
Rhubarb is the fleshy, edible stalks (petioles) of species and hybrids of Rheum in the family Polygonaceae, which are cooked and used for food. The plant is a herbaceous perennial that grows from short, thick rhizomes. Historically, different plants have been called "rhubarb" in English. The large, triangular leaves contain high levels of oxalic acid and anthrone glycosides, making them inedible. The small flowers are grouped in large compound leafy greenish-white to rose-red inflorescences.

Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although S. aureus usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. S. aureus is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine. Despite much research and development, no vaccine for S. aureus has been approved.
Ampicillin/sulbactam is a fixed-dose combination medication of the common penicillin-derived antibiotic ampicillin and sulbactam, an inhibitor of bacterial beta-lactamase. Two different forms of the drug exist. The first, developed in 1987 and marketed in the United States under the brand name Unasyn, generic only outside the United States, is an intravenous antibiotic. The second, an oral form called sultamicillin, is marketed under the brand name Ampictam outside the United States, and generic only in the United States. Ampicillin/sulbactam is used to treat infections caused by bacteria resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics. Sulbactam blocks the enzyme which breaks down ampicillin and thereby allows ampicillin to attack and kill the bacteria.

Sultamicillin, sold under the brand name Unasyn among others, is an oral form of the penicillin antibiotic combination ampicillin/sulbactam. It is used for the treatment of bacterial infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract, the kidneys and urinary tract, skin and soft tissues, among other organs. It contains esterified ampicillin and sulbactam.

Flucloxacillin, also known as floxacillin, is an antibiotic used to treat skin infections, external ear infections, infections of leg ulcers, diabetic foot infections, and infection of bone. It may be used together with other medications to treat pneumonia, and endocarditis. It may also be used prior to surgery to prevent Staphylococcus infections. It is not effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). It is taken by mouth or given by injection into a vein or muscle.

Anthrone is a tricyclic aromatic ketone. It is used for a common cellulose assay and in the colorimetric determination of carbohydrates.

Dicloxacillin is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It is used to treat infections caused by susceptible (non-resistant) Gram-positive bacteria. It is active against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus, which would otherwise be resistant to most penicillins. Dicloxacillin is available under a variety of trade names including Diclocil (BMS).

Oxacillin is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class developed by Beecham.

Rheum is a genus of about 60 herbaceous perennial plants in the family Polygonaceae. Species are native to eastern Europe, southern and eastern temperate Asia, with a few reaching into northern tropical Asia. Rheum is cultivated in Europe and North America. The genus includes the vegetable rhubarb. The species have large somewhat triangular shaped leaves with long, fleshy petioles. The flowers are small, greenish-white to rose-red, and grouped in large compound leafy inflorescences. A number of cultivars of rhubarb have been domesticated both as medicinal plants and for human consumption. While the leaves are slightly toxic, the stalks are used in pies and other foods for their tart flavor.

For the parent molecule 9,10-anthraquinone, see anthraquinone

Rheum officinale, the Chinese rhubarb, or Indian rhubarb is a rhubarb from the family Polygonaceae native to China. In Chinese it is called yào yòng dà huáng, literally meaning medicinal rhubarb.

Emodin (6-methyl-1,3,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone) is a chemical compound, of the anthraquinone family, that can be isolated from rhubarb, buckthorn, and Japanese knotweed. Emodin is particularly abundant in the roots of the Chinese rhubarb, knotweed and knotgrass as well as Hawaii ‘au‘auko‘i cassia seeds or coffee weed. It is specifically isolated from Rheum palmatum L. It is also produced by many species of fungi, including members of the genera Aspergillus, Pyrenochaeta, and Pestalotiopsis, inter alia. The common name is derived from Rheum emodi, a taxonomic synonym of Rheum australe, and synonyms include emodol, frangula emodin, rheum emodin, 3-methyl-1,6,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone, Schüttgelb (Schuttgelb), and Persian Berry Lake.

Beta-lactamases are a family of enzymes involved in bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. In bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics, the bacteria have beta-lactamase which degrade the beta-lactam rings, rendering the antibiotic ineffective. However, with beta-lactamase inhibitors, these enzymes on the bacteria are inhibited, thus allowing the antibiotic to take effect. Strategies for combating this form of resistance have included the development of new beta-lactam antibiotics that are more resistant to cleavage and the development of the class of enzyme inhibitors called beta-lactamase inhibitors. Although β-lactamase inhibitors have little antibiotic activity of their own, they prevent bacterial degradation of beta-lactam antibiotics and thus extend the range of bacteria the drugs are effective against.

Ceftobiprole (Zevtera/Mabelio) is a fifth-generation cephalosporin for the treatment of hospital-acquired pneumonia and community-acquired pneumonia. It is marketed by Basilea Pharmaceutica in the United Kingdom, Germany, Switzerland and Austria under the trade name Zevtera, in France and Italy under the trade name Mabelio. Like other cephalosporins, ceftobiprole exerts its antibacterial activity by binding to important penicillin-binding proteins and inhibiting their transpeptidase activity which is essential for the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. Ceftobiprole has high affinity for penicillin-binding protein 2a of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains and retains its activity against strains that express divergent mecA gene homologues. Ceftobiprole also binds to penicillin-binding protein 2b in Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-intermediate), to penicillin-binding protein 2x in Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-resistant), and to penicillin-binding protein 5 in Enterococcus faecalis.
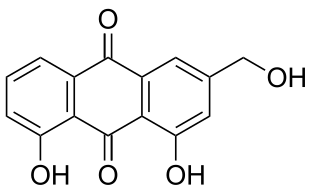
Aloe emodin is an anthraquinone and an isomer of emodin present in aloe latex, an exudate from the aloe plant. It has a strong stimulant-laxative action. Aloe emodin is not carcinogenic when applied to the skin, although it may increase the carcinogenicity of some kind of radiation.
mecA is a gene found in bacterial cells which allows them to be resistant to antibiotics such as methicillin, penicillin and other penicillin-like antibiotics.

Senna reticulata, the mangerioba grande or maria mole in Portuguese, is a pioneer tree species found on highly fertile floodplains in South America. It has some medicinal uses, but is regarded by farmers as a noxious weed, named matapasto due to its ability to grow fast and outshade neighbouring plants.

Verbascoside is a caffeoyl phenylethanoid glycoside in which the phenylpropanoid caffeic acid and the phenylethanoid hydroxytyrosol form an ester and an ether bond respectively, to the rhamnose part of a disaccharide, namely β-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→3)-β-D-(4-O-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside.

Rheum australe, synonym Rheum emodi, is a flowering plant in the family Polygonaceae. It is commonly known as Himalayan rhubarb, Indian rhubarb and Red-veined pie plant. It is a medicinal herb used in the Indian Unani system of medicine, and formerly in the European system of medicine where it was traded as Indian rhubarb. The plant is found in the sub-alpine and alpine Himalayas at an altitude of 4000 m.

Chrysophanol, also known as chrysophanic acid, is a fungal isolate and a natural anthraquinone. It is a C-3 methyl substituted chrysazin of the trihydroxyanthraquinone family.



















