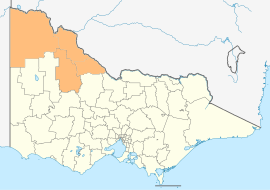
The Rural City of Mildura is a local government area in Victoria, Australia, located in the north-western part of the state. It covers an area of 22,083 square kilometres (8,526 sq mi) being the largest LGA in the state. In August 2021 the area had a population of 56,972. It includes the city of Mildura and the towns of Merbein, Red Cliffs, Irymple, Ouyen, Werrimull, Murrayville, Walpeup and Hattah. It was formed in 1995 from the amalgamation of the City of Mildura, Shire of Mildura and Shire of Walpeup.

The Rural City of Swan Hill is a local government area in Victoria, Australia, located in the north-western part of the state. It covers an area of 6,115 square kilometres (2,361 sq mi) and, in August 2021, had a population of 21,403. It includes the towns of Swan Hill, Lake Boga, Manangatang, Nyah, Nyah West, Piangil, Robinvale, Ultima and Woorinen South. It was formed in 1995 from the amalgamation of the City of Swan Hill, Shire of Swan Hill and part of the Shire of Kerang.

The Shire of Yarriambiack is a local government area of Victoria, Australia, located in the north-western part of the state. It covers an area of 7,326 square kilometres (2,829 sq mi) and, in June 2018, had a population of 6,658, having fallen from 7,438 in 2008. It includes the towns of Hopetoun, Murtoa, Rupanyup and Warracknabeal. It was formed in 1995 from the amalgamation of the Shire of Warracknabeal, Shire of Karkarooc, and parts of the Shire of Dunmunkle and Shire of Wimmera.

Mildura is a regional city in north-west Victoria, Australia. Located on the Victorian side of the Murray River, Mildura had a population of 34,565 in 2021. When nearby Wentworth, Irymple, Nichols Point, Merbein and Red Cliffs are included, the combined urban area had a population of 58,914 in 2021, having grown marginally at an average annual rate of 1.3% year-on-year over the preceding five years.
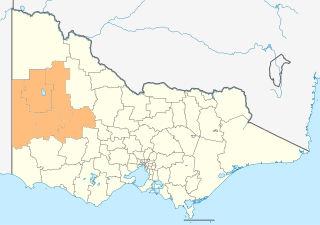
The Victorian government's Wimmera Southern Mallee subregion is part of the Grampians region in western Victoria. It includes most of what is considered the Wimmera, and part of the southern Mallee region. The subregion is based on the social catchment of Horsham, its main settlement.

Sunraysia is a region located in northwestern Victoria and southwestern New South Wales in Australia. The region is renowned for its sunshine, intensive horticulture including grapes and oranges. Its main centre is Mildura, Victoria.

Robinvale is a town on the south bank of the Murray River in north western Victoria, Australia. It is connected by a bridge to Euston on the other side of the river in New South Wales. At the 2021 census, Robinvale had a population of 3,740, however a population study conducted by the Rural City of Swan Hill that was undertaken in 2019 identified Robinvale had an estimated population of between 7,000 in November and 8,800 in March each year.

The Loddon River, an inland river of the north–central catchment, part of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the lower Riverina bioregion and Central Highlands and Loddon Mallee regions of the Australian state of Victoria. The headwaters of the Loddon River rise on the northern slopes of the Great Dividing Range east of Daylesford and descend to flow north into the Little Murray River, near Swan Hill. The river is impounded by the Cairn Curran and Laanecoorie reservoirs.

North Central Victoria is a rural region in the Australian state of Victoria. The region lies to the south of the Victorian/New South Wales border as defined by the Murray River, to the southwest of the Hume region, to the west of the Great Dividing Range contained within the Central Highlands and Victorian Alps, to the north of Greater Melbourne, to the northeast of the Wimmera, and to the east of the Mallee region.

