The following is a list of marine ecoregions, as defined by the WWF and The Nature Conservancy
The WWF/Nature Conservancy scheme groups the individual ecoregions into 12 marine realms, which represent the broad latitudinal divisions of polar, temperate, and tropical seas, with subdivisions based on ocean basins. The marine realms are subdivided into 62 marine provinces, which include one or more of the 232 marine ecoregions.
The WWF/Nature Conservancy scheme currently encompasses only coastal and continental shelf areas. [lower-alpha 1] [lower-alpha 2]
(no provinces identified)
The Global 200 is the list of ecoregions identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the global conservation organization, as priorities for conservation. According to WWF, an ecoregion is defined as a "relatively large unit of land or water containing a characteristic set of natural communities that share a large majority of their species dynamics, and environmental conditions". For example, based on their levels of endemism, Madagascar gets multiple listings, ancient Lake Baikal gets one, and the North American Great Lakes get none.
A marine ecoregion is an ecoregion, or ecological region, of the oceans and seas identified and defined based on biogeographic characteristics.

The Arctic realm is one of the planet's twelve marine realms, as designated by the WWF and Nature Conservancy. It includes the coastal regions and continental shelves of the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas, including the Arctic Archipelago, Hudson Bay, and the Labrador Sea of northern Canada, the seas surrounding Greenland, the northern and eastern coasts of Iceland, and the eastern Bering Sea.

The Tropical Atlantic realm is one of twelve marine realms that cover the world's coastal seas and continental shelves.

The Tropical Eastern Pacific is one of the twelve marine realms that cover the coastal waters and continental shelves of the world's oceans. The Tropical Eastern Pacific extends along the Pacific Coast of the Americas, from the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula in the north to northern Peru in the south. It is bounded on the north by the Temperate Northern Pacific realm, and on the south by the Temperate South America realm.

The Bass Strait Shelf Province is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It covers the central Bass Strait between Tasmania and the southern Australian mainland. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system. The Bassian and adjacent Tasmanian Shelf provinces correspond to the Bassian marine ecoregion in the WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system.
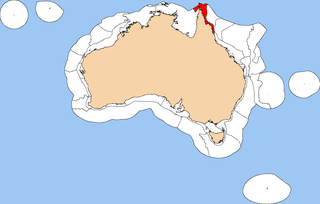
The Northeast Shelf Transition is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It includes the tropical coastal waters of the northern Great Barrier Reef and the Torres Strait in northeastern-most Australia. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system. It corresponds to the Torres Strait and Northern Great Barrier Reef marine ecoregion in the WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system.
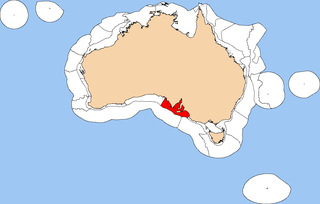
The Spencer Gulf Shelf Province, also known as the South Australian Gulfs marine ecoregion, is a biogeographic region of Australia's continental shelf and coastal waters. It includes the warm temperate coastal waters of South Australia's central coast. It is a provincial bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system.

The Tasmanian Shelf Province is a biogeographic region of Tasmania's coastal and continental shelf waters. It covers the western, eastern, and southern coasts of Tasmania. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system. The Tasmanian Shelf and adjacent Bass Strait Shelf provinces correspond to the Bassian marine ecoregion in the WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system.

The Western Bass Strait Shelf Transition is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It is a transitional region between the cold-temperate Bass Strait Shelf and Tasmanian Shelf provinces and the warm-temperate Spencer Gulf Shelf Province. It is a provincial bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system. It is the southern portion of the Western Bassian marine ecoregion in the World Wildlife Fund's (WWF) Marine Ecoregions of the World system.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and introduction to Oceanography.

The Western Indo-Pacific is a biogeographic region of the Earth's seas, comprising the tropical waters of the eastern and central Indian Ocean. It is part of the larger Indo-Pacific, which includes the tropical Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two in the general area of Indonesia. The Western Indo-Pacific may be classified as a marine realm, one of the great biogeographic divisions of the world's ocean basins, or as a subrealm of the Indo-Pacific.

The Central Indo-Pacific is a biogeographic region of Earth's seas, comprising the tropical waters of the western Pacific Ocean, the eastern Indian Ocean, and the connecting seas.

The Temperate Northern Pacific is a biogeographic region of the Earth's seas, comprising the temperate waters of the northern Pacific Ocean.

The borders of the oceans are the limits of Earth's oceanic waters. The definition and number of oceans can vary depending on the adopted criteria. The principal divisions of the five oceans are the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern (Antarctic) Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, gulfs, bays, straits, and other terms. Geologically, an ocean is an area of oceanic crust covered by water.

Temperate Australasia is a biogeographic region of the Earth's seas, comprising the temperate and subtropical waters of Australia and New Zealand, including both the Indian Ocean and Pacific coasts of the continent and adjacent islands.

The Temperate Northern Atlantic is a biogeographic region of the Earth's seas, comprising the temperate and subtropical waters of the North Atlantic Ocean and connecting seas, including the Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea, and northern Gulf of Mexico.

The Bassian ecoregion is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It includes the cold-temperate waters surrounding Tasmania, including the central Bass Strait between Tasmania and the southern Australian mainland. This ecoregion, designated in the Marine Ecoregions of the World system by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), includes both the Bass Strait Shelf and Tasmanian Shelf provincial level bioregions from the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system.