
Mercury is the first planet from the Sun and the smallest in the Solar System. In English, it is named after the ancient Roman god Mercurius (Mercury), god of commerce and communication, and the messenger of the gods. Mercury is classified as a terrestrial planet, with roughly the same surface gravity as Mars. The surface of Mercury is heavily cratered, as a result of countless impact events that have accumulated over billions of years. Its largest crater, Caloris Planitia, has a diameter of 1,550 km (960 mi) and one-third the diameter of the planet. Similarly to the Earth's Moon, Mercury's surface displays an expansive rupes system generated from thrust faults and bright ray systems formed by impact event remnants.

Caloris Planitia is a plain within a large impact basin on Mercury, informally named Caloris, about 1,550 km (960 mi) in diameter. It is one of the largest impact basins in the Solar System. "Calor" is Latin for "heat" and the basin is so-named because the Sun is almost directly overhead every second time Mercury passes perihelion. The crater, discovered in 1974, is surrounded by the Caloris Montes, a ring of mountains approximately 2 km (1.2 mi) tall.

Yeats is an impact crater on the planet Mercury. The crater is named after William Butler Yeats, an Irish poet and dramatist. The name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1976.

Sinan is an impact crater on the planet Mercury, 134 kilometers in diameter. It is located northeast of the crater Yeats and southeast of the crater Li Po. It has one craterlet on the south-southwestern side of the crater floor, and it has a symmetrical pit slightly west of the center. Together with a smaller unnamed crater on its southern border, the crater Sinan forms a shape similar to that of the spade found in card games. The crater is named after Mimar Sinan, a 16th-century Turkish architect. The name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1976.
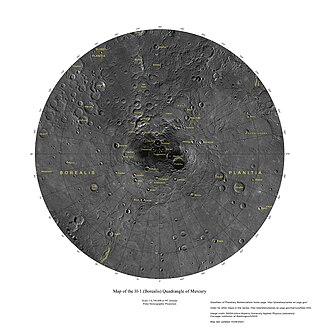
The Borealis quadrangle is a quadrangle on Mercury surrounding the north pole down to 65° latitude. It was mapped in its entirety by the MESSENGER spacecraft, which orbited the planet from 2008 to 2015, excluding areas of permanent shadow near the north pole. Only approximately 25% of the quadrangle was imaged by the Mariner 10 spacecraft during its flybys in 1974 and 1975. The quadrangle is now called H-1.

The Tolstoj quadrangle in the equatorial region of Mercury runs from 144 to 216° longitude and -25 to 25° latitude. It was provisionally called "Tir", but renamed after Leo Tolstoy by the International Astronomical Union in 1976. Also called Phaethontias.

The Shakespeare quadrangle is a region of Mercury running from 90 to 180° longitude and 20 to 70° latitude. It is also called Caduceata.

The Kuiper quadrangle, located in a heavily cratered region of Mercury, includes the young, 55-km-diameter crater Kuiper, which has the highest albedo recorded on the planet, and the small crater Hun Kal, which is the principal reference point for Mercurian longitude. Impact craters and basins, their numerous secondary craters, and heavily to lightly cratered plains are the characteristic landforms of the region. At least six multiringed basins ranging from 150 km to 440 km in diameter are present. Inasmuch as multiringed basins occur widely on that part of Mercury photographed by Mariner 10, as well as on the Moon and Mars, they offer a potentially valuable basis for comparison between these planetary bodies.

The Beethoven quadrangle is located in the equatorial region of Mercury, in the center of the area imaged by Mariner 10. Most pictures of the quadrangle were obtained at high sun angles as the Mariner 10 spacecraft receded from the planet. Geologic map units are described and classified on the basis of morphology, texture, and albedo, and they are assigned relative ages based on stratigraphic relations and on visual comparisons of the density of superposed craters. Crater ages are established by relative freshness of appearance, as indicated by topographic sharpness of their rim crests and degree of preservation of interior and exterior features such as crater floors, walls, and ejecta aprons. Generally, topography appears highly subdued because of the sun angle, and boundaries between map units are not clearly defined.

The Eminescu quadrangle (H-9) is one of fifteen quadrangles on Mercury. It runs from 216 to 288° longitude and from -25 to 25° latitude. Named after the Eminescu crater, it was mapped in detail for the first time after MESSENGER entered orbit around Mercury in 2011. It had not been mapped prior to that point because it was one of the six quadrangles that was not illuminated when Mariner 10 made its flybys in 1974 and 1975. These six quadrangles continued to be known by their albedo feature names, with this one known as the Solitudo Criophori quadrangle.

The Michelangelo quadrangle is in the southern hemisphere of the planet Mercury, where the imaged part is heavily cratered terrain that has been strongly influenced by the presence of multiring basins. At least four such basins, now nearly obliterated, have largely controlled the distribution of plains materials and structural trends in the map area. Many craters, interpreted to be of impact origin, display a spectrum of modification styles and degradation states. The interaction between basins, craters, and plains in this quadrangle provides important clues to geologic processes that have formed the morphology of the mercurian surface.

Sholem Aleichem is a crater on Mercury, named after the Yiddish writer Sholem Aleichem. The inter-crater plain deposits have been deformed by linear ridges.

Vyāsa is a crater on Mercury. It was named by the IAU in 1979, after the Indian poet Vyasa. It is Tolstojan in age.

Li Po is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 120 kilometers. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1976. Li Po is named for the Chinese poet Li Bai, who lived from 701 to 762.
Ghost craters on the planet Mercury have tectonic features such as graben and wrinkle ridges. These features were formed by extensional and contractional forces originating in tectonic processes such as uplift and global contraction. The combination of graben and wrinkle ridges inside ghost craters found on Mercury has not been observed on any of the other terrestrial planets.

Inter-crater plains on Mercury are a land-form consisting of plains between craters on Mercury.

Sōtatsu is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the IAU in 1976, after the Japanese artist Tawaraya Sōtatsu. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Tintoretto is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the IAU in 1976, after the Italian painter Tintoretto. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Rilke is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1976. Rilke is named for the German poet Rainer Maria Rilke.


















