


A slip-off slope is a depositional landform that occurs on the inside convex bank of a meandering river. The term can refer to two different features: one in a freely meandering river with a floodplain and the other in an entrenched river.



A slip-off slope is a depositional landform that occurs on the inside convex bank of a meandering river. The term can refer to two different features: one in a freely meandering river with a floodplain and the other in an entrenched river.
In a freely meandering river, a slip-off slope is characterized by a gentle slope composed of sand and pebbles on the inside convex bank of a meander loop, across the channel from a cut bank or river-cut cliff. [1] As water in a meandering river travels around a bend, it moves in a secondary corkscrew-like flow as it travels downstream, in a pattern called helicoidal flow. [2] This phenomenon causes increased water velocity in the outside bend of the meander, driving lateral bank erosion. It is also responsible for slower water velocity on the inner bend of the meander. This low velocity allows eroded sediments from the cut bank side to be deposited on the inner bank. The deposition of material at the toe of a slip-off slope often results in the formation of a point bar. [3] Geologically, the environment in which a slip-off slope is deposited is considered to be one of low energy.
This continual process of erosion of the outer bank and deposition on the inside bank causes the migration of meanders and formation of oxbow lakes as the meander necks are narrowed and eventually cut through by the river. [4] Because they are low-lying, slip-off slopes are easily inundated during high water events, contributing to floodplain evolution in the middle and lower courses of a river. [5]
The slip-off slope of an entrenched meander is a gently sloping bedrock surface that rises from the inside, concave bank of an asymmetrically entrenched river. A thin, discontinuous layer of alluvium often covers this gently sloping bedrock surface. This type of slip-off slope is formed by the contemporaneous migration of a meander as a river cuts downward into bedrock. [3] [6] A terrace on the slip-off slope of a meander spur, known as slip-off slope terrace, can be formed by a brief halt during the irregular incision by an actively meandering river. [7]

Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone through lithification.

An entrenched river, or entrenched stream is a river or stream that flows in a narrow trench or valley cut into a plain or relatively level upland. Because of lateral erosion streams flowing over gentle slopes over a time develops meandering course. Meanders form where gradient is very gentle, for example in floodplain and delta. Meandering is the feature of the middle and final course of the river. But very deep and wide meanders can also be found cutting hard rocks. Such meanders are called incised or entrenched meanders. The exception is that entrenched meanders are formed during the upliftment of land where river is young. They widen and deepen over time and can be found as deep gorges or canyons in hard rock. In the case of or either an entrenched stream or river, it is often presumed that the watercourse has inherited its course by cutting down into bedrock from a pre-existing plain with little modification of the original course. The down-cutting of the river system could be the result not only of tectonic uplift but also of other factors such as river piracy, decrease of load, increase of runoff, extension of the drainage basin, or change in base level such as a fall in sea level. General, nongeneric terminology for either a river or stream that flows in a narrow trench or valley, for which evidence of a preexisting plain or relatively level upland can be either absent or present is either valley meander or meander valley with the latter term being preferred in literature.

A braided river, or braided channel, consists of a network of river channels separated by small, often temporary, islands called braid bars or, in British English usage, aits or eyots.

In geography and geology, fluvial processes are associated with rivers and streams and the deposits and landforms created by them. When the stream or rivers are associated with glaciers, ice sheets, or ice caps, the term glaciofluvial or fluvioglacial is used.
Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as their creating process, shape, elevation, slope, orientation, rock exposure, and soil type.

An oxbow lake is a U-shaped lake or pool that forms when a wide meander of a river is cut off, creating a free-standing body of water. In South Texas, oxbows left by the Rio Grande are called resacas. In Australia, oxbow lakes are called billabongs. The word "oxbow" can also refer to a U-shaped bend in a river or stream, whether or not it is cut off from the main stream.

An alluvial plain is a largely flat landform created by the deposition of sediment over a long period of time by one or more rivers coming from highland regions, from which alluvial soil forms. A floodplain is part of the process, being the smaller area over which the rivers flood at a particular period of time, whereas the alluvial plain is the larger area representing the region over which the floodplains have shifted over geological time.
Fluvial terraces are elongated terraces that flank the sides of floodplains and fluvial valleys all over the world. They consist of a relatively level strip of land, called a "tread", separated from either an adjacent floodplain, other fluvial terraces, or uplands by distinctly steeper strips of land called "risers". These terraces lie parallel to and above the river channel and its floodplain. Because of the manner in which they form, fluvial terraces are underlain by fluvial sediments of highly variable thickness. River terraces are the remnants of earlier floodplains that existed at a time when either a stream or river was flowing at a higher elevation before its channel downcut to create a new floodplain at a lower elevation. Changes in elevation can be due to changes in the base level of the fluvial system, which leads to headward erosion along the length of either a stream or river, gradually lowering its elevation. For example, downcutting by a river can lead to increased velocity of a tributary, causing that tributary to erode toward its headwaters. Terraces can also be left behind when the volume of the fluvial flow declines due to changes in climate, typical of areas which were covered by ice during periods of glaciation, and their adjacent drainage basins.
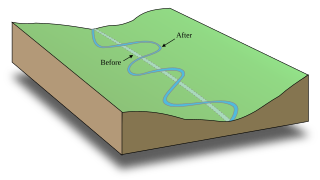
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank and deposits sediments on an inner, convex bank which is typically a point bar. The result of this coupled erosion and sedimentation is the formation of a sinuous course as the channel migrates back and forth across the axis of a floodplain.

