Savoyard state | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1003–1861 | |||||||||
| Motto: FERT | |||||||||
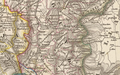
 The Savoyard state in 1839 | |||||||||
| Status | Former plurinational independent state Former constituent territories of the Holy Roman Empire | ||||||||
| Capital | Montmélian (1006–1295) Chambéry (1295–1562) Turin (1562–1792; 1815–1861) Cagliari (1792–1815) | ||||||||
| Common languages | French, Italian, Piedmontese, Arpitan, Occitan, Latin | ||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism | ||||||||
| Government | County, Duchy, and Kingdom | ||||||||
| Count Duke King | |||||||||
• 1003–1048 | Humbert I White Hands (first) | ||||||||
• 1849–1861 | Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia (last) | ||||||||
| Historical era | Medieval era Modern era | ||||||||
• Humbert I became Count of Savoy | 1003 | ||||||||
| 1861 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | France Italy | ||||||||
The Savoyard state comprised the states ruled by the counts and dukes of Savoy from the Middle Ages to the formation of the Kingdom of Italy. Although it was an example of composite monarchy, [1] [2] it is a term applied to the polity by historians and was not in contemporary use. At the end of the 17th century, its population was about 1.4 million. [3] [4] [5] It was part of the Holy Roman Empire until 1797, with its territory being split between the constituent kingdoms of Burgundy (Savoy proper, Nice) and Italy (Piedmont and the rest). From 1720 it also included the island of Sardinia, which was ethnically Italian but outside of the Empire.