The North American Plate is a tectonic plate containing most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of 76 million km2 (29 million sq mi), it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacific Plate.
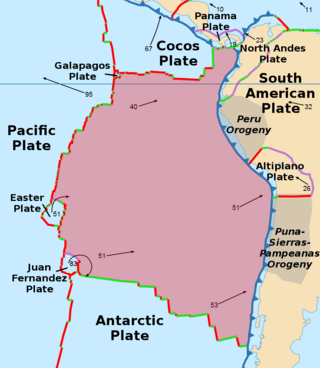
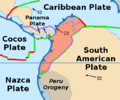
The Nazca Plate or Nasca Plate, named after the Nazca region of southern Peru, is an oceanic tectonic plate in the eastern Pacific Ocean basin off the west coast of South America. The ongoing subduction, along the Peru–Chile Trench, of the Nazca Plate under the South American Plate is largely responsible for the Andean orogeny. The Nazca Plate is bounded on the west by the Pacific Plate and to the south by the Antarctic Plate through the East Pacific Rise and the Chile Rise, respectively. The movement of the Nazca Plate over several hotspots has created some volcanic islands as well as east-west running seamount chains that subduct under South America. Nazca is a relatively young plate in terms of the age of its rocks and its existence as an independent plate, having been formed from the breakup of the Farallon Plate about 23 million years ago. The oldest rocks of the plate are about 50 million years old.

The Cocos Plate is a young oceanic tectonic plate beneath the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Central America, named for Cocos Island, which rides upon it. The Cocos Plate was created approximately 23 million years ago when the Farallon Plate broke into two pieces, which also created the Nazca Plate. The Cocos Plate also broke into two pieces, creating the small Rivera Plate. The Cocos Plate is bounded by several different plates. To the northeast it is bounded by the North American Plate and the Caribbean Plate. To the west it is bounded by the Pacific Plate and to the south by the Nazca Plate.
The East Pacific Rise (EPR) is a mid-ocean rise, at a divergent tectonic plate boundary, located along the floor of the Pacific Ocean. It separates the Pacific Plate to the west from the North American Plate, the Rivera Plate, the Cocos Plate, the Nazca Plate, and the Antarctic Plate. It runs south from the Gulf of California in the Salton Sea basin in Southern California to a point near 55°S130°W, where it joins the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge (PAR) trending west-south-west towards Antarctica, near New Zealand. Much of the rise lies about 3,200 km (2,000 mi) off the South American coast and reaches a height about 1,800–2,700 m (5,900–8,900 ft) above the surrounding seafloor.

The Caribbean Plate is a mostly oceanic tectonic plate underlying Central America and the Caribbean Sea off the northern coast of South America.

The Central American Volcanic Arc is a chain of volcanoes which extends parallel to the Pacific coastline of the Central American Isthmus, from Mexico to Panama. This volcanic arc, which has a length of 1,100 kilometers is formed by an active subduction zone, with the Cocos Plate subducting underneath the Caribbean Plate. The region has been volcanically and geologically active for at least the past several million years. Numerous volcanoes are spread throughout various Central American countries; many have been active in the geologic past, some more so than others.

The Carnegie Ridge is an aseismic ridge on the Nazca Plate that is being subducted beneath the South American Plate. The ridge is thought to be a result of the passage of the Nazca Plate over the Galapagos hotspot. It is named for the research vessel Carnegie, which discovered it in 1929.

The Galapagos Microplate (GMP) is a geological feature of the oceanic crust located at 1°50' N, offshore of the west coast of Colombia. The GMP is collocated with the Galapagos Triple Junction, which is an atypical ridge-ridge-ridge triple junction. At the Galapagos Triple Junction, the Pacific Plate, Cocos Plate, and Nazca Plate meet incompletely, forming two counter-rotating microplates at the junction of the Cocos-Nazca, Pacific-Cocos, and Pacific-Nazca spreading ridges.
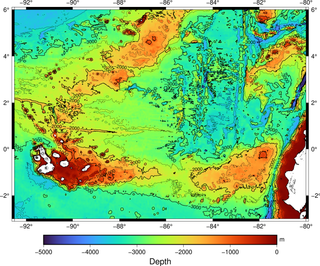
The Galápagos hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the East Pacific Ocean responsible for the creation of the Galápagos Islands as well as three major aseismic ridge systems, Carnegie, Cocos and Malpelo which are on two tectonic plates. The hotspot is located near the Equator on the Nazca Plate not far from the divergent plate boundary with the Cocos Plate. The tectonic setting of the hotspot is complicated by the Galapagos Triple Junction of the Nazca and Cocos plates with the Pacific Plate. The movement of the plates over the hotspot is determined not solely by the spreading along the ridge but also by the relative motion between the Pacific Plate and the Cocos and Nazca Plates.

