
The king cobra is a venomous snake endemic to Asia. The sole member of the genus Ophiophagus, it is not taxonomically a true cobra, despite its common name and some resemblance. With an average length of 3.18 to 4 m and a record length of 5.85 m (19.2 ft), it is the world's longest venomous snake. The species has diversified colouration across habitats, from black with white stripes to unbroken brownish grey. The king cobra is widely distributed albeit not commonly seen, with a range spanning from the Indian Subcontinent through Southeastern Asia to Southern China. It preys chiefly on other snakes, including those of its own kind. This is the only ophidian that constructs an above-ground nest for its eggs, which are purposefully and meticulously gathered and protected by the female throughout the incubation period.

Bungarus is a genus of elapids native to Asia. Often found on the floor of tropical forests in South Asia, Southeast Asia and Southern China, they are medium-sized, highly venomous snakes with a length typically not exceeding 2 metres. These are nocturnal ophiophagious predators which prey primarily on other snakes at night, occasionally taking lizards, amphibians and rodents. Most species are with banded patterns acting as a warning sign to their predators. Despite being considered as generally docile and timid, kraits are capable of delivering highly potent neurotoxic venom which is medically significant with potential lethality to humans. The genus currently holds 16 species and 5 subspecies.

A snakebite is an injury caused by the bite of a snake, especially a venomous snake. A common sign of a bite from a venomous snake is the presence of two puncture wounds from the animal's fangs. Sometimes venom injection from the bite may occur. This may result in redness, swelling, and severe pain at the area, which may take up to an hour to appear. Vomiting, blurred vision, tingling of the limbs, and sweating may result. Most bites are on the hands, arms, or legs. Fear following a bite is common with symptoms of a racing heart and feeling faint. The venom may cause bleeding, kidney failure, a severe allergic reaction, tissue death around the bite, or breathing problems. Bites may result in the loss of a limb or other chronic problems or even death.

Snake venom is a highly toxic saliva containing zootoxins that facilitates in the immobilization and digestion of prey. This also provides defense against threats. Snake venom is injected by unique fangs during a bite, whereas some species are also able to spit venom.

The common krait, also known as Bengal krait, is a species of highly venomous snakes of the genus Bungarus in the Elapidae family native to the Indian subcontinent. It is one of the Big Four Indian snakes that inflict the most snakebites on humans in Pakistan, India and Bangladesh.

The banded krait is a species of elapids endemic to Asia, from Indian Subcontinent through Southeast Asia to Southern China. With a maximum length exceeding 2 m, it is the longest krait with a distinguishable gold and black pattern. While this species is generally considered timid and docile, resembling other members of the genus, its venom is highly neurotoxic which is potentially lethal to humans. Although toxicity of the banded krait based upon murine LD50 experiments is lower than that of many other kraits, its venom yield is the highest due to its size.

Rhabdophis subminiatus, commonly called the red-necked keelback or red-necked keelback snake, is a species of venomous snake in the subfamily Natricinae of the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to Asia.

The monocled cobra, also called monocellate cobra and Indian spitting cobra, is a venomous cobra species widespread across South and Southeast Asia and listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.

Microcephalophis gracilis, also known as the graceful small-headed seasnake, slender sea snake, narrow-headed sea snake, common small-headed sea snake, is a species of sea snake found in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is venomous.
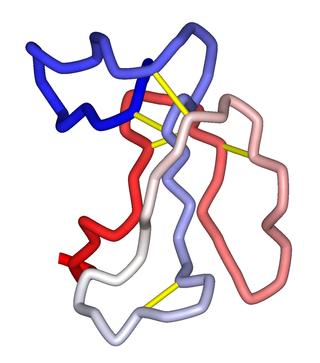
α-Bungarotoxin is one of the bungarotoxins, components of the venom of the elapid Taiwanese banded krait snake. It is a type of α-neurotoxin, a neurotoxic protein that is known to bind competitively and in a relatively irreversible manner to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor found at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis, respiratory failure, and death in the victim. It has also been shown to play an antagonistic role in the binding of the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in the brain, and as such has numerous applications in neuroscience research.
Flaccid paralysis is a neurological condition characterized by weakness or paralysis and reduced muscle tone without other obvious cause. This abnormal condition may be caused by disease or by trauma affecting the nerves associated with the involved muscles. For example, if the somatic nerves to a skeletal muscle are severed, then the muscle will exhibit flaccid paralysis. When muscles enter this state, they become limp and cannot contract. This condition can become fatal if it affects the respiratory muscles, posing the threat of suffocation. It also occurs in the spinal shock stage in complete transection of the spinal cord occurring in injuries such as gunshot wounds.

The many-banded krait, also known as the Taiwanese krait or the Chinese krait, is a highly venomous species of elapid snake found in much of central and southern China and Southeast Asia. The species was first described by the scientist Edward Blyth in 1861. Averaging 1 to 1.5 m in length, it is a black or bluish-black snake with many white bands across its body. The many-banded krait mostly inhabits marshy areas throughout its geographical distribution, though it does occur in other habitat types.
Bungarotoxins are toxins found in the venom of snakes and kraits. Bites from these animals can result in severe symptoms including bleeding or hemorrhage, paralysis and tissue damage that can result in amputation. The paralytic effects of venom are particularly dangerous as they can impair breathing. These symptoms are the result of bungarotoxin presence in the venom. In actuality, venom contains several distinct bungarotoxins, each varying in which receptors they act on and how powerful they are.

Calliophis bivirgatus is a species of snake in the family Elapidae known commonly as the blue coral snake or blue Malayan coral snake. It is native to Southeast Asia.

Trimeresurus sumatranus is a species of venomous pitviper found in the tropical forests of Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand. Arboreal by nature, its coloration is pale to neon-green, with some black vertical markings, and a red-tipped tail. As with other vipers, this species has prominent, “keeled” scales, which appear somewhat raised and give the snake a rough-textured appearance. Common names include Sumatran pitviper, Sumatran tree viper, and Sumatran pit viper.

Bungarus magnimaculatus, the Burmese krait, spotted krait or splendid krait, is a species of venomous snake of the genus Bungarus that is endemic to Myanmar.

κ-Bungarotoxin is a protein neurotoxin of the bungarotoxin family that is found in the venom of the many-banded krait, a snake found in Taiwan. κ-Bungarotoxin is a high affinity antagonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), particularly of CHRNA3; it causes a post-synaptic blockade of neurotransmission. Although there is significant variability in the clinical effects of snake bites, neuromuscular paralysis and respiratory failure are associated with krait bites.

Micrurus frontalis, also known as the southern coral snake or short-tailed coral snake, is a species of highly venomous coral snake in the family Elapidae. It is found in South America.

Snakebite envenomation is considered a public health problem in Latin America, with an estimated 70,000 cases annually, but due to underreporting, these numbers may be even higher.



















