
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not all oysters, are in the superfamily Ostreoidea.

Bivalvia, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. The class includes the clams, oysters, cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they are relatively safe from predation. Others lie on the sea floor or attach themselves to rocks or other hard surfaces. Some bivalves, such as the scallops and file shells, can swim. Shipworms bore into wood, clay, or stone and live inside these substances.

Crassostrea is a genus of true oysters containing some of the most important oysters used for food. Some species in the genus have been moved to the genus Magallana.

The Ostreidae, the true oysters, include most species of molluscs commonly consumed as oysters. Pearl oysters are not true oysters, and belong to the order Pteriida.

The Pacific oyster, Japanese oyster, or Miyagi oyster is an oyster native to the Pacific coast of Asia. It has become an introduced species in North America, Australia, Europe, and New Zealand.

Ostrea is a genus of edible oysters, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Ostreidae, the oysters.

Ostrea edulis, commonly known as the European flat oyster, is a species of oyster native to Europe. In Britain and Ireland, regional names include Colchester native oyster, mud oyster, or edible oyster. In France, Ostrea edulis are known as huîtres plates except for those that come from the Belon River estuary in Brittany, France, which are known as Belons.

Perna perna, the brown mussel, is an economically important mussel, a bivalve mollusc belonging to the family Mytilidae. It is harvested as a food source but is also known to harbor toxins and cause damage to marine structures. It is native to the waters of Africa, Europe, and South America and was introduced in the waters of North America.

Exogyra is an extinct genus of fossil marine oysters in the family Gryphaeidae, the foam oysters or honeycomb oysters. These bivalves were cemented by the more cupped left valve. The right valve is flatter, and the beak is curved to one side. Exogyra lived on solid substrates in warm seas during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.

Ostrea lurida, common name the Olympia oyster, after Olympia, Washington in the Puget Sound area, is a species of edible oyster, a marine bivalve mollusk in the family Ostreidae. This species occurs on the northern Pacific coast of North America. Over the years the role of this edible species of oyster has been partly displaced by the cultivation of non-native edible oyster species.

The dredge oyster, Bluff oyster or Chilean oyster, is also known in Chile as ostra verde, is a species of bivalve mollusc in the family Ostreidae.

Pycnodonte is a genus of extinct oysters, fossil marine bivalve mollusks in the family Gryphaeidae, the foam oysters or honeycomb oysters. Shells of species in this genus are found around the world in fossil shell beds from the Valanginian to the Early Pleistocene. They are a commonly found fossil in Cretaceous shellbeds of the Navesink Formation in New Jersey.

The truncate donax, abrupt wedge shell, wedge clam or coquina clam, is a bivalve species in the family Donacidae.
Ostrea compressirostra is a species of prehistoric saltwater oyster, a fossil that is found in the Yorktown Formation, Chowan River Formation, Waccamaw Formation, and their equivalents in Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia. Its maximum size is roughly 15 centimetres (5.9 in) in length.

Saccostrea cucullata, the hooded oyster or Natal rock oyster, is a species of rock oyster found mainly in the Indo-Pacific Ocean.

Acanthocardia tuberculata, the rough cockle, is a species of saltwater clam, a cockle, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Cardiidae. The genus Acanthocardia is present from the Upper Oligocene to the Recent.

Barbatia barbata is a species of ark clam, a marine bivalve mollusk in the family Arcidae, the ark clams.

Dosinia exoleta, common name the rayed artemis, is a saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Veneridae, the venus clams.
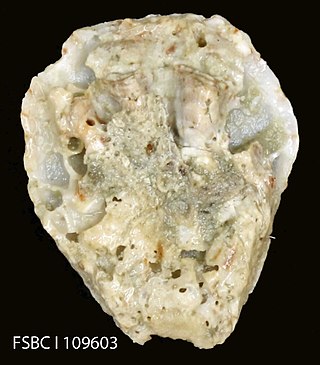
Ostrea equestris, commonly known as the crested oyster or horse oyster, is a species of bivalve mollusc in the family Ostreidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North and South America, ranging from Virginia to Patagonia.
Thousands of years prior to European settlement of the Pacific Northwest of the United States the native oyster species Ostrea lurida had been established as a valuable dietary resource for indigenous people living on the coastal waters. European settlers who began to colonize the Pacific Northwest developed an acquired taste for shellfish, especially oysters, a delicacy that were considered to be a symbol of wealth. In the early history of the Pacific Northwest, people satisfied their hunger for shellfish by harvesting naturally occurring oyster beds. It was initially believed that the populations of indigenous oysters were sufficient to supply both tribal and commercial harvest. A marketable industry was created on the export of oysters and soon exploitation of harvesting had depleted the natural oyster beds in California and Oregon. As a result, Washington state became the main supplier to areas along the coast which had failed to establish any conservation practices. Noticing the economic value and decline of natural availability, farmers began efforts to cultivate oysters to try to satisfy demand. Over the years the oyster industry of the Pacific Northwest has gone from extremely lucrative to completely nonexistent, but still the industry has been able to adapt and survive.






















