Cobalt(II) cyanide is the inorganic compound with the formula Co(CN)2. It is coordination polymer that has attracted intermittent attention over many years in the area of inorganic synthesis and homogeneous catalysis.
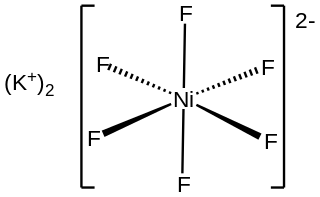
Potassium hexafluoronickelate(IV) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula K
2NiF
6. It can be produced through the reaction of potassium fluoride, nickel dichloride, and fluorine.

Rhodium hexafluoride, also rhodium(VI) fluoride, (RhF6) is the inorganic compound of rhodium and fluorine. A black volatile solid, it is a highly reactive material, and a rare example of a rhodium(VI) compound. It is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides.

The cyanonickelates are a class of chemical compound containing anions consisting of nickel atoms, and cyanide groups. The most important of these are the tetracyanonickelates containing four cyanide groups per nickel. The tetracyanonickelates contain the [Ni(CN)4]2− anion. This can exist in solution or in solid salts. The ion has cyanide groups arranged in a square around the central nickel ion. The symmetry of the ion is D4h. The distance from the nickel atom to the carbon is 1.87 Å, and the carbon-nitrogen distance is 1.16 Å. Tetracyanonickelate(II) can be oxidised electrochemically in solution to yield tetracyanonickelate(III) [Ni(CN)4]−. [Ni(CN)4]− is unstable and Ni(III) oxidises the cyanide to cyanate OCN−. Tetracyanonickelate(III) can add two more cyanide groups to form hexacyanonickelate(III).

Praseodymium(IV) oxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula PrO2.
Iron(II) cyanide is an inorganic compound with the empirical formula Fe(CN)2. It may have a Fe2[Fe(CN)6] structure.

Neodymium(III) hydroxide is an insoluble inorganic compound with the chemical formula Nd(OH)3.

Samarium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Sm(OH)3.
Thulium(II) chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula TmCl2.

Erbium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Er(OH)3.

Dysprosium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Dy(OH)3.

Neptunium(III) chloride or neptunium trichloride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula NpCl3. This salt is strongly radioactive.

Potassium tetracyanonickelate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2Ni(CN)4. It is usually encountered as the monohydrate but the anhydrous salt is also known. Both are yellow, water-soluble, diamagnetic solids. The salt consists of potassium ions and the tetracyanonickelate coordination complex, which is square planar.
Potassium pertechnetate is a chemical compound of technetium and potassium, with the chemical formula of KTcO4.

Nickel(II) perchlorate is a inorganic compound with the chemical formula of Ni(ClO4)2, and it is a strong oxidizing agent. Its colours are different depending on water. For example, the hydrate forms cyan crystals, the pentahydrate forms green crystals, but the hexahydrate (Ni(ClO4)2·6H2O) forms blue crystals.
Praseodymium(III) carbonate is an inorganic compound, with a chemical formula of Pr2(CO3)3. The anhydrous form is olive green, and many of its hydrates such as heptahydrate and octahydrate are known. They are all insoluble in water.

Thulium(III) iodide is an iodide of thulium, with the chemical formula of TmI3. Thulium(III) iodide is used as a component of metal halide lamps.

Cerium acetate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of Ce(CH3COO)3. It is a white powder that is soluble in water. Its 1.5 hydrate loses water at 133°C to obtain an amorphous anhydrous form, and the amorphous phase changes to crystal at 212°C, and phase changes again at 286°C.
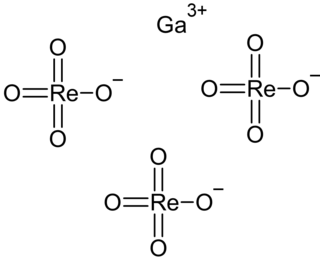
Gallium perrhenate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of Ga(ReO4)3. It exists in the anhydrous and hydrate forms.
A niobate is an oxo-acid salt formed by niobium(V), and the common forms are metaniobate (NbO3−) and orthoniobate (NbO43−). The most common niobates are lithium niobate (LiNbO3) and potassium niobate (KNbO3).




![K2[Ni(CN)4] (tetracyanonickelate) solution) Potassium tetracyanonickelate solution.jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ab/Potassium_tetracyanonickelate_solution.jpg/100px-Potassium_tetracyanonickelate_solution.jpg)














