
The Pinwheel Galaxy is a face-on, unbarred, and counterclockwise spiral galaxy located 21 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781 and was communicated that year to Charles Messier, who verified its position for inclusion in the Messier Catalogue as one of its final entries.

The Sombrero Galaxy is a peculiar galaxy of unclear classification in the constellation borders of Virgo and Corvus, being about 9.55 megaparsecs from the Milky Way galaxy. It is a member of the Virgo II Groups, a series of galaxies and galaxy clusters strung out from the southern edge of the Virgo Supercluster. It has an isophotal diameter of approximately 29.09 to 32.32 kiloparsecs, making it slightly bigger in size than the Milky Way.

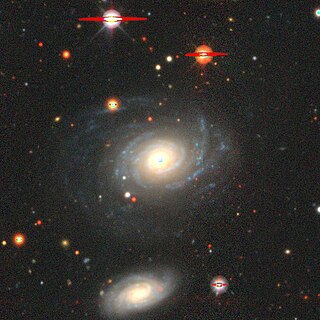
Messier 96 is an intermediate spiral galaxy about 31 million light-years away in the constellation Leo.
NGC 1 is an intermediate spiral galaxy of the morphological type Sbc, located in the constellation of Pegasus. It was discovered on 30 September 1861 by Heinrich d'Arrest.

NGC 891 is an edge-on unbarred spiral galaxy about 30 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda. It was discovered by William Herschel on October 6, 1784. The galaxy is a member of the NGC 1023 group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster. It has an H II nucleus.

The NGC 5866 Group is a small group of galaxies located in the constellation Draco. The group is named after NGC 5866, the galaxy with the highest apparent magnitude in the group, although some galaxy group catalogs list NGC 5907 as the brightest member.

NGC 2441 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the northern constellation of Camelopardalis. Its velocity with respect to the cosmic microwave background is 3492 ± 2 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 168.0 ± 11.8 Mly (51.51 ± 3.61 Mpc). In addition, 16 non-redshift measurements give a distance of 176.16 ± 16.80 Mly (54.012 ± 5.151 Mpc). The galaxy was discovered by German astronomer Wilhelm Tempel on 8 August 1882.

NGC 1270 is an elliptical galaxy located about 250 million light-years away in the constellation Perseus. It was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on February 14, 1863. NGC 1270 is a member of the Perseus Cluster and has an estimated age of about 11 billion years. However, Greene et al. puts the age of NGC 1270 at about 15.0 ± 0.50 Gy.

NGC 669 is an edge-on spiral galaxy with an active galactic nucleus located 200 million light-years away in the constellation Triangulum. NGC 669 was discovered by astronomer Édouard Stephan on November 28, 1883 and is a member of Abell 262.

NGC 703 is a lenticular galaxy located 240 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on September 21, 1786 and is also a member of Abell 262.

NGC 714 is a lenticular galaxy located 190 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer Bindon Blood Stoney on October 28, 1850 and is a member of Abell 262.

NGC 973 is a giant spiral galaxy located in the constellation Triangulum. It is located at a distance of circa 200 million light-years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 973 is about 230,000 light years across. It was discovered by Lewis Swift on October 30, 1885.

NGC 765 is an intermediate spiral galaxy located in the constellation Aries. It is located at a distance of circa 220 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 765 is about 195,000 light years across. It was discovered by Albert Marth on October 8, 1864. The galaxy has an extensive hydrogen (HI) disk with low surface brightness, whose diameter is estimated to be 240 kpc.

NGC 931 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Triangulum. It is located at a distance of circa 200 million light-years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 931 is about 200,000 light years across. It was discovered by Heinrich d'Arrest on September 26, 1865. It is classified as a Seyfert galaxy.

NGC 3073 is a dwarf lenticular galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It is at a distance of about 65 million light-years from Earth. NGC 3073 was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel on 1 April 1790.

NGC 4221 is a barred lenticular galaxy located about 75.9 million light-years away in the constellation of Draco. It was discovered on April 3, 1832, by the astronomer John Herschel. NGC 4221 is notable for having an outer ring that surrounds the inner barred central region of the galaxy.

NGC 4359 is a dwarf barred spiral galaxy seen edge-on that is about 56 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on March 20, 1787. It is a member of the NGC 4274 Group, which is part of the Coma I Group or Cloud.

NGC 3516 is a barred lenticular galaxy in the constellation of Ursa Major. NGC 3516 is located about 150 million light years away from Earth, which means, given its apparent dimensions, that NGC 3516 is approximately 100,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 3, 1785.

NGC 2523 is a barred spiral galaxy located around 168 million light-years away in the constellation Camelopardalis. NGC 2523 was discovered on 7 September 1885 by the American astronomer Edward Swift, and is approximately 120,000 light-years across. NGC 2523 does not have much star formation, and it does not have an active galactic nucleus.

NGC 2550A is a spiral galaxy in the constellation of Camelopardalis. Its velocity with respect to the cosmic microwave background is 3670 ± 10 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 176.5 ± 12.4 Mly (54.12 ± 3.79 Mpc). The discovery of this galaxy is credited to Philip C. Keenan, in his paper Studies of Extra-Galactic Nebulae. Part I: Determination of Magnitudes, published in The Astrophysical Journal in 1935.




















