Electoral systems of the Australian states and territories are broadly similar to the electoral system used in federal elections in Australia.
In the United Kingdom, the boundary commissions are non-departmental public bodies responsible for determining the boundaries of parliamentary constituencies for elections to the House of Commons. There are four boundary commissions: one each for England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.

The Tasmanian Legislative Council is the upper house of the Parliament of Tasmania in Australia. It is one of the two chambers of the Parliament, the other being the House of Assembly. Both houses sit in Parliament House in the state capital, Hobart. Members of the Legislative Council are often referred to as MLCs.

In the United Kingdom, the Electoral Commission is the national election commission, created in 2001 as a result of the Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000. It is an independent agency that regulates party and election finance and sets standards for how elections should be run.

The Australian Electoral Commission (AEC) is the independent statutory authority and agency of the Australian Government responsible for the management of federal Australian elections, by-elections and referendums.
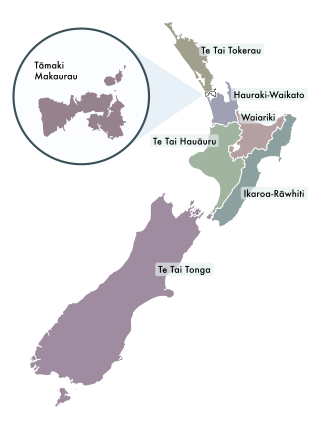
In New Zealand politics, Māori electorates, colloquially known as the Māori seats, are a special category of electorate that give reserved positions to representatives of Māori in the New Zealand Parliament. Every area in New Zealand is covered by both a general and a Māori electorate; as of 2020, there are seven Māori electorates. Since 1967, candidates in Māori electorates have not needed to be Māori themselves, but to register as a voter in the Māori electorates people need to declare that they are of Māori descent.
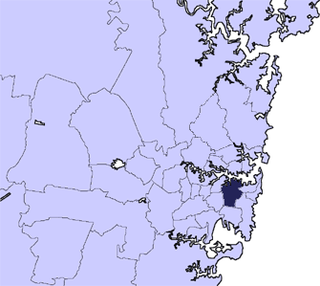
The City of Sydney is the local government area covering the Sydney central business district and surrounding inner city suburbs of the greater metropolitan area of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Established by Act of Parliament in 1842, the City of Sydney is the oldest, and the oldest-surviving, local government authority in New South Wales, and the second-oldest in Australia, with only the City of Adelaide being older by two years.

Electorates of the Australian House of Representatives are single member electoral districts for the lower house of the Parliament of the Commonwealth. There are currently 151 electorates.
The Victorian Electoral Commission, or VEC, is the statutory body responsible for the running of state, municipal and various non-government elections in Victoria, Australia.
An electoral roll is a compilation that lists persons who are entitled to vote for particular elections in a particular jurisdiction. The list is usually broken down by electoral districts, and is primarily prepared to assist election officials at polling places. Most jurisdictions maintain permanent electoral rolls, which are updated continuously or periodically, while some jurisdictions compile new electoral rolls before each election. Electoral rolls are the result of a process of voter registration. In most jurisdictions, voter registration is a prerequisite for voting at an election. Some jurisdictions do not require voter registration, and do not use electoral rolls, such as the state of North Dakota in the United States. In those jurisdictions a voter must provide identification and proof of entitlement to vote before being permitted to vote.

Murray-Darling is a former electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales.
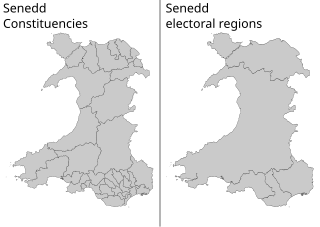
The Senedd constituencies and electoral regions are the electoral districts used to elect members of the Senedd to the Senedd, and have been used in some form since the first election of the then National Assembly for Wales in 1999. New boundaries were introduced for the 2007 elections and currently consist of forty constituencies and five regions. The five electoral regions are: Mid and West Wales, North Wales, South Wales Central, South Wales East, and South Wales West, with the forty constituencies listed below. Voting last took place in all districts in the 2021 Senedd election, and is not used for local government.
In Australia, a redistribution is the process of redrawing the boundaries of electoral divisions for the House of Representatives arising from changes in population and changes in the number of representatives. There is no redistribution for the Senate as each State constitutes a division, though with multiple members. The Australian Electoral Commission (AEC), an independent statutory authority, oversees the apportionment and redistribution process for federal divisions, taking into account a number of factors. Politicians, political parties and the public may make submissions to the AEC on proposed new boundaries, but any interference with their deliberations is considered a serious offence.

