
Dissorophidae is an extinct family of medium-sized, temnospondyl amphibians that flourished during the late Carboniferous and early Permian periods. The clade is known almost exclusively from North America.

Temnospondyli or temnospondyls is a diverse ancient order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carboniferous, Permian and Triassic periods, with fossils being found on every continent. A few species continued into the Jurassic and Early Cretaceous periods, but all had gone extinct by the Late Cretaceous. During about 210 million years of evolutionary history, they adapted to a wide range of habitats, including freshwater, terrestrial, and even coastal marine environments. Their life history is well understood, with fossils known from the larval stage, metamorphosis and maturity. Most temnospondyls were semiaquatic, although some were almost fully terrestrial, returning to the water only to breed. These temnospondyls were some of the first vertebrates fully adapted to life on land. Although temnospondyls are amphibians, many had characteristics such as scales and armour-like bony plates that distinguish them from the modern soft-bodied lissamphibians.
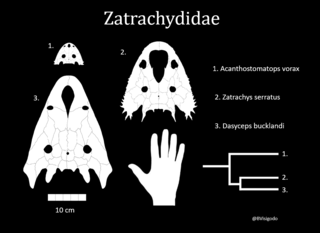
Zatracheidae is a family of Late Carboniferous and Early Permian temnospondyls known from North America and Europe. Zatracheidids are distinguished by lateral (sideways) bony protuberances of the quadratojugal bone of the skull, and a large opening in the snout called the internarial fontanelle that is bordered by enlarged premaxillae. The skull is flattened, with small orbits or eye sockets set far back. The opening in the snout may have housed a gland for producing a sticky substance so that prey would adhere to the tongue. If so, this indicates that these animals spent a large part of their time on land.

Platyhystrix is an extinct temnospondyl amphibian with a distinctive sail along its back, similar to the unrelated synapsids, Dimetrodon and Edaphosaurus. It lived during the boundary between the latest Carboniferous and earliest Permian periods throughout what is now known as the Four Corners, Texas, and Kansas about 300 million years ago.

Embolomeri is an order of tetrapods or stem-tetrapods, possibly members of Reptiliomorpha. Embolomeres first evolved in the Early Carboniferous (Mississippian) Period and were the largest and most successful predatory tetrapods of the Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) Period. They were specialized semiaquatic predators with long bodies for eel-like undulatory swimming. Embolomeres are characterized by their vertebral centra, which are formed by two cylindrical segments, the pleurocentrum at the rear and intercentrum at the front. These segments are equal in size. Most other tetrapods have pleurocentra and intercentra which are drastically different in size and shape.
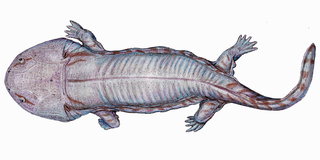
The Stereospondyli are a group of extinct temnospondyl amphibians that existed primarily during the Mesozoic period. They are known from all seven continents and were common components of many Triassic ecosystems, likely filling a similar ecological niche to modern crocodilians prior to the diversification of pseudosuchian archosaurs.

Archegosaurus is a genus of temnospondyl amphibian which lived during the Asselian to Wuchiapingian stages of the Permian, around 299-253 million years ago. The remains of this animal, consisting of at least 90 partial skeletons, have been found in Germany. The name Archegosaurus was coined by Goldfuss in 1847. Archegosaurus is a member of Archegosauridae and is that family's type genus.

Sclerothorax is an extinct genus of temnospondyl from the Early Triassic of Germany. It is distinguished from other temnospondyls by its short and very wide skull and the elongated neural spines that form a ridge along its back. Sclerothorax is a basal member of Capitosauria, a large clade of temnospondyls that lived throughout the Triassic.

Euskelia is a proposed clade of extinct temnospondyl amphibians. The naming derives from the ancient Greek eu, meaning "true", and skelos, meaning "limb", in reference to well-ossified limb bones with crests to which muscles were attached.

Sclerocephalus is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the lowermost Permian of Germany and Czech Republic with four valid species, including the type species S. haeuseri. It is one of the most completely preserved and most abundant Palaeozoic tetrapods. Sclerocephalus was once thought to be closely related to eryopoid temnospondyls, but it is now thought to be more closely related to archegosauroids. It is the only genus in the family Sclerocephalidae.

