Project management is the process of supervising the work of a team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time and budget. The secondary challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet predefined objectives.
New product development (NPD) or product development in business and engineering covers the complete process of launching a new product to the market. Product development also includes the renewal of an existing product and introducing a product into a new market. A central aspect of NPD is product design. New product development is the realization of a market opportunity by making a product available for purchase. The products developed by an commercial organisation provide the means to generate income.

A project manager is a professional in the field of project management. Project managers have the responsibility of the planning, procurement and execution of a project, in any undertaking that has a defined scope, defined start and a defined finish; regardless of industry. Project managers are first point of contact for any issues or discrepancies arising from within the heads of various departments in an organization before the problem escalates to higher authorities, as project representative.
A modeling language is any artificial language that can be used to express data, information or knowledge or systems in a structure that is defined by a consistent set of rules. The rules are used for interpretation of the meaning of components in the structure of a programming language.

In industry, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering, design and manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM integrates people, data, processes, and business systems and provides a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprises.
ISO/IEC/IEEE 12207Systems and software engineering – Software life cycle processes is an international standard for software lifecycle processes. First introduced in 1995, it aims to be a primary standard that defines all the processes required for developing and maintaining software systems, including the outcomes and/or activities of each process.

Business process modeling (BPM) is the action of capturing and representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current business processes may be analyzed, applied securely and consistently, improved, and automated.
Concurrent engineering (CE) or concurrent design and manufacturing is a work methodology emphasizing the parallelization of tasks, which is sometimes called simultaneous engineering or integrated product development (IPD) using an integrated product team approach. It refers to an approach used in product development in which functions of design engineering, manufacturing engineering, and other functions are integrated to reduce the time required to bring a new product to market.

The term process model is used in various contexts. For example, in business process modeling the enterprise process model is often referred to as the business process model.

Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) is the manufacturing approach of using computers to control the entire production process. This integration allows individual processes to exchange information with each part. Manufacturing can be faster and less error-prone by the integration of computers. Typically CIM relies on closed-loop control processes based on real-time input from sensors. It is also known as flexible design and manufacturing.

Operations management is concerned with designing and controlling the production of goods and services, ensuring that businesses are efficient in using resources to meet customer requirements.
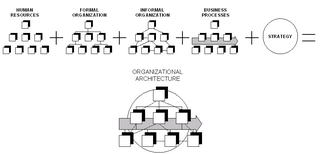
Organizational architecture, also known as organizational design, is a field concerned with the creation of roles, processes, and formal reporting relationships in an organization. It refers to architecture metaphorically, as a structure which fleshes out the organizations. The various features of a business's organizational architecture has to be internally consistent in strategy, architecture and competitive environment.
A software factory is a structured collection of related software assets that aids in producing computer software applications or software components according to specific, externally defined end-user requirements through an assembly process. A software factory applies manufacturing techniques and principles to software development to mimic the benefits of traditional manufacturing. Software factories are generally involved with outsourced software creation.

Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization.
Business process discovery (BPD) related to business process management and process mining is a set of techniques that manually or automatically construct a representation of an organisations' current business processes and their major process variations. These techniques use data recorded in the existing organisational methods of work, documentations, and technology systems that run business processes within an organisation. The type of data required for process discovery is called an event log. Any record of data that contains the case id, activity name, and timestamp. Such a record qualifies for an event log and can be used to discover the underlying process model. The event log can contain additional information related to the process, such as the resources executing the activity, the type or nature of the events, or any other relevant details. Process discovery aims to obtain a process model that describes the event log as closely as possible. The process model acts as a graphical representation of the process. The event logs used for discovery could contain noise, irregular information, and inconsistent/incorrect timestamps. Process discovery is challenging due to such noisy event logs and because the event log contains only a part of the actual process hidden behind the system. The discovery algorithms should solely depend on a small percentage of data provided by the event logs to develop the closest possible model to the actual behaviour.
A glossary of terms relating to project management and consulting.
Business process management (BPM) is the discipline in which people use various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, optimize, and automate business processes. Any combination of methods used to manage a company's business processes is BPM. Processes can be structured and repeatable or unstructured and variable. Though not required, enabling technologies are often used with BPM.
In software engineering, a software development process or software development life cycle (SDLC) is a process of planning and managing software development. It typically involves dividing software development work into smaller, parallel, or sequential steps or sub-processes to improve design and/or product management. The methodology may include the pre-definition of specific deliverables and artifacts that are created and completed by a project team to develop or maintain an application.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to project management:
Total productive maintenance (TPM) started as a method of physical asset management, focused on maintaining and improving manufacturing machinery in order to reduce the operating cost to an organization. After the PM award was created and awarded to Nippon Denso in 1971, the JIPM, expanded it to include 8 activities of TPM that required participation from all areas of manufacturing and non-manufacturing in the concepts of lean manufacturing. TPM is designed to disseminate the responsibility for maintenance and machine performance, improving employee engagement and teamwork within management, engineering, maintenance, and operations.






