In the course of the round ligament of liver, small veins (paraumbilical) are found which establish an anastomosis between the veins of the anterior abdominal wall and the hepatic portal, hypogastric, and iliac veins.

The round ligament of the liver is a degenerative string of tissue that exists in the free edge of the falciform ligament of the liver. The round ligament divides the left part of the liver into medial and lateral sections.

An anastomosis is a connection or opening between two things that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be normal or abnormal ; it may be acquired or innate ; and it may be natural or artificial. The reestablishment of an anastomosis that had become blocked is called a reanastomosis. Anastomoses that are abnormal, whether congenital or acquired, are often called fistulas.

The internal iliac vein begins near the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen, passes upward behind and slightly medial to the internal iliac artery and, at the brim of the pelvis, joins with the external iliac vein to form the common iliac vein.
The best marked of these small veins is one which commences at the umbilicus and runs backward and upward in, or on the surface of, the round ligament (ligamentum teres) between the layers of the falciform ligament to end in the left portal vein.
The navel is a protruding, flat, or hollowed area on the abdomen at the attachment site of the umbilical cord. All placental mammals including humans have a navel.
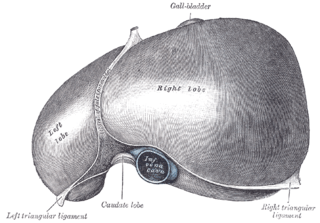
The falciform ligament is a ligament that attaches the liver to the anterior (ventral) body wall, and separates the liver into the left medial lobe and left lateral lobe. The falciform ligament, from Latin, meaning 'sickle-shaped', is a broad and thin fold of peritoneum, its base being directed downward and backward and its apex upward and backward. The falciform ligament droops down from the hilum of the liver.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

The portal vein or hepatic portal vein is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins.

The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. It enters the thigh from behind the inguinal ligament as the continuation of the external iliac artery.

The abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.

Caput medusae is the appearance of distended and engorged superficial epigastric veins, which are seen radiating from the umbilicus across the abdomen. The name caput medusae originates from the apparent similarity to Medusa's head, which had venomous snakes in place of hair. It is also a sign of portal hypertension. It is caused by dilation of the paraumbilical veins, which carry oxygenated blood from mother to fetus in utero and normally close within one week of birth, becoming re-canalised due to portal hypertension caused by liver failure.

In human anatomy, the hepatic veins are the veins that drain de-oxygenated blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava. There are usually three upper hepatic veins draining from the left, middle, and right parts of the liver. These are larger than the group of lower hepatic veins that can number from six to twenty. All of the hepatic veins drain into the inferior vena cava.

In human anatomy, inferior epigastric artery refers to the artery that arises from the external iliac artery and anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein, the inferior epigastric vein. These epigastric vessels form the lateral border of Hesselbach's triangle, which outlines the area through which direct inguinal hernias protrude.

In human anatomy, inferior epigastric vein refers to the vein that drains into the external iliac vein and anastomoses from the superior epigastric vein. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named artery, the inferior epigastric artery.
In human anatomy, the inguinal region refers to either the groin or the lower lateral regions of the abdomen. It may also refer to:

The deep inguinal ring is the entrance to the inguinal canal.

The lateral umbilical fold overlies the inferior epigastric artery and its accompanying veins. Unlike the median and medial umbilical folds, the contents of the lateral umbilical fold remain functional after birth. It originates just medial to the deep inguinal ring to the arcuate line on the posterior surface of the anterior abdominal wall.

The superficial epigastric artery arises from the front of the femoral artery about 1 cm below the inguinal ligament, and, passing through the femoral sheath and the fascia cribrosa, turns upward in front of the inguinal ligament, and ascends between the two layers of the superficial fascia of the abdominal wall nearly as far as the umbilicus.

The femoral sheath is formed by a prolongation downward, behind the inguinal ligament, of the abdominal fascia, the transverse fascia being continued down in front of the femoral vessels and the iliac fascia behind them. The femoral sheath is contained within the femoral triangle.
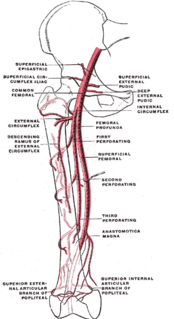
The superficial iliac circumflex artery, the smallest of the cutaneous branches of the femoral artery, arises close to the superficial epigastric artery, and, piercing the fascia lata, runs lateralward, parallel with the inguinal ligament, as far as the crest of the ilium.

The superficial external pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It arises from the medial side of the femoral artery, close to the superficial epigastric artery and superficial iliac circumflex artery.
The thoracoepigastric vein runs along the lateral aspect of the trunk between the superficial epigastric vein below and the lateral thoracic vein above and establishes an important communication between the femoral vein and axillary vein. This is an especially important vein when the inferior vena cava (IVC) becomes obstructed, by providing a means of collateral venous return. It creates a cavocaval anastomosis by connecting with superficial epigastric veins arising from femoral vein just below inguinal ligament.
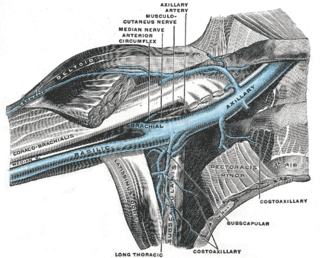
The lateral thoracic vein is a tributary of the axillary vein. It runs with the lateral thoracic artery and drains the Serratus anterior muscle and the Pectoralis major muscle.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The liver is grossly divided into two portions – a right and a left lobe, as viewed from the front (diaphragmatic) surface; but the underside shows it to be divided into four lobes and includes the caudate and quadrate lobes.



















