| Edops Temporal range: Late Carboniferous - Early Permian | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Skull of Edops craigi on display at Harvard | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Tetrapoda |
| Order: | † Temnospondyli |
| Superfamily: | † Edopoidea |
| Family: | † Edopidae Langston, 1953 |
| Genus: | † Edops Romer and Witter, 1936 |
| Type species | |
| †Edops craigi Romer and Witter, 1936 | |
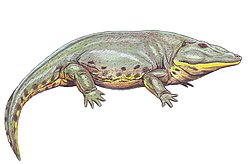
Edops ('swollen face') is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Late Carboniferous - Early Permian periods. [1] Unlike more advanced temnospondyls of the time, such as Eryops , Edops exhibited an archaic pattern of palatal bones, and still possessed various additional bones at the back of the skull. Edopoids also had particularly big premaxillae (the bones that form the tip of the snout) and proportionally small external nostrils. Within the clade, the most basal member seems to be Edops from the Early Permian Archer City Formation of the US, a broad-skulled animal with large palatal teeth.
Contents
Edops was fairly big, at 2 metres (6.6 ft) in length. Fragmentary remains from the Viséan of Scotland appear to come from Edops or a close relative and hence predate the type Edops material of the Permian. [2]