In geology, a terrace is a step-like landform. A terrace consists of a flat or gently sloping geomorphic surface, called a tread, that is typically bounded on one side by a steeper ascending slope, which is called a "riser" or "scarp". The tread and the steeper descending slope together constitute the terrace. Terraces can also consist of a tread bounded on all sides by a descending riser or scarp. A narrow terrace is often called a bench.

A point bar is a depositional feature made of alluvium that accumulates on the inside bend of streams and rivers below the slip-off slope. Point bars are found in abundance in mature or meandering streams. They are crescent-shaped and located on the inside of a stream bend, being very similar to, though often smaller than, towheads, or river islands.

A cut bank, also known as a river cliff or river-cut cliff, is the outside bank of a curve or meander in a water channel (stream), which is continually undergoing erosion. Cut banks are found in abundance along mature or meandering streams, they are located on the outside of a stream bend, known as a meander, opposite the slip-off slope on the inside of the bend. They are shaped much like a small cliff, and are formed by the erosion of soil as the stream collides with the river bank. As opposed to a point bar, which is an area of deposition, a cut bank is an area of erosion.

A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater stream, flowing on the surface or inside caves towards another waterbody at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, sea, bay, lake, wetland, or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground or becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as creek, brook, and rivulet. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities, a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and Northeast England, and "beck" in Northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague.

In sedimentary geology and fluvial geomorphology, avulsion is the rapid abandonment of a river channel and the formation of a new river channel. Avulsions occur as a result of channel slopes that are much less steep than the slope that the river could travel if it took a new course.

A bar in a river is an elevated region of sediment that has been deposited by the flow. Types of bars include mid-channel bars, point bars, and mouth bars. The locations of bars are determined by the geometry of the river and the flow through it. Bars reflect sediment supply conditions, and can show where sediment supply rate is greater than the transport capacity.
River channel migration is the geomorphological process that involves the lateral migration of an alluvial river channel across its floodplain. This process is mainly driven by the combination of bank erosion of and point bar deposition over time. When referring to river channel migration, it is typically in reference to meandering streams. In braided streams, channel change is driven by sediment transport.

An alluvial river is one in which the bed and banks are made up of mobile sediment and/or soil. Alluvial rivers are self-formed, meaning that their channels are shaped by the magnitude and frequency of the floods that they experience, and the ability of these floods to erode, deposit, and transport sediment. For this reason, alluvial rivers can assume a number of forms based on the properties of their banks; the flows they experience; the local riparian ecology; and the amount, size, and type of sediment that they carry.
Channel patterns are found in rivers, streams, and other bodies of water that transport water from one place to another. Systems of branching river channels dissect most of the sub-aerial landscape, each in a valley proportioned to its size. Whether formed by chance or necessity, by headward erosion or downslope convergence, whether inherited or newly formed. Depending on different geological factors such as weathering, erosion, depositional environment, and sediment type, different types of channel patterns can form.

A meander cutoff is a natural form of a cutting or cut in a river occurs when a pronounced meander (hook) in a river is breached by a flow that connects the two closest parts of the hook to form a new channel, a full loop. The steeper drop in gradient (slope) causes the river flow gradually to abandon the meander which will silt up with sediment from deposition. Cutoffs are a natural part of the evolution of a meandering river. Rivers form meanders as they flow laterally downstream, see sinuosity.

River incision is the narrow erosion caused by a river or stream that is far from its base level. River incision is common after tectonic uplift of the landscape. Incision by multiple rivers result in a dissected landscape, for example a dissected plateau. River incision is the natural process by which a river cuts downward into its bed, deepening the active channel. Though it is a natural process, it can be accelerated rapidly by human factors including land use changes such as timber harvest, mining, agriculture, and road and dam construction. The rate of incision is a function of basal shear-stress. Shear stress is increased by factors such as sediment in the water, which increase its density. Shear stress is proportional to water mass, gravity, and WSS:
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link)