127 watts maximum |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 21 November 2013, 07:10 UTC |
| Rocket | Dnepr |
| Launch site | Dombarovsky 370/13 |
| Entered service | 25 January 2014 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Sun-synchronous |
| Semi-major axis | 7,024.99 km (4,365.13 mi) [1] |
| Eccentricity | 0.0083597 [1] |
| Perigee altitude | 588.13 km (365.45 mi) [1] |
| Apogee altitude | 705.58 km (438.43 mi) [1] |
| Inclination | 97.6637 degrees [1] |
| Period | 97.66 minutes [1] |
| Mean motion | 14.74 [1] |
| Epoch | 10 September 2016, 08:01:29 UTC [1] |
NEE-02 Krysaor is an Ecuadorian technology demonstration satellite, and Ecuador's second satellite launched to space. Built by the Ecuadorian Civilian Space Agency (EXA), it is a single-unit CubeSat nanosatellite. [3] Krysaor is a Pegasus-class spacecraft, a "twin" of Ecuador's first satellite, NEE-01 Pegaso. [4] Like Pegaso, this spacecraft's instruments include a dual visible and infrared camera which allows the spacecraft to take pictures and transmit live video from space.

A CubeSat is a class of miniaturized satellite based around a form factor consisting of 10 cm (3.9 in) cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than 2 kg (4.4 lb) per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats are put into orbit by deployers on the International Space Station, or launched as secondary payloads on a launch vehicle. As of August 2021, more than 1,600 CubeSats have been launched.
The Operationally Responsive Space Office is a joint initiative of several agencies within the United States Department of Defense (DoD). The "stand up" of the office took place 21 May 2007 at Kirtland Air Force Base. The first director of the ORS Office was Col. Kevin McLaughlin, who was also dual-hatted as commander of the Space Development and Test Wing located at Kirtland. The ORS Office focuses on providing quick-response tactical space-based capabilities to the warfighter utilizing smaller satellites, such as the Tactical Satellite Program and smaller launch vehicles.

The Ecuadorian Civilian Space Agency is a private Ecuadorian organization founded in 2007 that conducts research on space and planetary sciences. It is a non-profit non-governmental organization with civilian oversight.
Strictly speaking, a satellite collision is when two satellites collide while in orbit around a third, much larger body, such as a planet or moon. This definition can be loosely extended to include collisions between sub-orbital or escape-velocity objects with an object in orbit. Prime examples are the anti-satellite weapon tests.

Launch Services Program (LSP) is responsible for NASA oversight of launch operations and countdown management, providing added quality and mission assurance in lieu of the requirement for the launch service provider to obtain a commercial launch license. It operates under the Human Exploration and Operations (HEO) Mission Directorate of NASA.

NEE-01 Pegaso is an Ecuadorian technology demonstration satellite, and Ecuador's first satellite launched to space. Built by the Ecuadorian Civilian Space Agency (EXA), it is a nanosatellite of the single-unit CubeSat class. The spacecraft's instruments include a dual visible and infrared camera which allows the spacecraft to take pictures and transmit live video from space.

KickSat was a satellite dispenser for small-satellite (femtosatellite) project inaugurated in early October 2011, to launch many very small satellites from a 3U CubeSat. The satellites have been characterized as being the size of a large postage stamp. and also as "cracker size". The mission launch was originally scheduled for late 2013 and was launched April 18, 2014.
Technology Education Satellite (TechEdSat) is a class of CubeSats built by San Jose State University and University of Idaho students in partnership with NASA's Ames Research Center. These satellites have tested communication technology for smallsats, and have contributed to the development of the Small Payload Quick Return (SPQR) concept.
SkySat is a constellation of sub-meter resolution Earth observation satellites owned by Planet Labs, providing imagery, high-definition video and analytics services. Planet acquired the satellites with their purchase of Terra Bella, a Mountain View, California-based company founded in 2009 by Dan Berkenstock, Julian Mann, John Fenwick, and Ching-Yu Hu, from Google in 2017.

SpaceX CRS-3, also known as SpX-3, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station (ISS), contracted to NASA, which was launched on 18 April 2014. It was the fifth flight for SpaceX's uncrewed Dragon cargo spacecraft and the third SpaceX operational mission contracted to NASA under a Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-1) contract.

Nanoracks LLC is a private in-space services company which builds tools to allow the re-purposing of in-space hardware and turn it into space stations.

Alexander, also known as PhoneSat 2.0 Beta or PhoneSat v2a is a technology demonstration satellite operated by NASA's Ames Research Center, which was launched in April 2013. Part of the PhoneSat programme, it was one of the first three PhoneSat spacecraft, and the first Phonesat-2.0 satellite, to be launched.
Graham, also known as PhoneSat 1.0a or PhoneSat v1a was a technology demonstration satellite operated by NASA's Ames Research Center, which was launched in April 2013. Part of the PhoneSat programme, it was one of the first three PhoneSat spacecraft to be launched.
TurkSat-3USat is a Turkish communications nanosatellite developed by the Space Systems Design and Test Laboratory and Radio Frequency Electronics Laboratory of Istanbul Technical University (ITU) in collaboration with the Türksat company along with Turkish Amateur Satellite Technology Organization (TAMSAT). It was launched on 26 April 2013.

Planet Labs PBC is an American public Earth imaging company based in San Francisco, California. Their goal is to image the entirety of the Earth daily to monitor changes and pinpoint trends.
Gaofen 1 is a Chinese high-resolution Earth observation satellite, and the first of the Gaofen series satellites.
ArgoMoon is a nanosatellite that will fly on NASA's Artemis 1 mission into a heliocentric orbit in cislunar space on the maiden flight of the Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft, in 2022. The satellite has the dimensions of a shoe box ; in CubeSat terms, it is a 6U.

Irvine CubeSat STEM Program (ICSP) is a joint educational endeavor to teach, train and inspire the next generation of STEM professionals. ICSP involves students from six high schools from Irvine, California, and its main objective is to assemble, test, and launch a CubeSat into low Earth orbit.
IRVINE02 is an educational 1U CubeSat mission that gives high school students the experience of building, testing, and controlling a nano-satellite to develop interest and talent in the science and engineering fields. The mission features the second orbital ion electrospray thruster developed by Accion Systems. Beyond the thruster, IRVINE02 utilizes magnetorquers, deployable solar arrays, a GPS unit, and a miniaturized 1.4 Watt blue laser communication module to transmit pictures and data back to Earth. The magnetorquers and the laser are both developed by the Ecuadorian Space Agency. This laser made IRVINE02 the first 1U cubesat to fly with an orbit-to-ground laser communications device. It transmits data and pictures to the Earth much faster than radio.