The regions of Victoria vary according to the different ways that the Australian state of Victoria is divided into distinct geographic regions. The most commonly used regions are those created by the state government for the purposes of economic development.
Others regions include those made for land management, such as agriculture or conservation, and for the gathering of information, such as statistical or meteorological. Although most regional systems were defined for specific purposes and given specific boundaries, many regions have similar names and extents according to the different regionalisations. As a result, the names and boundaries of regions can vary and overlap even in popular usage.
In addition to Greater Melbourne, the Victoria State Government has divided Victoria into five regions covering all parts of the state. The five regions are: [1]
The Barwon South West region stretches from the tip of the Queenscliff Heads to the border of South Australia. It is home to Victoria’s largest provincial centre, Geelong. The region includes the local government areas of Colac Otway, Corangamite, Glenelg, Greater Geelong, Moyne, Queenscliffe, Southern Grampians, Surf Coast and Warrnambool City. [2]
The Gippsland region stretches from the eastern outskirts of Melbourne to the southeastern tip of Victoria and north to the Black-Allan Line denoting the border with New South Wales. Its western boundary is defined by the Great Dividing Range and the Tasman Sea forms its eastern boundary. The region includes the local government areas of Bass Coast, Baw Baw, East Gippsland, Latrobe City, South Gippsland and Wellington. [3]
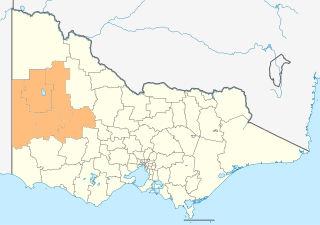
The Grampians region stretches from the western edge of Melbourne to the South Australian border and includes the Grampians National Park and significant gold mining heritage assets. The region includes the local government areas of Ararat City, Ballarat City, Golden Plains, Hepburn, Hindmarsh, Horsham City, Moorabool, Northern Grampians, Pyrenees, West Wimmera and Yarriambiack. The Grampians region has two sub-regions, Grampians Central Highlands and Wimmera Southern Mallee. [4]
The Hume region stretches south from the Murray River with its eastern boundary defined by the Great Dividing Range and the Victorian Alps, its southern boundary defined by Greater Melbourne and its western boundary characterised by the Goulburn and Broken river catchments and food bowl. The region includes the local government areas of Alpine, Benalla City, Indigo, Mansfield, Mitchell, Moira, Murrindindi, Greater Shepparton, Strathbogie, Towong, Wangaratta City, and Wodonga City. [5]
The Loddon Mallee region occupies more than a quarter of Victoria and stretches from Greater Melbourne to the northwest corner of the state that marks the boundaries with South Australia and New South Wales. The region includes the local government areas of Greater Bendigo City, Buloke, Campaspe, Central Goldfields, Gannawarra, Loddon, Macedon Ranges, Mildura City, Mount Alexander, and Swan Hill City. [6]
The approximately 80 local government areas of Victoria are grouped into 17 regions also known by the ABS as "statistical areas level 4". [7] The non-Melbourne areas are: North West, Warrnambool and South West, Bendigo, Ballarat, Geelong, Shepparton, Hume, Latrobe - Gippsland, Mornington Peninsula. Melbourne is divided into: Melbourne - Inner, Melbourne - Inner East, Melbourne - Inner South, Melbourne - North East, Melbourne - North West, Melbourne - Outer East, Melbourne - South East, Melbourne - West.
There are 8 electoral regions, which are used to form the Victorian Legislative Council. They are:
The Australian Bureau of Meteorology defines regions for its own purposes, some of which share names with the economic regions, even though the exact boundaries may not correlate. [8] As of November 2014, they are: Mallee, Wimmera, Northern Country, North East, East Gippsland, West & South Gippsland, Central, North Central, South West, Alpine and Melbourne.
Viticulture has a long history since colonisation of Victoria. Wine production is concentrated around the Central Highlands and its associated tablelands and includes the Grampians wine region, the Pyrenees, the Yarra Valley, and the Ovens and Murray region. In the state's north-west, the Murray Darling and Swan Hill regions also produce wine.
The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia places parts of Victoria in the following bioregions, some of which are wholly contained with the state, and others that cover two or more states and territories. [9]
The Country Fire Authority (CFA) divides Victoria into nine fire districts. From west to east, and north to south: Mallee, Wimmera, South West, Northern Country, North Central, Central, North East, East Gippsland, West & South Gippsland. [10]
A number of other regional terms are used to define certain areas, although their exact boundaries are unclear. For example:
Technical and further education or simply TAFE, is the common name in English-speaking countries in Oceania for vocational education, as a subset of tertiary education. TAFE institutions provide a wide range of predominantly vocational courses.

The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills, that runs roughly parallel to the east coast of Australia and forms the fifth-longest land-based mountain chain in the world, and the longest entirely within a single country. It is mainland Australia's most substantial topographic feature and serves as the definitive watershed for the river systems in eastern Australia, hence the name.
The Victorian government's Wimmera Southern Mallee subregion is part of the Grampians region in western Victoria. It includes most of what is considered the Wimmera, and part of the southern Mallee region. The subregion is based on the social catchment of Horsham, its main settlement.

