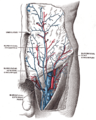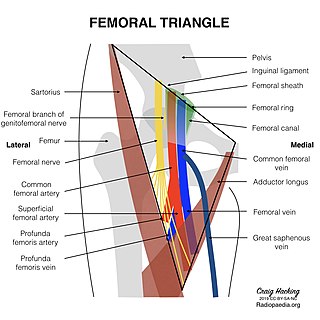
The femoral triangle is an anatomical region of the upper third of the thigh. It is a subfascial space which appears as a triangular depression below the inguinal ligament when the thigh is flexed, abducted and laterally rotated.
The great saphenous vein (GSV) or long saphenous vein is a large, subcutaneous, superficial vein of the leg. It is the longest vein in the body, running along the length of the lower limb, returning blood from the foot, leg and thigh to the deep femoral vein at the femoral triangle.
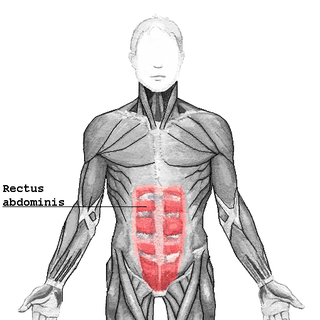
The rectus abdominis muscle, also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply the "abs", is a pair of segmented skeletal muscle on the ventral aspect of a person's abdomen. The paired muscle is separated at the midline by a band of dense connective tissue called the linea alba, and the connective tissue defining each lateral margin of the rectus abdominus is the linea semilunaris. The muscle extends from the pubic symphysis, pubic crest and pubic tubercle inferiorly, to the xiphoid process and costal cartilages of the 5th–7th ribs superiorly.

The gracilis muscle is the most superficial muscle on the medial side of the thigh. It is thin and flattened, broad above, narrow and tapering below.

In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath, then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath.

In human anatomy, inferior epigastric vein are 1-2 veins accompanying the inferior epigastric artery. They drain into the external iliac vein just proximal to the inguinal ligament.

In human anatomy, the superior epigastric veins are two or more venae comitantes which accompany either superior epigastric artery before emptying into the internal thoracic vein. They participate in the drainage of the superior surface of the diaphragm.

The conjoint tendon is a sheath of connective tissue formed from the lower part of the common aponeurosis of the abdominal internal oblique muscle and the transversus abdominis muscle, joining the muscle to the pelvis. It forms the medial part of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal.

The adductor canal is an aponeurotic tunnel in the middle third of the thigh giving passage to parts of the femoral artery, vein, and nerve. It extends from the apex of the femoral triangle to the adductor hiatus.

The lateral umbilical fold is an elevation of the peritoneum lining the inner/posterior surface of the lower anterior abdominal wall formed by the underlying inferior epigastric artery and inferior epigastric vein which the peritoneum covers. Superiorly, the lateral umbilical fold ends where the vessels reach and enter the rectus sheath at the arcuate line of rectus sheath; in spite of the name, the lateral umbilical folds do not extend as far superiorly as the umbilicus. Inferiorly, it extends to just medial to the deep inguinal ring.
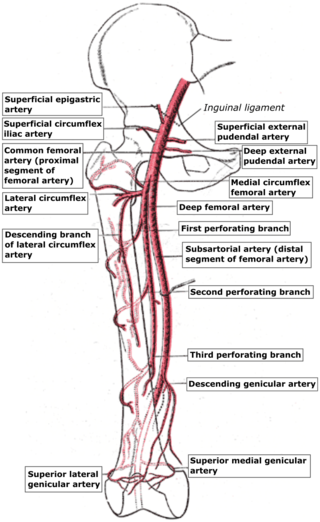
The superficial epigastric artery arises from the front of the femoral artery about 1 cm below the inguinal ligament, and, passing through the femoral sheath and the fascia cribrosa, turns upward in front of the inguinal ligament, and ascends between the two layers of the superficial fascia of the abdominal wall nearly as far as the umbilicus.

The submandibular triangle corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.

The carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The inferior carotid triangle, is bounded, in front, by the median line of the neck from the hyoid bone to the sternum; behind, by the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid; above, by the superior belly of the omohyoid.

The arcuate line of rectus sheath is a line of demarcation corresponding to the free inferior margin of the posterior layer of the rectus sheath inferior to which only the anterior layer of the rectus sheath is present and the rectus abdominis muscle is therefore in direct contact with the transversalis fascia. The arcuate line is concave inferior-wards.

The deep circumflex iliac artery is an artery in the pelvis that travels along the iliac crest of the pelvic bone.
The superficial iliac circumflex artery, the smallest of the cutaneous branches of the femoral artery, arises close to the superficial epigastric artery, and, piercing the fascia lata, runs lateralward, parallel with the inguinal ligament, as far as the crest of the ilium.

The superficial external pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It arises from the medial side of the femoral artery, close to the superficial epigastric artery and superficial iliac circumflex artery.
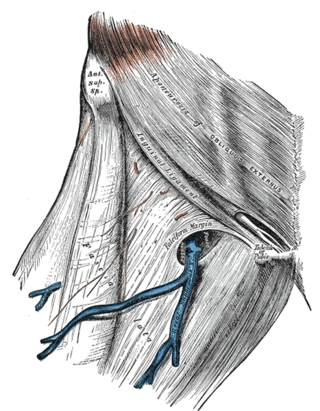
In anatomy, the saphenous opening is an oval opening in the upper mid part of the fascia lata of the thigh. It lies 3–4 cm below and lateral to the pubic tubercle and is about 3 cm long and 1.5 cm wide.
The cutaneous branch of the obturator nerve is an occasional continuation of the communicating branch to the femoral medial cutaneous branches and saphenous branches of the femoral to the thigh and leg. When present it emerges from beneath the distal/inferior border of the adductor longus muscle and descends along the posterior margin of the sartorius muscle to the medial side of the knee where it pierces the deep fascia and communicates with the saphenous nerve. When present, it provides sensory innervation to the skin of proximal/superior half of the medial side of the leg.