
Tuatara are reptiles endemic to New Zealand. Despite their close resemblance to lizards, they are part of a distinct lineage, the order Rhynchocephalia. The name tuatara is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back".

Synapsids are one of the two major clades of vertebrate animals in the group Amniota, the other being the sauropsids, which include reptiles and birds. The synapsids were the dominant land animals in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic, but the only extant group that survived into the Cenozoic are the mammals. Unlike other amniotes, synapsids have a single temporal fenestra, an opening low in the skull roof behind each eye orbit, leaving a bony arch beneath each; this accounts for their name. The distinctive temporal fenestra developed about 318 million years ago during the Late Carboniferous period, when synapsids and sauropsids diverged, but was subsequently merged with the orbit in early mammals.

Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolved from amphibian ancestors during the Carboniferous period and further diverged into two groups, namely the sauropsids and synapsids. They are distinguished from the other living tetrapod clade — the non-amniote lissamphibians — by the development of three extraembryonic membranes, thicker and keratinized skin, and costal respiration.

Ichthyosaurs are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia.

Rhynchocephalia is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a speciose group with high morphological and ecological diversity. The oldest record of the group is dated to the Middle Triassic around 238 to 240 million years ago, and they had achieved a worldwide distribution by the Early Jurassic. Most rhynchocephalians belong to the group Sphenodontia ('wedge-teeth'). Their closest living relatives are lizards and snakes in the order Squamata, with the two orders being grouped together in the superorder Lepidosauria.

Mesosaurs were a group of small aquatic reptiles that lived during the early Permian period (Cisuralian), roughly 299 to 270 million years ago. Mesosaurs were the first known aquatic reptiles, having apparently returned to an aquatic lifestyle from more terrestrial ancestors. It is uncertain which and how many terrestrial traits these ancestors displayed; recent research cannot establish with confidence if the first amniotes were fully terrestrial, or only amphibious. Most authors consider mesosaurs to have been aquatic, although adult animals may have been amphibious, rather than completely aquatic, as indicated by their moderate skeletal adaptations to a semiaquatic lifestyle. Similarly, their affinities are uncertain; they may have been among the most basal sauropsids or among the most basal parareptiles.

Acanthostega is an extinct genus of stem-tetrapod, among the first vertebrate animals to have recognizable limbs. It appeared in the late Devonian period about 365 million years ago, and was anatomically intermediate between lobe-finned fishes and those that were fully capable of coming onto land.
Phytosaurs are an extinct group of large, mostly semiaquatic Late Triassic archosauriform reptiles. Phytosaurs belong to the order Phytosauria. and are sometimes referred to as parasuchians. Phytosauria, Parasuchia, Parasuchidae, and Phytosauridae have often been considered equivalent groupings containing the same species. Some recent studies have offered a more nuanced approach, defining Parasuchidae and Phytosauridae as nested clades within Phytosauria as a whole. Phytosaurs were long-snouted and heavily armoured, bearing a remarkable resemblance to modern crocodilians in size, appearance, and lifestyle, as an example of convergence or parallel evolution. The name "phytosaur" means "plant reptile", as the first fossils of phytosaurs were mistakenly thought to belong to plant eaters.

Reptiliomorpha is a clade containing the amniotes and those tetrapods that share a more recent common ancestor with amniotes than with living amphibians (lissamphibians). It was defined by Michel Laurin (2001) and Vallin and Laurin (2004) as the largest clade that includes Homo sapiens, but not Ascaphus truei. Laurin and Reisz (2020) defined Pan-Amniota as the largest total clade containing Homo sapiens, but not Pipa pipa, Caecilia tentaculata, and Siren lacertina.

Temnospondyli or temnospondyls is a diverse ancient order of small to giant tetrapods — often considered primitive amphibians — that flourished worldwide during the Carboniferous, Permian and Triassic periods, with fossils being found on every continent. A few species continued into the Jurassic and Early Cretaceous periods, but all had gone extinct by the Late Cretaceous. During about 210 million years of evolutionary history, they adapted to a wide range of habitats, including freshwater, terrestrial, and even coastal marine environments. Their life history is well understood, with fossils known from the larval stage, metamorphosis, and maturity. Most temnospondyls were semiaquatic, although some were almost fully terrestrial, returning to the water only to breed. These temnospondyls were some of the first vertebrates fully adapted to life on land. Although temnospondyls are amphibians, many had characteristics such as scales and armour-like bony plates that distinguish them from the modern soft-bodied lissamphibians.