Swan Hill is a city in the northwest of Victoria, Australia on the Murray Valley Highway and on the south bank of the Murray River, downstream from the junction of the Loddon River. At 2021 census, Swan Hill had a population of 11,508.
Woorinen South is a town in Victoria, Australia. It is situated within the Rural City of Swan Hill within the Mallee region of north-west Victoria. At the 2011 census, Woorinen South had a population of 311. The town is located 350 kilometres (217 mi) north-west of Melbourne and 10 kilometres (6 mi) km north-west of the regional centre Swan Hill. The town contains a number of small businesses and is in the centre of a prosperous and diverse agricultural area which produces wine, stone fruit, vegetables, wool, and cereal crops. The town hosts the annual Vintage Steam Rally.
The Electoral district of Swan Hill was a rural Lower House electoral district of the Victorian Parliament. It was located within the Northern Victoria Region of the Legislative Council.

The Shire of Kerang was a local government area located in northwestern Victoria, Australia, along the Murray River. The shire covered an area of 3,254.45 square kilometres (1,256.6 sq mi), and existed from 1862 until 1995. From 1966 onwards, Kerang itself was managed by a separate entity; the Borough of Kerang.

The Shire of Swan Hill was a local government area in north-western Victoria, Australia, along the Murray River. The shire covered an area of 6,550 square kilometres (2,529.0 sq mi), and existed from 1893 until 1995. From 1939 onwards, Swan Hill itself was managed by a separate entity; the City of Swan Hill. After a large-scale statewide amalgamation program by the Victorian Government in 1994–1995, they were reunited under the Rural City of Swan Hill.

Victoria is the southernmost mainland state of Australia. With an area of 227,444 km2 (87,817 sq mi), it is Australia's sixth largest state/territory, comparable in size to the island of Great Britain or the U.S. state of Utah. It is bound to the northwest by South Australia, directly north by New South Wales, and also shares a maritime border with Tasmania across the Bass Strait to the south. Most of Victoria's northern border lies along the Murray River. The eastern half of the state is dominated by the Australian Alps and the surrounding highlands of the Great Dividing Range, which also to a lesser extent extend far into the west of the state and ease off after The Grampians. By comparison the north and northwest of the state is extremely flat with little prominence.
The regions of Victoria vary according to the different ways that the Australian state of Victoria is divided into distinct geographic regions. The most commonly used regions are those created by the state government for the purposes of economic development.

The Grampians is an economic rural region located in the western part of Victoria, Australia. The 48,646-square-kilometre (18,782 sq mi) region lies to the northwest of the western suburbs of Greater Melbourne, to the state's western border with South Australia and includes the Grampians National Park and significant gold mining heritage assets. The Grampians region has two sub-regions: the Central Highlands and Wimmera Southern Mallee.
In South Australia, one of the states of Australia, there are many areas which are commonly known by regional names. Regions are areas that share similar characteristics. These characteristics may be natural such as the Murray River, the coastline, desert or mountains. Alternatively, the characteristics may be cultural, such as common land use. South Australia is divided by numerous sets of regional boundaries, based on different characteristics. In many cases boundaries defined by different agencies are coterminous.
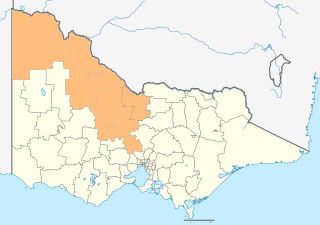
The Loddon Mallee is an economic rural region located in the north-western part of Victoria, Australia. Occupying more than a quarter of the state, it stretches from Greater Melbourne to the northernmost point of Victoria, sharing a border with South Australia and New South Wales, and has one of the most consistently warm climates in Victoria. It has two major regional cities Bendigo and Mildura and also contains the major settlements of Castlemaine, Echuca, Gisborne, Kerang, Kyneton, Maryborough, Swan Hill, Wedderburn and Wycheproof.