Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 also known as ABL1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ABL1 gene located on chromosome 9. c-Abl is sometimes used to refer to the version of the gene found within the mammalian genome, while v-Abl refers to the viral gene, which was initially isolated from the Abelson murine leukemia virus.

Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2, also known as Grb2, is an adaptor protein involved in signal transduction/cell communication. In humans, the GRB2 protein is encoded by the GRB2 gene.

Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11 (PTPN11) also known as protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1D (PTP-1D), Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-2 (SHP-2), or protein-tyrosine phosphatase 2C (PTP-2C) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN11 gene. PTPN11 is a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) Shp2.

Adapter molecule crk also known as proto-oncogene c-Crk is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRK gene.

Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK also known as interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase or simply ITK, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITK gene. ITK is a member of the TEC family of kinases and is highly expressed in T cells.

Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FYN gene.

Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3R1 gene.
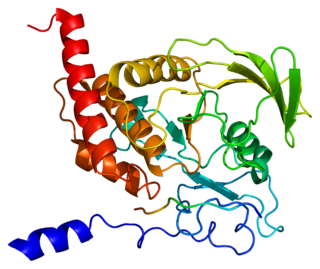
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 6, also known as Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-1 (SHP-1), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN6 gene.

Cbl is a mammalian gene family. CBL gene, a part of the Cbl family, encodes the protein CBL which is an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase involved in cell signalling and protein ubiquitination. Mutations to this gene have been implicated in a number of human cancers, particularly acute myeloid leukaemia.

Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HCK gene.

KH domain-containing, RNA-binding, signal transduction-associated protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KHDRBS1 gene.

Docking protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DOK1 gene.

Protein tyrosine kinase 2 beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTK2B gene.
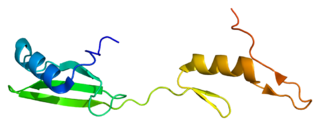
Cytoplasmic protein NCK1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCK1 gene.

Rho GTPase-activating protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ARHGAP1 gene.

Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPRA gene.
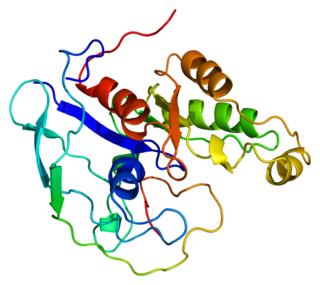
Activated CDC42 kinase 1, also known as ACK1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TNK2 gene. TNK2 gene encodes a non-receptor tyrosine kinase, ACK1, that binds to multiple receptor tyrosine kinases e.g. EGFR, MERTK, AXL, HER2 and insulin receptor (IR). ACK1 also interacts with Cdc42Hs in its GTP-bound form and inhibits both the intrinsic and GTPase-activating protein (GAP)-stimulated GTPase activity of Cdc42Hs. This binding is mediated by a unique sequence of 47 amino acids C-terminal to an SH3 domain. The protein may be involved in a regulatory mechanism that sustains the GTP-bound active form of Cdc42Hs and which is directly linked to a tyrosine phosphorylation signal transduction pathway. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified from this gene, but the full-length nature of only two transcript variants has been determined.

Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MATK gene.

Ras GTPase-activating protein 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RASA3 gene.
A non-receptor tyrosine kinase (nRTK) is a cytosolic enzyme that is responsible for catalysing the transfer of a phosphate group from a nucleoside triphosphate donor, such as ATP, to tyrosine residues in proteins. Non-receptor tyrosine kinases are a subgroup of protein family tyrosine kinases, enzymes that can transfer the phosphate group from ATP to a tyrosine residue of a protein (phosphorylation). These enzymes regulate many cellular functions by switching on or switching off other enzymes in a cell.