
Vandenberg Space Force Base, previously Vandenberg Air Force Base, is a United States Space Force Base in Santa Barbara County, California. Established in 1941, Vandenberg Space Force Base is a space launch base, launching spacecraft from the Western Range, and also performs missile testing. The United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 30 serves as the host delta for the base, equivalent to an Air Force air base wing. In addition to its military space launch mission, Vandenberg Space Force Base also hosts space launches for civil and commercial space entities, such as NASA and SpaceX.

Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.

The Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) is a scientific research and development detachment of the United States Air Force Materiel Command dedicated to leading the discovery, development, and integration of direct-energy based aerospace warfighting technologies, planning and executing the Air Force science and technology program, and providing warfighting capabilities to United States air, space, and cyberspace forces. It controls the entire Air Force science and technology research budget which was $2.4 billion in 2006.

The Space-Based Infrared System (SBIRS) is a United States Space Force system intended to meet the United States' Department of Defense infrared space surveillance needs through the first two to three decades of the 21st century. The SBIRS program is designed to provide key capabilities in the areas of missile warning, missile defense, battlespace characterization and technical intelligence via satellites in geosynchronous Earth orbit (GEO), sensors hosted on satellites in highly elliptical orbit (HEO), and ground-based data processing and control.

The United States Army Space and Missile Defense Command (USASMDC) is the Army Service Component Command (ASCC) for United States Strategic Command and United States Space Command. It was established in 1985 as the Army Strategic Defense Command, responsible for ballistic missile defense. In 1992, it merged with Army Space Command to become Army Space and Strategic Defense Command. In 1997, it became an Army Major Command and was redesignated Army Space and Missile Defense Command.
Lockheed Martin Space is one of the four major business divisions of Lockheed Martin. It has its headquarters in Littleton, Colorado, with additional sites in Valley Forge, Pennsylvania; Sunnyvale, California; Santa Cruz, California; Huntsville, Alabama; and elsewhere in the United States and United Kingdom. The division currently employs about 20,000 people, and its most notable products are commercial and military satellites, space probes, missile defense systems, NASA's Orion spacecraft, and the Space Shuttle external tank.
The Aerospace Corporation is an American nonprofit corporation that operates a federally funded research and development center (FFRDC). The corporation provides technical guidance and advice on all aspects of space missions to military, civil, and commercial customers. As the FFRDC for national-security space, Aerospace works closely with organizations such as the United States Space Force (USSF) and the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) to provide "objective technical analyses and assessments for space programs that serve the national interest". Although the USSF and NRO are primary customers, Aerospace performs work for civil agencies such as NASA and NOAA as well as international organizations and governments in the national interest. Aerospace, as part of its charter, also provides expertise to commercial entities, both established companies and startups, domestically and abroad.

The Minotaur I, or just Minotaur is an American expendable launch system derived from the Minuteman II missile. It is used to launch small satellites for the US Government, and is a member of the Minotaur family of rockets produced by Orbital Sciences Corporation.

TacSat-2 is the first in a series of U.S. military experimental technology and communication satellites.TacSat-2 (also known as JWS-D1 was an experimental satellite built by the USAF's Air Force Research Laboratory with an operational life expected to be not more than one year as part of the "Advanced Concept Technology Demonstration" program.
The Space Test Program (STP) is the primary provider of spaceflight for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) space science and technology community. STP is managed by a group within the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate, a directorate of the Space and Missile Systems Center of the United States Space Force. STP provides spaceflight via the International Space Station (ISS), piggybacks, secondary payloads and dedicated launch services.

Space Systems Command (SSC) is the United States Space Force's space development, acquisition, launch, and logistics field command. It is headquartered at Los Angeles Air Force Base, California, and manages the United States' space launch ranges.

TacSat-1 was an experimental satellite built by the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) on behalf of the United States Department of Defense (DoD) Office of Force Transformation (OFT). It was the planned payload of the sixth launch of the SpaceX Falcon 1. It was however never launched into space. The second satellite in the series, TacSat-2, launched before TacSat-1 and this led to the cancellation of TacSat-1's launch.
The Operationally Responsive Space Office is a joint initiative of the United States Department of Defense (DoD). The "stand up" of the office took place 21 May 2007 at Kirtland Air Force Base. The first director of the ORS Office was Col. Kevin McLaughlin, who was also the commander of the Space Development and Test Wing located at Kirtland. The ORS Office focuses on providing quick-response tactical space-based capabilities; utilizing smaller satellites, such as the Tactical Satellite Program and smaller launch vehicles.
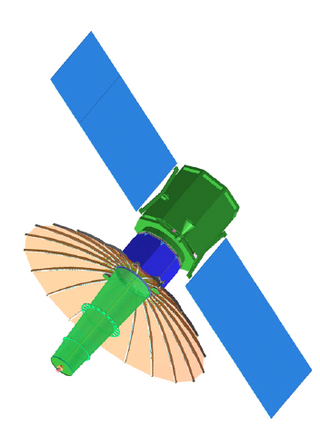
TacSat-4 is the third in a series of U.S. military experimental technology and communication satellites. The United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is the program manager. The Office of Naval Research (ONR) sponsored the development of the payload and funded the first year of operations. The Office of the Director of Defense Research and Engineering (DDR&E) funded the standardized spacecraft bus and the Operationally Responsive Space Office (ORS) funded the launch that will be performed by the Air Force's Space and Missile Systems Center (SMC).

The year 2012 saw a number of significant events in spaceflight. In May and October, the first Commercial Orbital Transportation Services resupply missions took place, during which the SpaceX Dragon became the first private spacecraft to dock with the International Space Station (ISS). In June, China launched the crewed Shenzhou 9 orbital mission, and North Korea achieved its first successful orbital launch in December. 2012 also saw China's first successful asteroid exploration mission, and the landing of NASA's Curiosity rover on Mars. The Vega and Unha-3 rockets made their maiden flights in 2012, while the Proton-K made its last.

SpaceX COTS Demo Flight 1 was the first orbital spaceflight of the Dragon cargo spacecraft, and the second overall flight of the Falcon 9 rocket manufactured by SpaceX. It was also the first demonstration flight for NASA's Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) program. The primary mission objectives were to test the orbital maneuvering and reentry of the Dragon capsule. The mission also aimed to test fixes to the Falcon 9 rocket, particularly the unplanned roll of the first stage that occurred during flight 1. Liftoff occurred on 8 December 2010 at 15:43 UTC.

The United States Space Force (USSF) is the space force branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is one of two independent space forces in the world.

While the United States Space Force gained its independence on 20 December 2019, the history of the United States Space Force can be traced back to the beginnings of the military space program following the conclusion of the Second World War in 1945. Early military space development was begun within the United States Army Air Forces by General Henry H. Arnold, who identified space as a crucial military arena decades before the first spaceflight. Gaining its independence from the Army on 18 September 1947, the United States Air Force began development of military space and ballistic missile programs, while also competing with the United States Army and United States Navy for the space mission.