Teleosauridae is a family of extinct typically marine crocodylomorphs similar to the modern gharial that lived during the Jurassic period. Teleosaurids were thalattosuchians closely related to the fully aquatic metriorhynchoids, but were less adapted to an open-ocean, pelagic lifestyle. The family was originally coined to include all the semi-aquatic thalattosuchians and was equivalent to the modern superfamily Teleosauroidea. However, as teleosauroid relationships and diversity was better studied in the 21st century, the division of teleosauroids into two distinct evolutionary lineages led to the establishment of Teleosauridae as a more restrictive family within the group, together with its sister family Machimosauridae.

Pleurosaurus is an extinct genus of aquatic reptiles belonging to the group Rhynchocephalia, extinct relatives of the modern tuatara. Pleurosaurus fossils have been discovered in the Solnhofen Limestone of Bavaria, Germany and the Canjuers lagerstatte near Canjuers, France, both dating to the Late Jurassic. It contains two species, P. goldfussi and P. ginsburgi.

Crocodylomorpha is a group of pseudosuchian archosaurs that includes the crocodilians and their extinct relatives. They were the only members of Pseudosuchia to survive the end-Triassic extinction.

Pleurosauridae is an extinct family of sphenodontian reptiles, known from the Jurassic of Europe. Members of the family had long-snake like bodies with reduced limbs that were adapted for aquatic life in marine environments. It contains two genera, Palaeopleurosaurus, which is known from the Early Jurassic (Toarcian) Posidonia Shale of Germany, as well as Pleurosaurus from the Late Jurassic of Germany and France. Paleopleurosaurus is more primitive than the later Pleurosaurus, with a skull similar to those of other sphenodontians, while that of Pleurosaurus is highly modified relative to other sphendontians. They likely swam via anguilliform locomotion. Vadasaurus and Derasmosaurus from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of Europe have been placed as part of this family in some studies, but lack the body elongation that typifies the other two genera.
Hupehsuchia is an order of diapsid reptiles closely related to ichthyosaurs. The group was short-lasting, with a temporal range restricted to the late Olenekian age, spanning only a few million years of the Early Triassic. The order gets its name from Hubei Province, China, from which many specimens have been found. They are probable members of the clade Ichthyosauromorpha.
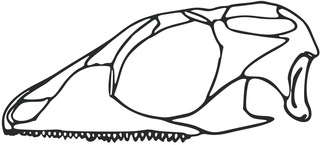
Gephyrosaurus is a genus of early rhynchocephalian first described and named in 1980 by Susan E. Evans. They are distantly related to the extant Sphenodon with which they shared a number of skeletal features including a large tooth row along the side of the palatine bone and posterior process of the dentary bone. The type species, G. bridensis, lived during Early Jurassic in Wales, UK. Whiteside & Duffin (2017) described the second species, G. evansae, known from a partial maxilla recovered from Late Triassic (Rhaetian) fissure fills in Carboniferous Limestone in Somerset. Gephyrosaurus, other potential gephyrosaurids and Wirtembergia are the only rhynchocephalians to lie outside Sphenodontia in modern definitions of the group, and have been found to be more closely related to squamates in some phylogenetic analyses.
Reptiles arose about 320 million years ago during the Carboniferous period. Reptiles, in the traditional sense of the term, are defined as animals that have scales or scutes, lay land-based hard-shelled eggs, and possess ectothermic metabolisms. So defined, the group is paraphyletic, excluding endothermic animals like birds that are descended from early traditionally-defined reptiles. A definition in accordance with phylogenetic nomenclature, which rejects paraphyletic groups, includes birds while excluding mammals and their synapsid ancestors. So defined, Reptilia is identical to Sauropsida.

Vadasaurus is an extinct genus of rhynchocephalian closely related to the aquatic pleurosaurids. Although this genus was not as specialized as the eel-like pleurosaurs for aquatic life, various skeletal features support the idea that it had a semiaquatic lifestyle. The type species, Vadasaurus herzogi, was described and named in 2017. It was discovered in the Solnhofen Limestone in Germany, which is dated to the Late Jurassic. The generic name "Vadasaurus" is derived from "vadare", which is Latin for "to go" or "to walk forth", and "saurus", which means "lizard". "Vadare" is the root of the English word "wade", which is the reason it was chosen for this genus, in reference to its perceived semiaquatic habits. The specific name, "herzogi", refers to Werner Herzog, a Bavarian filmmaker.

Clevosaurs are an extinct group of rhynchocephalian reptiles from the Triassic and Jurassic periods.

Sapheosaurs are an extinct group of rhynchocephalian reptiles from the Late Jurassic period. "Sapheosaurs" is an informal name for a group of rhynchocephalians closely related to the genus Sapheosaurus. It was first recognized as a group containing multiple genera by Hoffstetter in 1955. The group has sometimes been given a formal taxonomic name as the family Sapheosauridae, although in some analyses this group belongs to the family Sphenodontidae and thus cannot be assigned its own family. They were fairly advanced rhynchocephalians which may have had semiaquatic habits.




















