
Dartmouth Dam is a large rock-fill embankment dam with an uncontrolled chute spillway across the Mitta Mitta, Gibbo, and Dart rivers, the Morass Creek and a number of small tributaries. The dam is located near Mount Bogong in the north-east of the Australian state of Victoria. The dam's purpose includes irrigation, the generation of hydro-electric power, water supply and conservation. The impounded reservoir is called Dartmouth Reservoir, sometimes called Lake Dartmouth. The Dartmouth Power Station, a hydro-electric power station that generates power to the national grid, is located near the dam wall.

Mitta Mitta River, a perennial river and a direct tributary of the Murray River within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Alpine district of Victoria, Australia.

Murray Valley Highway is a 663-kilometre (412 mi) state highway located in Victoria and New South Wales, Australia. The popular tourist route mostly follows the southern bank of the Murray River and effectively acts as the northernmost highway in Victoria. For all but the western end's last three kilometres, the highway is allocated route B400.

Omeo is a town in Victoria, Australia on the Great Alpine Road, east of Mount Hotham, in the Shire of East Gippsland. At the 2016 census, Omeo had a population of 406. The name is derived from an Aboriginal word for 'mountains' or 'hills'. Omeo is affectionately known as the City of the Alps with many historic buildings remaining in the town. The town is still the commercial hub for the Omeo Region and is a service centre for outlying communities such as Benambra, Cobungra, Cassilis, Swifts Creek, and Ensay.

The electoral district of Benambra is one of the electoral districts of Victoria, Australia, for the Victorian Legislative Assembly. It covers an area of 10,037 square kilometres (3,875 sq mi) in north-eastern Victoria. The largest settlement is the city of Wodonga. Benambra also includes the towns of Baranduda, Barnawartha, Beechworth, Chiltern, Corryong, Eskdale, Kiewa, Mitta Mitta, Mount Beauty, Rutherglen, Tallangatta, Tangambalanga, Tawonga, Wahgunyah, and Yackandandah. It lies in the Northern Victoria Region of the upper house, the Legislative Council.

Benambra is a small town 28 kilometres (17 mi) north-east of Omeo and 430 kilometres (267 mi) east of the state capital Melbourne, in the Australian Alps of East Gippsland, Victoria, Australia. Nearby towns include Swifts Creek, Ensay, and the major town of Bairnsdale. At the 2016 census, Benambra and the surrounding area had a population of 149.

The Tambo River or Berrawan is a perennial river of the Mitchell River catchment, located in the East Gippsland region of the Australian state of Victoria. With a total length in excess of 186 kilometres (116 mi), the Tambo River is one of the longest rivers in the East Gippsland drainage basin, extending from the steep forested southern slopes of the Victorian Alps through forest and farmland to the Gippsland Lakes.

The Lerderderg River is a perennial river of the Port Phillip catchment, located in the Western District region of the Australian state of Victoria.
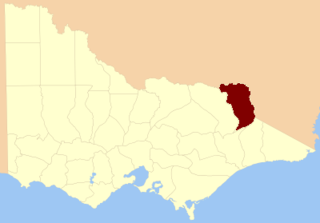
The County of Benambra is one of the 37 counties of Victoria which are part of the cadastral divisions of Australia, used for land titles. It is located between the Mitta Mitta River in the west, and the Murray River to the north and east. The town of Benambra is located near the southern edge. The area of the county roughly corresponds with the Electoral district of Benambra. Corryong is the largest town in the county. The county was proclaimed in 1871.

The Coliban River, an inland perennial river of the north–central catchment, part of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the lower Riverina bioregion and Central Highlands region of the Australian state of Victoria. The headwaters of the Coliban River rise on the northern slopes of the Great Dividing Range and descend to flow north into the Campaspe River with the impounded Lake Eppalock.
Lake Burrumbeet is a large but shallow eutrophic lake in central western Victoria, Australia. Located 20 kilometres (12 mi) west of Ballarat and 140 kilometres (87 mi) west of Melbourne, the lake has been progressively emptying since 1997 and was declared completely dry in 2004. It has however in recent years refilled because of good rainfalls, making water sports in the lake once again possible, with recreational jet skiing and boating taking place in the winter of 2010. The lake is a major wetland for the region because of its size and is utilised as a recreational area for boating, fishing and camping.
The Timbarra River is a perennial river of the Mitchell River catchment, located in the East Gippsland region of the Australian state of Victoria.

The Mount Emu Creek, a perennial creek of the Glenelg Hopkins catchment, is located in the Western District of Victoria, Australia.
The Jordan River, a perennial river of the West Gippsland catchment, is located in the Alpine region of the Australian state of Victoria.

The Bundara River, a perennial river of the North-East Murray catchment of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the East Gippsland and Alpine regions of Victoria, Australia.

Mount Gibbo is a mountain in the Australian Alps. It is 38 kilometres to the north-east of Benambra in Victoria, Australia and lies within the Mount Gibbo Natural Features and Scenic Reserve managed by Parks Victoria. The reserve, which covers 1493.1 hectares, was established in 1979. On the northern side of the mountain, Ordovician sediments are exposed on the steep slopes. Surrounding peaks include Mount Pinnibar to the north, Mount Hope to the south-east and Mount Sassafras to the west. Plant species found in the reserve include the rare Alpine Phebalium and the endangered Kosciuszko Grevillea. The area was extensively burned by a bushfire in 2003.

The Dandongadale River, a perennial river of the North-East Murray catchment of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the Alpine region of Victoria, Australia. It flows from the northern slopes of the Alpine National Park in the Australian Alps, joining with the Buffalo River in remote national park territory.
The Dart River, a perennial river of the North-East Murray catchment of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the Alpine region of Victoria, Australia. It flows from the northwestern slopes of the Alpine National Park in the Australian Alps, south and joins with the Mitta Mitta River within Lake Dartmouth.
The Taponga River, an inland perennial river of the Goulburn Broken catchment, part of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the lower South Eastern Highlands bioregion, Alpine and Northern Country/North Central regions of the Australian state of Victoria. It flows from the northwestern slopes of the Australian Alps, north and joins with the Big River.
The Royston River, an inland perennial river of the Goulburn Broken catchment, part of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the lower South Eastern Highlands bioregion and Northern Country/North Central regions of the Australian state of Victoria. The headwaters of the Royston River rise on the western slopes of the Victorian Alps and descend to flow into the Rubicon River.














