
The Tonga Trench is an oceanic trench located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It is the deepest trench in the Southern hemisphere and the second deepest on Earth after the Mariana Trench. The fastest plate-tectonic velocity on Earth is occurring at this location, as the Pacific plate is being subducted westward in the trench.

The Australian plate is a major tectonic plate in the eastern and, largely, southern hemispheres. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, Australia remained connected to India and Antarctica until approximately 100 million years ago when India broke away and began moving north. Australia and Antarctica had begun rifting by 96 million years ago and completely separated a while after this, some believing as recently as 45 million years ago, but most accepting presently that this had occurred by 60 million years ago.
The Solomon Sea plate is a minor tectonic plate to the northwest of the Solomon Islands archipelago in the south Pacific Ocean. It roughly corresponds with the Solomon Sea east of Papua New Guinea. The plate boundaries are associated with high earthquake activity as part of the New Britain subduction zone.

The 1,600 kilometres (990 mi) long Macquarie fault zone is a major right lateral-moving transform fault along the seafloor of the south Pacific Ocean which runs from New Zealand southwestward towards the Macquarie triple junction. It is also the tectonic plate boundary between the Australian plate to the northwest and the Pacific plate to the southeast. As such it is a region of high seismic activity and recorded the largest strike-slip event on record up to 23 May 1989, of at least 8.0

The Balmoral Reef plate is a small tectonic plate (microplate) located in the south Pacific north of Fiji. Clockwise from the north, it borders the Pacific plate, the Australian plate, Conway Reef plate, and the New Hebrides plate. The northern and western borders are a divergent boundary while the rest of the borders are transform and convergent boundaries. The Balmoral Reef plate's ocean crust is less than 12 million years old and is spreading between the New Hebrides and Tonga subduction. The plate forms the west central part of the seafloor of the North Fiji Basin.

The Caroline plate is a minor tectonic plate that straddles the Equator in the eastern hemisphere located north of New Guinea. It forms a subduction zone along the border with the Bird's Head plate and other minor plates of the New Guinea region to the south. A transform boundary forms the northern border with the Pacific plate. Along the border with the Philippine Sea plate is a convergent boundary that transitions into a rift.

The Conway Reef plate is a small tectonic plate (microplate) located in the south Pacific west of Fiji. The western boundary is with the New Hebrides plate while the eastern is with the Australian plate. A short transform boundary also exists with the Balmoral Reef plate. Much of the plate underlies the south central portion of the North Fiji Basin.
The South Bismarck plate is a small tectonic plate located mainly in the southern Bismarck Sea. The eastern part of New Guinea and the island of New Britain are on this plate. It is associated with high earthquake and volcanic activity as part of the New Britain subduction zone within the Pacific Ring of Fire.

The Woodlark plate is a small almost triangular shaped tectonic plate located east of the island of New Guinea and situated mainly within the northern half of the Woodlark Basin. It is located in a very complex tectonic environment, that because of associated features, has been extensively studied since it was first proposed to exist. It is now known to be much smaller than originally proposed, mainly because of information from GPS stations on islands and sea floor studies that have fully defined its margins.

The Lau Basin is a back-arc basin at the Australian-Pacific plate boundary. It is formed by the Pacific plate subducting under the Australian plate. The Tonga-Kermadec Ridge, a frontal arc, and the Lau-Colville Ridge, a remnant arc, sit to the eastern and western sides of the basin, respectively. The basin has a raised transition area to the south where it joins the Havre Trough.

The West Melanesian Trench is an oceanic trench in the Bismarck Sea north of Papua New Guinea delineating the plate tectonic boundary between the Caroline and North Bismarck plates.

The Pacific Ocean evolved in the Mesozoic from the Panthalassic Ocean, which had formed when Rodinia rifted apart around 750 Ma. The first ocean floor which is part of the current Pacific plate began 160 Ma to the west of the central Pacific and subsequently developed into the largest oceanic plate on Earth.
The 1999 Ambrym earthquake occurred on November 27 at with a moment magnitude of 7.4 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. The back arc thrust event occurred within the Vanuatu archipelago, just to the south of the volcanic island of Ambrym. Vanuatu, which was previously known as New Hebrides, is subject to volcanic and earthquake activity because it lies on an active and destructive plate boundary called the New Hebrides Subduction Zone. While the National Geophysical Data Center classified the total damage as moderate, a destructive local tsunami did result in some deaths, with at least five killed and up to 100 injured.

