
In hydrology, a stream pool is a stretch of a river or stream in which the water depth is above average and the water velocity is below average. [1]

In hydrology, a stream pool is a stretch of a river or stream in which the water depth is above average and the water velocity is below average. [1]
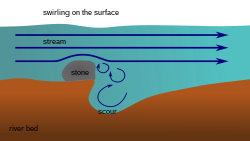
A stream pool may be bedded with sediment or armoured with gravel, and in some cases the pool formations may have been formed as basins in exposed bedrock formations. Plunge pools, or plunge basins, are stream pools formed by the action of waterfalls. Pools are often formed on the outside of a bend in a meandering river. [2]
The depth and lack of water velocity often leads to stratification in stream pools, especially in warmer regions. In warm arid regions of the Western United States, surface waters were found to be 3–9 °C higher than those at the bottom [3]
This portion of a stream often provides a specialized aquatic ecosystem habitat for organisms that have difficulty feeding or navigating in swifter reaches of the stream or in seasonally warmer water. Such pools can be important fish habitat, especially where many streams reach high summer temperatures and very low-flow dry season characteristics. In warm and arid regions, the stratification of stream pools provide cooler water for fish that prefer low water temperatures, such as the redband trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in the Western United States. [4] Mosquito larvae, which prefer still and often stagnant water, can be found in stream pools due to the low water velocity. [5]