The Loddon River, an inland river of the north–central catchment, part of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the lower Riverina bioregion and Central Highlands and Loddon Mallee regions of the Australian state of Victoria. The headwaters of the Loddon River rise on the northern slopes of the Great Dividing Range east of Daylesford and descend to flow north into the Little Murray River, near Swan Hill. The river is impounded by the Cairn Curran and Laanecoorie reservoirs. The Tullaroop Creek tributary, which joins just above Laanecoorie Reservoir, is impounded by the Tullaroop Reservoir (72,950ML).

North Central Victoria is a rural region in the Australian state of Victoria. The region lies to the south of the Victorian/New South Wales border as defined by the Murray River, to the southwest of the Hume region, to the west of the Great Dividing Range contained within the Central Highlands and Victorian Alps, to the north of Greater Melbourne, to the northeast of the Wimmera, and to the east of the Mallee region.

The Mallee is a sub-region of Loddon Mallee covering the most north-westerly part of Victoria, Australia and is bounded by the South Australian and New South Wales borders. Definitions of the south-eastern boundary vary, however, all are based on the historic Victorian distribution of mallee eucalypts. These trees dominate the surviving vegetation through most of Mallee,. Its biggest settlements are Mildura and Swan Hill.

Victoria is a state in southeastern Australia. It is the second-smallest state, with a land area of 227,444 km2 (87,817 sq mi); the second-most-populated state, with a population of over 6.6 million; and the most densely populated state in Australia. Victoria is bordered by New South Wales to the north and South Australia to the west, and is bounded by the Bass Strait to the south, the Great Australian Bight portion of the Southern Ocean to the southwest, and the Tasman Sea to the southeast. The state encompasses a range of climates and geographical features from its temperate coastal and central regions to the Victorian Alps in the northeast and the semi-arid north-west.

The Wimmera River, an inland intermittent river of the Wimmera catchment, is located in the Grampians and Wimmera regions of the Australian state of Victoria. Rising in the Pyrenees, on the northern slopes of the Great Dividing Range, the Wimmera River flows generally north by west and drains into Lake Hindmarsh and Lake Albacutya, a series of ephemeral lakes that, whilst they do not directly empty into a defined watercourse, form part of the Murray River catchment of the Murray-Darling basin.
In the state of New South Wales, Australia, there are many areas which are commonly known by regional names. Regions are areas that share similar characteristics. These characteristics may be natural such as the Murray River, the coastline, or the Snowy Mountains. Alternatively, the characteristics may be cultural, such as a viticulture land use. New South Wales is divided by numerous regional boundaries, based on different characteristics. In many cases boundaries defined by different agencies are coterminous.
The Catchment Management Authorities (CMAs) were established in Victoria under the Catchment and Land Protection Act 1994. Originally known as Catchment and Land Protection Boards, the CMAs were changed to their present name in 1997.

Victoria is the southernmost mainland state of Australia. With an area of 227,594 km2 (87,875 sq mi), it is Australia's sixth largest state/territory, comparable in size to the island of Great Britain or the U.S. state of Utah. It is bound to the northwest by South Australia, directly north by New South Wales, and also shares a maritime border with Tasmania across the Bass Strait to the south. Most of Victoria's northern border lies along the Murray River. The eastern half of the state is dominated by the Australian Alps and the surrounding highlands of the Great Dividing Range, which also to a lesser extent extend far into the west of the state and ease off after The Grampians. By comparison the north and northwest of the state is extremely flat with little prominence.

Members of the Victorian Legislative Council, the upper house of the Parliament of the Australian State of Victoria, are elected from eight multi-member electorates called regions. The Legislative Council has 40 members, five from each of the eight regions.
Bowls Victoria, established in 1880 is the governing body for the sport of bowls in the State of Victoria. In addition to its specific responsibility for governing the sport and the development of the game at all levels, it also has a social objective to enhance existing bowling communities and to position bowls clubs and the sport in the wider community.

The Hume is an economic rural region located in the north-eastern part of Victoria, Australia. Comprising an area in excess of 40,000 square kilometres (15,000 sq mi) with a population that ranges from 263,000 to 300,000, the Hume region includes the local government areas of Alpine Shire, Rural City of Benalla, City of Wodonga, City of Greater Shepparton, Shire of Indigo, Shire of Mansfield, Shire of Strathbogie, Shire of Towong and the Rural City of Wangaratta, and also includes five unincorporated areas encompassing the alpine ski resorts in the region.

The Grampians is an economic rural region located in the western part of Victoria, Australia. The 48,646-square-kilometre (18,782 sq mi) region lies to the northwest of the western suburbs of Greater Melbourne, to the state's western border with South Australia and includes the Grampians National Park and significant gold mining heritage assets. The Grampians region has two sub-regions, Grampians Central Highlands and Wimmera Southern Mallee.
In South Australia, one of the states of Australia, there are many areas which are commonly known by regional names. Regions are areas that share similar characteristics. These characteristics may be natural such as the Murray River, the coastline, desert or mountains. Alternatively, the characteristics may be cultural, such as common land use. South Australia is divided by numerous sets of regional boundaries, based on different characteristics. In many cases boundaries defined by different agencies are coterminous.
Water management in Victoria deals with the management of water resources in and by the Australian State of Victoria.

The Northern Plains Grassland (NPGL) is an open, shrubby temperate grassland community located in northern Victoria straddling the Murray Darling Depression and Wimmera, extending to the Riverina and South Western Slopes regions in southern New South Wales. Floristically rich, the area features 30 native plant species per 100 m2.