Rhinesuchidae is a family of tetrapods that lived primarily in the Permian period. They belonged to the broad group Temnospondyli, a successful and diverse collection of semiaquatic tetrapods which modern amphibians are probably descended from. Rhinesuchids can be differentiated from other temnospondyls by details of their skulls, most notably the interior structure of their otic notches at the back of the skull. They were among the earliest-diverging members of the Stereospondyli, a subgroup of temnospondyls with flat heads and aquatic habits. Although more advanced stereospondyls evolved to reach worldwide distribution in the Triassic period, rhinesuchids primarily lived in the high-latitude environments of Gondwana during the Guadalupian and Lopingian epochs of the Permian. The taxonomy of this family has been convoluted, with more than twenty species having been named in the past; a 2017 review recognized only eight of them to be valid. While several purported members of this group have been reported to have lived in the Triassic period, most are either dubious or do not belong to the group. However, at least one valid genus of rhinesuchid is known from the early Triassic, a small member known as Broomistega. The most recent formal definition of Rhinesuchidae, advocated by Mariscano et al. (2017) is that of a stem-based clade containing all taxa more closely related to Rhinesuchus whaitsi than to Lydekkerina huxleyi or Peltobatrachus pustulatus. A similar alternate definition is that Rhinesuchidae is a stem-based clade containing all taxa more closely related to Uranocentrodon senekalensis than to Lydekkerina huxleyi, Trematosaurus brauni, or Mastodonsaurus giganteus.
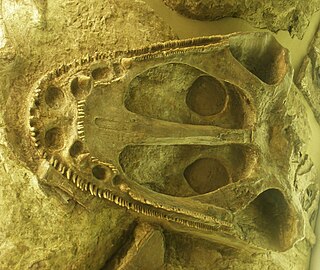
Mastodonsauridae is a family of capitosauroid temnospondyls. Fossils belonging to this family have been found in North America, Greenland, Europe, Asia, and Australia. The family Capitosauridae is synonymous with Mastodonsauridae.

Stereospondylomorpha is a clade of temnospondyls. It includes the superfamily Archegosauroidea and the more diverse group Stereospondyli. Stereospondylomorpha was first proposed by Yates and Warren (2000), who found Archegosauroidea and Stereospondyli to be sister taxa in their phylogenetic analysis. A similar clade is Archegosauriformes, named by Schoch and Milner (2000), which includes Stereospondyli and some Permian temnospondyls that are similar in appearance to stereospondyls, including the archegosauroids. However, according to Schoch and Milner's phylogeny, Archegosauroidea is a paraphyletic group of taxa that are successively basal to Stereospondyli, rather than a monophyletic sister taxon.

Lapillopsis is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl within the family Lapillopsidae. Fossils belonging to the genus have been found in the Arcadia Formation of Queensland, Australia.

Capitosauria is an extinct group of large temnospondyl amphibians with simplified stereospondyl vertebrae. Mainly living as piscivores in lakes and rivers, the Capitosauria and its sister taxon Trematosauria were the only major labyrinthodonts that existed during the Mesozoic in ecological niches broadly similar to those of modern crocodiles, and some grew to very large sizes. At 6 meters in length, the Mid-Triassic Mastodonsaurus giganteus is not only thought to have been the largest capitosaur, but possibly also the largest amphibian to have lived. The latest known remains are from the Rhaetian of Germany and are referred to Cyclotosaurus.

Caerorhachis is an extinct genus of early tetrapod from the Early Carboniferous of Scotland, probably from the Serpukhovian stage. Its placement within Tetrapoda is uncertain, but it is generally regarded as a primitive member of the group. The type species C. bairdi was named in 1977.
Parioxys is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Early Permian of Texas.

Eutemnospondyli is a clade of temnospondyl amphibians that includes most temnospondyls except edopoids. Eutemnospondyli was named by German paleontologist Rainer R. Schoch in 2013. He defined it as a stem-based taxon including all temnospondyls more closely related to Stereospondyli than to Edopoidea. In his phylogenetic analysis, Eutemnospondyli included dendrerpetontids and a clade he referred to as Rhachitomi. Rhachitomi is defined to include four major and well-supported clades of temnospondyls: Dvinosauria, Eryopidae, Stereospondyli and a clade formed by Zatracheidae and Dissorophoidea. Below is a cladogram from Schoch's analysis:

Eryopiformes is a group of rhachitomi temnospondyls. Eryopiformes was named by the German paleontologist Rainer R. Schoch in 2013. He defined it as a node-based taxon to include Eryopidae and Stereospondylomorpha. Unlike previous analyses, a phylogenetic analysis he performed found no support for a monophyletic Euskelia, that is defined to include Dissorophoidea and Eryopidae, in relation to Stereospondylomorpha. In this analysis, Eryopidae and Stereospondylomorpha usually formed a monophyletic clade that excludes the clade formed by Zatracheidae and Dissorophoidea. Thus, he named this newly identified group as Eryopiformes.
Scapanops is an extinct genus of dissorophid temnospondyl amphibian known from the Early Permian Nocona Formation of north-central Texas, United States. It contains only the type species Scapanops neglecta, which was named by Rainer R. Schoch and Hans-Dieter Sues in 2013. Scapanops differs from other dissorophids in having a very small skull table, which means that its eye sockets are unusually close to the back of the skull. The eye sockets are also very large and spaced far apart. Scapanops was probably small-bodied with a proportionally large head and short trunk and tail. Like other dissorophids, it probably spent most of its life on land.




