The North Fiji Basin (NFB) is an oceanic basin west of Fiji in the south-west Pacific Ocean. It is an actively spreading back-arc basin delimited by the Fiji islands to the east, the inactive Vitiaz Trench to the north, the Vanuatu/New Hebrides island arc to the west, and the Hunter fracture zone to the south. Roughly triangular in shape with its apex located at the northern end of the New Hebrides Arc, the basin is actively spreading southward and is characterised by three spreading centres and an oceanic crust younger than 12 Ma. The opening of the NFB began when a slab roll-back was initiated beneath the New Hebrides and the island arc started its clockwise rotation. The opening of the basin was the result of the collision between the Ontong Java Plateau and the Australian plate along the now inactive Solomon–Vitiaz subduction system north of the NFB. The NFB is the largest and most developed back-arc basin of the south-west Pacific. It is opening in a complex geological setting between two oppositely verging subduction systems, the New Hebrides/Vanuatu and Tonga trenches and hence its ocean floor has the World's largest amount of spreading centres per area.
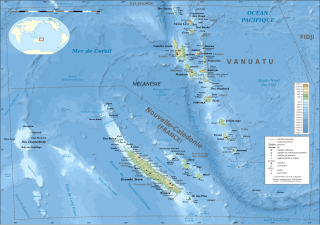
The d'EntrecasteauxRidge (DER) is a double oceanic ridge in the south-west Pacific Ocean, north of New Caledonia and west of Vanuatu Islands. It forms the northern extension of the New Caledonia–Loyalty Islands arc, and is now actively subducting in the Vanuatu subduction zone under the Vanuatu/New Hebrides arc. The subduction of the DER is responsible for the anomalous morphology of the central part of New Hebrides arc whose movement more closely matches the north-east direction of the subducting Australian Plate.

Oblique subduction is a form of subduction for which the convergence direction differs from 90° to the plate boundary. Most convergent boundaries involve oblique subduction, particularly in the Ring of Fire including the Ryukyu, Aleutian, Central America and Chile subduction zones. In general, the obliquity angle is between 15° and 30°. Subduction zones with high obliquity angles include Sunda trench and Ryukyu arc.

The New Hebrides Trench is an oceanic trench which is over 7.1 km (4.4 mi) deep in the Southern Pacific Ocean. It lies to the northeast of New Caledonia and the Loyalty Islands, to the southwest of Vanuatu, east of Australia, and south of Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands. The trench was formed as a result of a subduction zone. The Australian plate is being subducted under the New Hebrides plate causing volcanism which produced the Vanuatu archipelago.

The Hunter fracture zone is a sinistral (left-lateral) transform faulting fracture zone, that to its south is part of a triple junction with the New Hebrides Trench, and the North Fiji Basin Central Spreading Ridge. The Hunter fracture zone, with the Hunter Ridge, an area with recent volcanic activity to its north, is the southern boundary of the North Fiji Basin. This boundary area in the south-western part of the Hunter fracture zone is associated with hot subduction, and a unique range of volcanic geochemistry.
The Vanuatu subduction zone is currently one of the most active subduction zones on Earth, producing great earthquakes, with potential for tsunami hazard to all coastlines of the Pacific Ocean. There are active volcanoes associated with arc volcanism.

The Norfolk Basin, which has been subdivided into the North Norfolk Basin and South Norfolk Basin, is an ocean floor sedimentary basin between the Norfolk Ridge to the east and the Three Kings Ridge to the west, on the edge of the submerged continent of Zealandia. The northern boundary is the Cook fracture zone and the southern is the Regina ridge projecting from Northland Peninsula, New Zealand. While it has back-arc basin characteristics its formation and structure are not able to be explained by historic back-arc basin theory.














