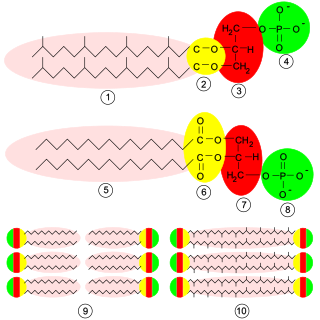
Glycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes in eukaryotic cells. They are a type of lipid, of which its composition affects membrane structure and properties. Two major classes are known: those for bacteria and eukaryotes and a separate family for archaea.

Glycerophospholipids of biochemical relevance are divided into three subclasses based on the substitution present at the sn-1 position of the glycerol backbone: acyl, alkyl and alkenyl. Of these, the alkyl and alkenyl moiety in each case form an ether bond, which makes for two types of ether phospholipids, plasmanyl, and plasmenyl. Plasmalogens are plasmenyls with an ester linked lipid at the sn-2 position of the glycerol backbone, chemically designated 1-0(1Z-alkenyl)-2-acyl-glycerophospholipids. The lipid attached to the vinyl ether at sn-1 can be C16:0, C18:0, or C18:1, and the lipid attached to the acyl group at sn-2 can be C22:6 ω-3 or C20:4 ω-6, . Plasmalogens are classified according to their head group, mainly as PC plasmalogens (plasmenylcholines) and PE plasmalogens (plasmenylethalomines) Plasmalogens should not be confused with plasmanyls.

In an organic chemistry general sense, an ether lipid implies an ether bridge between an alkyl group and an unspecified alkyl or aryl group, not necessarily glycerol. If glycerol is involved, the compound is called a glyceryl ether, which may take the form of an alkylglycerol, an alkyl acyl glycerol, or in combination with a phosphatide group, a phospholipid.
In enzymology, a hexadecanol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.164) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phosphatidylcholine desaturase (EC 1.14.19.22, previously EC 1.3.1.35) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] desaturase (EC 1.14.19.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Alkylglycerol monooxygenase (AGMO) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydroxylation of alkylglycerols, a specific subclass of ether lipids. This enzyme was first described in 1964 as a pteridine-dependent ether lipid cleaving enzyme. In 2010 finally, the gene coding for alkylglycerol monooxygenase was discovered as transmembrane protein 195 (TMEM195) on chromosome 7. In analogy to the enzymes phenylalanine hydroxylase, tyrosine hydroxylase, tryptophan hydroxylase and nitric oxide synthase, alkylglycerol monooxygenase critically depends on the cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin and iron.
In enzymology, a linoleoyl-CoA desaturase (also Delta 6 desaturase, EC 1.14.19.3) is an enzyme that converts between types of fatty acids, which are essential nutrients in the human body. The enzyme mainly catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phosphatidylcholine 12-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.26) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alkenylglycerophosphocholine hydrolase (EC 3.3.2.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alkenylglycerophosphoethanolamine hydrolase (EC 3.3.2.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase (EC 3.1.1.47) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme alkylglycerophosphoethanolamine phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.39) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1-alkylglycerophosphocholine O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1-alkylglycerophosphocholine O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycerophospholipid acyltransferase (CoA-dependent) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In the field of enzymology, a glycerophospholipid arachidonoyl-transferase (CoA-independent) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a plasmalogen synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a platelet-activating factor acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction




