
The Shire of East Gippsland is a local government area in Gippsland, Victoria, Australia, located in the eastern part of the state. It covers an area of 20,940 square kilometres (8,080 sq mi) and in June 2018 had a population of 46,818.

East Gippsland is the eastern region of Gippsland, Victoria, Australia covering 31,740 square kilometres (14%) of Victoria. It has a population of 80,114.
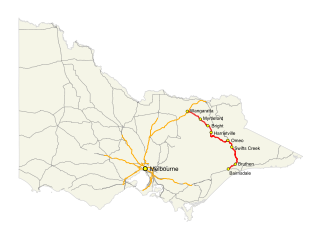
The Great Alpine Road (B500) is a country tourist road in Victoria, Australia, running from Wangaratta in the north to Bairnsdale in the east, and passing through the Victorian Alps. The road was given its current name because it was considered the mountain equivalent to Victoria's world-famous Great Ocean Road in the south-west of the state. The road usually remains open during winter; however, vehicles travelling between Harrietville and Omeo are required to carry diamond-pattern snow chains during the declared snow season.

The Mitchell River is a perennial river of the East Gippsland catchment, located in the Australian state of Victoria. The unregulated river provides a unique example of riparian ecology, flowing generally south with the catchment area drawing from the steep mountains of the Victorian Alps to enter Lake King, one of the Gippsland Lakes, and then empty into the Bass Strait.

The Thomson River, a perennial river of the West Gippsland catchment, is located in the Gippsland region of the Australian state of Victoria.

Bruthen is a small town located alongside the Tambo River between Bairnsdale and Ensay on the Great Alpine Road in East Gippsland, Victoria, Australia. At the 2016 census, Bruthen had a population of 814. Bruthen is 26 km (16 mi) east of Bairnsdale and 311 km (193 mi) east of the state capital Melbourne.

The Tambo River or Berrawan is a perennial river of the Mitchell River catchment, located in the East Gippsland region of the Australian state of Victoria. With a total length in excess of 186 kilometres (116 mi), the Tambo River is one of the longest rivers in the East Gippsland drainage basin, extending from the steep forested southern slopes of the Victorian Alps through forest and farmland to the Gippsland Lakes.

The Shire of Omeo was a local government area about 390 kilometres (242 mi) east-north-east of Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria, Australia. The shire covered an area of 5,641 square kilometres (2,178.0 sq mi), and existed from 1872 until 1994.

The Suggan Buggan River is a perennial river of the Snowy River catchment, located in the Alpine region of the Australian state of Victoria.

The Nicholson River is a perennial river of the Mitchell River catchment, located in the East Gippsland region of the Australian state of Victoria.
The Yeerung River is a perennial river located in the East Gippsland region of the Australian state of Victoria.
The Wentworth River is a perennial river of the Mitchell River catchment, located in the East Gippsland region of the Australian state of Victoria.

The Big River, a perennial river of the North-East Murray catchment of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the East Gippsland and alpine regions of Victoria, Australia. It flows from the northern slopes of Falls Creek in the Australian Alps, joining with the Cobungra River near Anglers Rest to form the Mitta Mitta River.

The Bundara River, a perennial river of the North-East Murray catchment of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the East Gippsland and alpine regions of Victoria, Australia.

The Moroka River is a perennial river of the Mitchell River catchment, located in the Alpine region of the Australian state of Victoria.
The Back River is a perennial river of the Mitchell River catchment, located in the Alpine region of the Australian state of Victoria.
The Little River is a perennial river of the Mitchell River catchment, located in the East Gippsland region of the Australian state of Victoria.
The Dry River is a perennial river of the Mitchell River catchment, located in the Alpine region of the Australian state of Victoria.
The Little River is a perennial river of the Mitchell River catchment, located in the Alpine region of the Australian state of Victoria.
The Gibbo River, a perennial river of the North-East Murray catchment of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the alpine and East Gippsland regions of Victoria, Australia. It flows from the northwestern slopes of the Australian Alps, south and joins with Morass Creek southeast of Lake Dartmouth.