The Court of Disputed Returns in New South Wales is a court within the Australian court hierarchy established initially in 1928 pursuant to the Parliamentary Electorates and Elections Amendment Act, and since 2017 pursuant to the Electoral Act 2017. The jurisdiction of the Court is exercised by the Supreme Court of New South Wales and the Court considers petitions concerning the validity of any election or return under the Act. The Court is concerned with elections held for the New South Wales Parliament and local government elections within the state.

Local government in Queensland, Australia, includes the institutions and processes by which towns and districts can manage their own affairs to the extent permitted by the Local Government Act 1993–2007. Queensland is divided into 78 local government areas, which may be called Cities, Towns, Shires, or Regions. Each area has a council that is responsible for providing a range of public services and utilities and derives its income from both rates and charges on resident ratepayers and grants and subsidies from the state and Commonwealth governments.

There are five types of elections in the United Kingdom: elections to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, elections to devolved parliaments and assemblies, local elections, mayoral elections, and police and crime commissioner elections. Within each of those categories, there may also be by-elections. Elections are held on Election Day, which is conventionally a Thursday, and under the provisions of the Dissolution and Calling of Parliament Act 2022 the timing of general elections can be held at the discretion of the prime minister during any five-year period. All other types of elections are held after fixed periods, though early elections to the devolved assemblies and parliaments can occur in certain situations. The five electoral systems used are: the single member plurality system (first-past-the-post), the multi-member plurality, the single transferable vote, the additional member system, and the supplementary vote.
Suffrage in Australia is the voting rights in the Commonwealth of Australia, its six component states and territories, and local governments. The colonies of Australia began to grant universal male suffrage from 1856, with women's suffrage following between the 1890s and 1900s. Some jurisdictions introduced racial restrictions on voting from 1885, and by 1902 most Australian residents who were not of European descent were explicitly or effectively excluded from voting and standing for office, including at the Federal level. Such restrictions had been removed by 1966. Today, the right to vote at all levels of government is held by citizens of Australia over the age of 18 years, excluding some prisoners and some people with disabilities.

The 2012 United Kingdom local elections were held across England, Scotland and Wales on 3 May 2012. Elections were held in 128 English local authorities, all 32 Scottish local authorities and 21 of the 22 Welsh unitary authorities, alongside three mayoral elections including the London mayoralty and the London Assembly. Referendums were also held in 11 English cities to determine whether or not to introduce directly elected mayors.
The NSW Aboriginal Land Council (NSWALC) is the peak representative body of Aboriginal Australians in New South Wales. It has the mandate, under the Aboriginal Land Rights Act 1983 (NSW), to develop land rights among Aboriginal people in New South Wales through its network of 120 Local Aboriginal Land Councils (LALCs). Its functions include the creation of an economic base for Aboriginal communities, as well as the continued passing and enhancement of Aboriginal culture, identity and heritage through the management of traditional sites and other cultural materials within NSW. It acts as an advisor to governments and others to ensure the preservation of Aboriginal land rights.
In Australia, voter registration is called enrolment. Enrolment is a prerequisite for voting at federal elections, by-elections and referendums, as well as all state and local government elections; and it is generally compulsory for enrolled persons to vote unless otherwise exempted or excused. Enrolment is compulsory for Australian citizens over 18 years of age who have lived at their current address for at least one month. Enrolment is not compulsory for persons with no fixed address who are not already enrolled. Residents in Australia who had been enrolled as British subjects on 25 January 1984, though not Australian citizens, continue to be enrolled, and cannot opt out of enrolment. For local government elections, an elector generally does not require to be an Australian citizen. Once enrolled, a person cannot opt out of enrolment. Enrolment is optional for 16- or 17-year-olds, but they cannot vote until they turn 18, and persons who have applied for Australian citizenship may also apply for provisional enrolment which takes effect on the granting of citizenship.