The Galapagos Triple Junction is a geological area in the eastern Pacific Ocean several hundred miles west of the Galapagos Islands where three tectonic plates - the Cocos Plate, the Nazca Plate and the Pacific Plate - meet. It is an unusual type of triple junction in which the three plates do not meet at a simple intersection. Instead, the junction includes two small microplates, the Galapagos Microplate and the Northern Galapagos Microplate, caught in the junction, turning synchronously with respect to each other and separated by the Hess Deep rift.
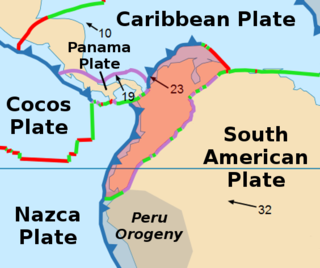
The North Andes Plate or North Andes Block is a small tectonic plate (microplate) located in the northern Andes. It is squeezed between the faster moving South American Plate and the Nazca Plate to the southwest. Due to the subduction of the Coiba and Malpelo plates, this area is very prone to volcanic and seismic activity, with many historical earthquakes.

The Panama Plate is a small tectonic plate (microplate) that exists between two actively spreading ridges and moves relatively independently of its surrounding plates. The Panama Plate is located between the Cocos Plate and the Nazca Plate to the south and the Caribbean Plate to the north. Most of its borders are convergent boundaries, including a subduction zone to the west. It consists, for the most part, of the countries of Costa Rica and Panama.

The Malpelo Plate is a small tectonic plate (microplate) located off the coasts west of Ecuador and Colombia. It is the 57th plate to be identified. It is named after Malpelo Island, the only emerged part of the plate. It is bounded on the west by the Cocos Plate, on the south by the Nazca Plate, on the east by the North Andes Plate, and on the north by the Coiba Plate, separated by the Coiba Transform Fault (CTF). This microplate was previously assumed to be part of the Nazca Plate. The Malpelo Plate borders three major faults of Pacific Colombia, the north to south striking Bahía Solano Fault in the north and the Naya-Micay and Remolino-El Charco Faults in the south.
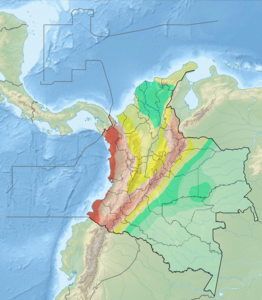
The Romeral Fault System is a megaregional system of major parallel and anastomosing faults in the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes and the Cauca, Amagá, and Sinú-San Jacinto Basins. The system spans across ten departments of Colombia, from northeast to south Bolívar, Sucre, Córdoba, Antioquia, Caldas, Risaralda, Quindío, Valle del Cauca, Cauca and Nariño. The fault zone extends into Ecuador where it is known as the Peltetec Fault System. The in detail described part of the Romeral Fault System south of Córdoba has a total length of 697.4 kilometres (433.3 mi) with a cumulative length of 1,787.9 kilometres (1,110.9 mi) and runs along an average north to south strike of 017.6 ± 16, cross-cutting the central-western portion of Colombia.

The Bahía Solano Fault, Utría Fault or Utría-Bahía Solano Fault is a westward dipping thrust fault in the department of Chocó on the Pacific Coast of Colombia. The fault has a total length of 290.6 kilometres (180.6 mi) and runs along an average north–south strike of 347 ± 13 from the Panama-Colombia border to Bajo Baudó. The fault is partly offshore in the bays of Solano and Utría and crosses the Chocó Basin and the coastal Serranía del Baudó. Movement of the fault produced the Mw 6.5 1970 Bahía Solano earthquake.
The Ibagué Fault is a major dextral slightly oblique strike-slip fault in the department of Tolima in central Colombia. The fault has a total length of 123.9 kilometres (77.0 mi) and runs along an average east-northeast to west-southwest strike of 067.9 ± 11 cross-cutting the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes.
The geology of Costa Rica is part of the Panama Microplate, which is slowly moving north relative to the stable Caribbean Plate.
The Malpelo Ridge is an elevated part of Nazca Plate off the Pacific coast of Colombia. It is a faulted chain of volcanic rock of tholeiitic composition. The Malpelo Ridge may have originated simultaneously as Carnegie Ridge, and thus represent an old continuation of Cocos Ridge. It is thought to have acquired it present position due to tectonic movements along the Panama Fracture Zone.

The Chile Ridge, also known as the Chile Rise, is a submarine oceanic ridge formed by the divergent plate boundary between the Nazca Plate and the Antarctic Plate. It extends from the triple junction of the Nazca, Pacific, and Antarctic plates to the Southern coast of Chile. The Chile Ridge is easy to recognize on the map, as the ridge is divided into several segmented fracture zones which are perpendicular to the ridge segments, showing an orthogonal shape toward the spreading direction. The total length of the ridge segments is about 550–600 km.