
Lemon balm is a perennial herbaceous plant in the mint family and native to south-central Europe, the Mediterranean Basin, Iran, and Central Asia, but now naturalised elsewhere.

Salvia rosmarinus, commonly known as rosemary, is a shrub with fragrant, evergreen, needle-like leaves and white, pink, purple, or blue flowers. It is native to the Mediterranean region, as well as Portugal and Spain. Until 2017, it was known by the scientific name Rosmarinus officinalis, now a synonym.

Herbal teas, technically known as herbal infusions, and less commonly called tisanes, are beverages made from the infusion or decoction of herbs, spices, or other plant material in hot water. Often herb tea, or the plain term tea, is used as a reference to all sorts of herbal teas. Many herbs used in teas/tisanes are also used in herbal medicine and in folk medicine.

Rhododendron is a very large genus of about 1,024 species of woody plants and in the heath family (Ericaceae). They can be either evergreen or deciduous. Most species are native to eastern Asia and the Himalayan region, but smaller numbers occur elsewhere in Asia, and in North America, Europe and Australia.

Anise, also called aniseed or rarely anix, is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae native to the eastern Mediterranean region and Southwest Asia.

Mentha pulegium, commonly (European) pennyroyal, or pennyrile, also called mosquito plant and pudding grass, is a species of flowering plant in the mint family, Lamiaceae, native to Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. Crushed pennyroyal leaves emit a very strong fragrance similar to spearmint. Pennyroyal is a traditional folk remedy, emmenagogue, abortifacient, and culinary herb, but is toxic to the liver and has caused some deaths. European pennyroyal is related to an American species, Hedeoma pulegioides. Though they differ in genera, they share similar chemical properties.

Filipendula ulmaria, commonly known as meadowsweet or mead wort, is a perennial herbaceous plant in the family Rosaceae that grows in damp meadows. It is native throughout most of Europe and Western Asia. It has been introduced and naturalised in North America.

Bryonia is a genus of flowering plants in the gourd family. Bryony is its best-known common name. They are native to western Eurasia and adjacent regions, such as North Africa, the Canary Islands and South Asia.

Bearberries are three species of dwarf shrubs in the genus Arctostaphylos. Unlike the other species of Arctostaphylos, they are adapted to Arctic and subarctic climates, and have a circumpolar distribution in northern North America, Asia and Europe.

Labrador tea is a common name for three closely related plant species in the genus Rhododendron as well as a herbal tea made from their leaves. All three species are primarily wetland plants in the heath family. Labrador tea has been a favorite beverage for a long time among Athabaskan First Nations and Inuit.

Dysphania ambrosioides, formerly Chenopodium ambrosioides, known as epazote, Jesuit's tea, Mexican tea or wormseed, is an annual or short-lived perennial herb native to the Americas.

Ledum was a genus in the family Ericaceae, including eight species of evergreen shrub native to cool temperate and subarctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and commonly known as Labrador tea. It is now recognised as a subsection of section Rhododendron, subgenus Rhododendron, of the genus Rhododendron.

Actaea spicata, the baneberry or herb Christopher, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Actaea, native from Europe to western Siberia and northern Iran. It is often found on limestone edges and in deciduous woodland; key factors are shade, low competition, and a cool, protected root run.

Rhododendron groenlandicum is a flowering shrub with white flowers and evergreen leaves that is used to make a herbal tea.

Equisetum palustre, the marsh horsetail, is a perennial herbaceous pteridophyte belonging to the subclass of horsetails (Equisetidae). It is widespread in cooler regions of Eurasia and North America.
Marsh rosemary may refer to:

Herbs are a widely distributed and widespread group of plants, excluding vegetables and other plants consumed for macronutrients, with savory or aromatic properties that are used for flavoring and garnishing food, for medicinal purposes, or for fragrances. Culinary use typically distinguishes herbs from spices. Herbs generally refers to the leafy green or flowering parts of a plant, while spices are usually dried and produced from other parts of the plant, including seeds, bark, roots and fruits.

Rhododendron columbianum, commonly known as western Labrador tea, swamp tea, or muskeg tea, is a shrub that is widespread in the western United States and in western Canada, reported from British Columbia, Alberta, Washington, Oregon, Idaho, California, Montana, Wyoming, Utah, Nevada, and Colorado. It grows in wet places from sea level up to 3,500 m (11,000 ft). It was formerly known as Ledum columbianum. Its origins date back to the late Pliocene.
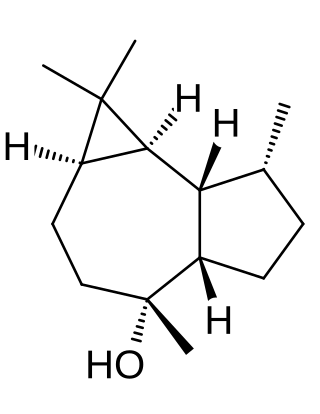
Ledol is a poisonous sesquiterpene that can cause cramps, paralysis, and delirium. Caucasian peasants used Rhododendron plants for these effects in shamanistic rituals.

















